* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Crusades1
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
First Crusade wikipedia , lookup
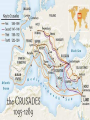
The Power of the Church and its Reform Kings but no real leaders – CHURCH emerged as a powerful institution, much involvement in political affairs Middle Ages – time of power struggles between popes and kings POPE vs. KING To win in disagreements, Pope threatened excommunication – no salvation Smart kings ally with Pope Christianity – Why Popular? •Embraced all people – men, women, poor, nobles – bonded people together •Gave hope to powerless, promised eternal life after death for all •Provided stability among warfare and turmoil •Middle Ages becomes known as the Age of Faith Problems and Reforms Problems in Church: •church officials are rich and corrupt •priests illiterate •Pope’s questionable morals •priests had families •sold church positions Reforms: •Monks try to restore purity of church •Inquisition – church court who sought out and punished heretics No need for proof, used torture CRUSADES Comes from the Latin word “crux” meaning “cross” – those who fought were called crusaders because they vowed to “take up the cross” Military expeditions by European Christians to regain the Holy Land – Jerusalem Deus Vult! – For God!! Goals of the Crusades • Christians want to regain Palestine (Holy Land) • Reunite Christendom • Send quarrelsome knights off to war • Why go? – Land – Power – Forgiveness of sins – Adventure – Expand markets – Temporary release from peasantry First Crusade •3 armies traveled separately from W. Europe •Ill-prepared for war, no strategy for capturing Jerusalem •Many killed Jews along the way •Met in Constantinople in 1097 – made way to Jerusalem •1099 – Jerusalem fell to Crusaders after 2 months •Many knights returned home, some set up homes •Only Crusade that Christians won Second Crusade (1147-1149) •Muslims reconquered Holy Land •Second Crusade to recapture fallen cities •Christians unsuccessful due to fighting leaders Third Crusade •Muslim leader Saladin united forces & captured Jerusalem 1187 •“Crusade of Kings” – Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, Richard the Lion-Hearted of England •Only Richard made it •Defeated Muslims in several battles, but couldn't’t win over Saladin’s well-trained and dedicated forces •Signed a truce – Muslims kept control of Jerusalem but allowed Christians to visit holy sites EFFECTS •Other Crusades unsuccessful in winning permanent Christian control of Palestine •Failure of Crusades lessened power of Pope •Lords funded Crusades through loans, Crusades failed and couldn’t pay off loans, had to forfeit fiefs and serfs/peasants gave money to be free •Feudalism declined, Power of kings increased •Contact b/w Crusaders and other civilizations = broadened world view & curiosity EFFECTS •Increased trade – prosperous towns •Contact with East – demand for luxury goods – spices, sugar, silk, tapestries •Improved technology – better built ships, more accurate maps, magnetic compass, new military skills, siege techniques, improved weaponry •Muslims remembered the intolerance and prejudice displayed by Christians – led to bitterness and hatred Why did Crusades end? •People started to lose interest after all of the failures •They were curious about other areas of the world = Exploration •Church lost respect Exit Question • What do you think is the most compelling reason for Christians to fight in the Crusades?