* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
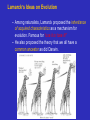
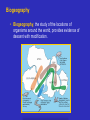
EVOLUTION Lynn English High School Biology Ms. Mezzetti The Idea of Evolution • Evolution is the process of change in the inherited characteristics within populations over generations such that new types of organisms develop from preexisting types. Evolutionary Relationships Between Whales and Hoofed Mammals Ideas of Darwin’s Time – Scientific understanding of evolution began to develop in the 17th and 18th centuries as geologists and naturalists compared geologic processes and living and fossil organisms around the world. Ideas about Geology – Among geologists, Cuvier promoted the idea of catastrophism, and Lyell promoted uniformitarianism. Cuvier Lyell Lamarck’s Ideas on Evolution – Among naturalists, Lamarck proposed the inheritance of acquired characteristics as a mechanism for evolution. Famous for “use it or lose it!” – He also proposed the theory that we all have a common ancestor as did Darwin. Darwin’s Ideas • Descent with Modification – Darwin wrote On the Origin of Species, in which he argued that descent with modification occurs, that all species descended from common ancestors, and that natural selection is the mechanism for evolution. Darwin’s Voyage Natural Selection – Organisms in a population adapt to their environment as the proportion of individuals with genes for favorable traits increases. – Those individuals that pass on more genes are considered to have greater fitness. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution • Natural Selection: species adapt to their environment over long periods of time • Descent with modification: species are modifications of their ancestors before them • Genetic Variation: offspring are variations of their parents • Darwin’s theories were influenced by Thomas Malthus, a clergyman who wrote about how populations are affected by adverse conditions such as war, disease and limited resources. Natural Selection EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION The Fossil Record • Evidence of evolution can be found by comparing several kinds of data, including the fossil record, biogeography, anatomy and development, and biological molecules. • Evolutionary theories are supported when several kinds of evidence support similar conclusions. The Age of Fossils – Geologic evidence supports theories about the age and development of Earth. The Distribution of Fossils – The fossil record shows that the types and distribution of organisms on Earth have changed over time. Transitional Species – Fossils of transitional species show evidence of descent with modification. Evidence of Whale Evolution Biogeography • Biogeography, the study of the locations of organisms around the world, provides evidence of descent with modification. Anatomy and Physiology • In organisms, analogous structures are similar in function but have different evolutionary origins. • Homologous structures have a common evolutionary origin. Analogous Homologous Anatomy and Physiology, continued • A species with a vestigial structure probably shares ancestry with a species that has a functional form of the structure. Embryological Structures • Related species show similarities in embryological development. Biological Molecules • Similarity in the subunit sequences of biological molecules such as RNA, DNA, and proteins indicates a common evolutionary history. Hemoglobin Comparison Case Study: Caribbean Anole Lizards On going examples of evolution among living organisms can be observed, recorded, and tested. • In convergent evolution, organisms that are not closely related resemble each other because they have responded to similar environments. • Divergence and Radiation – In divergent evolution, related populations become less similar as they respond to different environments. – Adaptive radiation is the divergent evolution of a single group of organisms in a new environment. Divergent? Convergent? Radiation? Divergent? Convergent? Radiation? Divergent? Convergent? Radiation? Natural Selection of Anole Lizard Species Artificial Selection • The great variety of dog breeds is an example of artificial selection. Coevolution • Plant pollinators are an excellent example of co-evolution. • Each animal has an adaptation to retrieve pollen and help to pollinate plants. Review • • • • Name 3 theories Darwin is famous for. How was Lamarck’s theory different that Darwin’s? Name 3 ways science substantiates the theory of evolution. Name 3 people responsible for helping Darwin with his theory of evolution. • What is genetic variation? • And no! we did not evolve from monkeys!