* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KUMC 31 Nasal Cavity Student
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
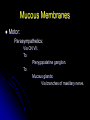
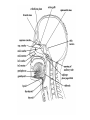
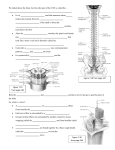
NASAL CAVITY Skeletal Framework Parts: Alae. Dorsum. Bridge. Skeletal components: Nasal bones. Frontal process of maxillary. Nasal part of frontal bone. Skeletal Framework Cartilages: Septal. Lateral. Alar. Mucous Membranes Sensory innervation: Anterior ethmoidal nerves. Nasopalatine nerves. Mucous Membranes Motor: Parasympathetics: Via CN VII. To: Pterygopalatine ganglion. To: Mucous glands: Via branches of maxillary nerve. Mucous Membranes Motor: Sympathetics: To: Blood vessels. From: Superior cervical ganglion. Via: Maxillary nerve. Paranasal Sinuses Maxillary: Largest. Present at birth. Opens to: Middle meatus. Via semilunar hiatus. Nerve supply: Superior alveolar nerve. Infraorbital nerves. Paranasal Sinuses Frontal: Paired. Opens to: Middle meatus. Via frontonasal duct. Nerve supply: Supratrochlear nerves. Supraorbital nerves. Paranasal Sinuses Sphenoidal: Paired. Opens to: Nasal cavity. Via sphenoethmoidal recess. Nerve supply: Maxillary nerves. Ethmoidal nerves. Paranasal Sinuses Ethmoidal: Group of ethmoidal air cells. Anterior and middle cells: Open into middle meatus. Posterior air cells: Open into superior meatus. Nasopharynx From base of skull to soft palate. Pharyngeal tonsils: Embedded in posterior wall. Enlarged = adenoids. Nasopharynx Salpingopharyngeal fold (muscle): Created by named muscle. Muscle extends from auditory tube cartilage to palatopharyngeus muscle. Opening for: Eustachian tube. Torus tubarius.