* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Notes
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
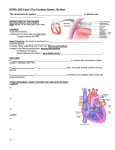
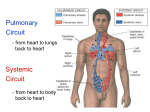
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Chapter 15 OVERVIEW BASIC FUNCTION: Bulk Transport – Move nutrients and gases to tissue areas Nutrients for energy, building materials Oxygen for cellular respiration – Remove wastes from tissue areas Urea and other metabolic wastes Carbon dioxide BASIC STRUCTURE: Heart + Vessels – Heart – force pump – Pulmonary Circuit – blood to lungs and back to heart Pulmonary Artery alveoli + pulmonary capillaries pulmonary veins – Systemic Circuit – circulation to all parts of body Arteries – take blood away from heart Capillaries – material exchange Veins – take blood towards heart DIAGRAM HEART STRUCTURE Coverings – Pericardium Outer layer Serous membrane – Mycardium – cardiac muscle tissue Thickest – Endocardium – lines chambers Purkinje fibers DIAGRAM Chambers – Atria – upper (L & R) Double layered Separated by pericardial cavity – Epicardium – visceral pericardium INTERACTIVE DIAGRAM Auricles – outside flaps – Ventricles – lower (L & R) – Ineratrial and interventricle septums Valves one way flow – Chordae Tendinae and Papillary muscles – Tricuspid – b/w R. Atria & R. Ventricle – Bicuspid (mitral) – b/w L. Atria & L. Ventricle – Pulmonary Semilunar – b/w R. Ventricle & Pulmonary Arteries – Aortic Semilunar – b/w L. Ventricle & Aorta VALVE DIAGRAM HEART STRUCTURE Order of Blood Flow (Deoxygenated Blood) – Veins from Systemic (Body) Circuit – Superior/ Inferior Vena Cava – Right Atria – Tricuspid Valve – Right Ventricle – Pulmonary Semilunar Valve – Pulmonary Arteries – Lungs (capillaries) HEART DIAGRAM Order of Blood Flow (Oxygenated Blood) – – – – – – – – Lungs (capillaries) Pulmonary Arteries Left Atria Bicuspid Valve Left Ventricle Aortic Semilunar Valve Aorta Arteries of Systemic Circuit Heart circulation – Coronary arteries capillaries cardiac veins coronary sinus CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM Specialized tissue to transmit muscle impulse for proper heart contractions – Functional synctium – Self-excitatory Cardiac cycle – 1 complete heartbeat – Blood through A-V valves – SA (sinoatrial) node Pacemaker Transmit impulse to atria “lub” – “dup” – 1st sound – A-V valves – 2nd sound – semilunar valves Atria diastole; Ventricle systole – AV (atrialventricular) node AV bundle (Bundle of His) purkinje fibers – Blood forced through semilunar valves – “Lub” – AV valves slam shut – Systole – contraction – Diastole – relaxation Atria systole; Ventricle diastole Murmur - defect Atria diastole; Ventricle diastole – Heart resets DIAGRAM EKG AND HEART ACTIONS Electrocardiogram – graph of electrical activity of heart during cardiac cycle – P wave – depolarization of atria Impulse causes atria systole – P-Q interval – flat line Impulse travels from atria to ventricular fibers No contraction – QRS Complex – depolarization of ventricles; repolarization of atria Ventricular systole Atria returning to relaxed state – T wave – repolarization of ventricles DIAGRAM FACTORS AFFECTING CARDIAC CYCLE Parasympathetic pathways – inhibit – Ach – Vegas Nerve Sympathetic pathway – excitatory – Norepinephrine Controlled by cardiac center (medulla oblongata) – Baroreceptors in carotid arteries and aorta – Cerebrum and hypothalamus Fainting – slow down Anxiety – speed up – Temperature – Ions Arrythmias – irregular heartrate (ECG) – Clinical Application 15.3 – P. 588 - 589 – Tachycardia, bradycardia, ventricular fibrillation – ECG interactive tool LAYERS OF THE HEART OPERATION OF VALVES ECG – Depolarization and Repolarization of cardiac tissue CORONARY ARTERIES & CARDIAC VEINS