* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory system function
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
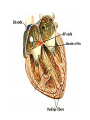
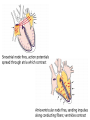
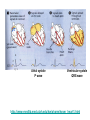
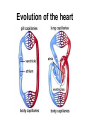
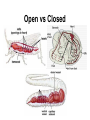
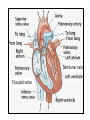
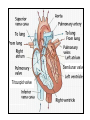
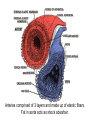
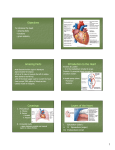
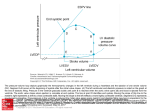
Bundle of His R T P Q S Atrial systole P wave Ventricular systole QRS wave http://www-medlib.med.utah.edu/kw/pharm/hyper_heart1.html Sinoatrial node (PACEMAKER) Generates electrical impulses that initiate heartbeats. CARDIAC CYCLE: Diastole: Relaxation of atria and ventricles Systole: Contraction of atria and ventricles Circulatory system function Digested food (as glucose) and fuel to cook the food (oxygen) need to be carried to every cell of the body for metabolism. Evolution of the heart Circulatory system Open (Mollusks and arthropods): Hemolymph (blood) flows through a system of channels and cavities. Closed (from annelids on): Circulating fluid always enclosed within vessels that transport blood to and from a pump (heart). Open vs Closed Circuits • Pulmonary: Circulation between heart and lungs. • Systemic: Circulation between heart and rest of body. Semilunar valve ventricle Tricuspid valve Semilunar valve ventricle Tricuspid valve Blood vessels • Arteries: Blood leaving heart. Branch out to arterioles and then capillaries. • Veins: Blood returning to heart. After gas exchange, blood is collected in venules leading to veins. Check your homework after reading this slide! Arteries comprised of 3 layers and made up of elastic fibers. Fat in aorta acts as shock absorber. Composition of blood PLASMA: extracellular environment (proteins, ions, hormones, etc.) BLOOD CELLS • Erythrocytes (RBC): Oxygen transport • Leukocytes (WBC): Immunological defense • Platelets: Blood clotting Erythocytes = red; platelets = yellow; T-lymphocyte = light green (SEM x 9,900). Copyright Dennis Kunkel, www.DennisKunkel.com