* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.6.1 AND 6.2 ACROSS - Hackettstown School District
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
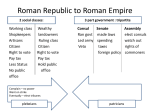
CHAPTER 6 CROSSWORD PUZZLE REVIEW 2. The common farmers, artisans and merchants who made up the majority of the population PLEBEIANS 7. The gap between these two groups only grew larger as time went on and often led to conflict RICH AND POOR 9. Daring Carthaginian general who invaded the Italian peninsula by taking elephants across the Alps HANNIBAL 10. 90% of Rome's population did this for a living FARMING 13. Like kings, these two people controlled the army and directed the government in the Roman republic CONSULS 15. Egyptian queen who made power plays through relationships with Roman leaders CLEOPATRA 16. A Roman virtue that valued strength, power, discipline and usefulness GRAVITAS 18. Rome challenged this trade rival for supremacy of the Mediterranean CARTHAGE 19. The Greeks, Latins and _____ settled early Rome and helped developed their unique culture. ETRUSCANS 20. The lifeblood of the Roman Empire; reliant upon a vast network of roads and shipping lanes TRADE 21. This group held the real power in the Roman Republic SENATE 22. The First ____ consisted of Pompey, Crassus and Julius Caesar TRIUMVERATE 23. His assassination in 44 BC ironically led to the end of the Roman Republic JULIUS CAESAR 24. Aristocratic class of Roman citizens; usually wealthy landowners PATRICIANS 1. The constant battle for power within the republic and empire often resulted in this CIVIL WAR 3. "The Roman Peace"; a time of peace and prosperity PAX ROMANA 4. The largest units of Rome's armies, made up of at least 5,000 foot soldiers LEGION 5. Would become Rome's first emperor; known as Augustus OCTAVIAN 6. They were elected members who represented the rights of the of the plebeians TRIBUNES 8. In times of crisis this absolute ruler was appointed to serve, but no longer than six months DICTATOR 11. Series of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage with Rome emerging as the new power of the Mediterranean PUNIC WARS 12. Rome was settled along this river TIBER 14. They were considered property, not people SLAVES 17. The written system of laws which later became the basis for later Roman law TWELVE TABLES 7. Became the basis of legal systems in most of Europe and the United States ROMAN LAW 9. New name given to the Roman capital; name after the emperor CONSTANTINOPLE 13. The religion of Christianity is based upon the life and teachings of this man JESUS 14. What happened to Christianity when Roman emperors persecuted the Church SPREAD QUICKLY 15. Classical civilization is also called this, because it is a blending of the two cultures GRECO ROMAN 18. Leader of the Huns; as they swept westward, German tribes began moving south, invading the Roman Empire ATTILA 19. Christianity offered the promise of this after believers died ETERNAL LIFE 20. City that was destroyed in AD 79 after the eruption of Mount Vesuvius POMPEII 1. He split the Empire in two, feeling that it had become too large for one person to rule DIOCLETIAN 2. These soldiers were hired into Rome's legions, but were only loyal to gold and their commanding general MERCENARIES 3. Engineering marvel created by the Romans to supply their cities with water AQUEDUCTS (Typo on the puzzle- there is one extra box- cross out the box with the 3 in it) 4. Roman empire's economy suffered from this when the value of their money dropped quickly INFLATION 5. Language spoken by people in the western part of the empire; became the language of scholars in the west LATIN 6. Roman historian concerned with Rome's lack of morality TACITUS 8. Title for the bishop of Rome POPE 9. As emperor, he outlawed the persecution of Christians in AD 313 CONSTANTINE 10. A leader in the Christian church who supervised several churches; usually one of these for each major city BISHOP 11. Paul was an example of this; a person who spreads a religion MISSIONARY 12. Emperor Constantine moved the capital of the empire to this eastern city, shifting power from Rome to the east BYZANTIUM 16. Languages that find their roots of the Roman language ROMANCE 17. Famous Roman poet who wrote epics similar to those of Homer VIRGIL 21. Meaning "savior"; many Jews believed that Jesus was this MESSIAH WHAT YEAR IS MOST RECOGNIZED BY HISTORIANS AS BEING THE OFFICIAL FALL OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE? 476 A.D.