* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cells of the immune system
Survey
Document related concepts
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
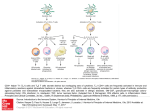
Lecture Outline Lymphocytes T-cells B-cells Natural Killer (NK) cells Acquired Immune Responses Humoral Cell-mediated Antigen Presentation (Introduction) Cytokines CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE LYMPHOCYTES (25-40% of WBC) CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE LYMPHOCYTES T-lymphocytes (T-cells) -Different subpopulations: -helper T-cells, cytotoxic/suppressor T-cells, intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) -Subpopulations of helper T-cells: TH1 & TH2 cells -Specific molecules or surface “markers” (i.e. CD4 and CD8) -T cell receptor (TCR). -T cells mature and further develop in the thymus. -Destroy infected cells, Cytokine Production, and Memory T-lymphocytes are Generated in the Thymus Specific molecules or surface “markers” of T-cells TCR ! CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE LYMPHOCYTES B-lymphocytes (B-cells) -Mature and develop in lymphoid tissues. -The antibody producing cells of the immune system. -Antibody secreting B-cells are also known as Plasma Cells. -B-cells also express antibody (immunoglobulins) on their surface. -Surface expressed antibody is called the B-cell receptor (BCR). -Clonal expansion of antigen-specific B-cells. -Exhibit immunological memory. Antibody production, Antigen Presentation, Memory Specific molecules or surface “markers” of B-cells BCR ! B-cells and T-cells are both found in Lymph Nodes CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE LYMPHOCYTES Natural Killer (NK) cells -Large granular lymphocytes. -Central cell of innate immune responses. -Participates in Cell Mediated Immune (CMI) Responses. -Efficient at recognizing and killing pathogen-infected host cells. -Also recognize and destroy damaged or altered host cells (i.e. tumors). -Not antigen specific. -NK-specific markers include; -CD56+ (CD3 negative) -Killer Ig-like Receptor (KIR+) -Low affinity FcR (CD16+) -Do NOT express TCR nor BCR! COOPERATION, COORDINATION, and COMMUNICATION The WBC of the immune system work together through a variety of complex interactions to defend the host. These interactions are essential and have evolved to rid the body of pathogens and other foreign substances. There are two sites at which pathogens may be located: 1. Extracellular sites 2. Intracellular sites Depending on the location of the pathogen, the immune response can be; 1. Humoral 2. Cell mediated (CMI) Innate Humoral Acquired Cell Mediated CD4+ TH1 TH2 CD8+ HUMORAL RESPONSE (TH2) vs. EXTRACELLULAR PATHOGENS Antibodies are important for; Neutralization -Bind to bacterial toxins. -Bind to molecules that pathogens use to attach to host cells. Opsonization -Facilitate uptake of pathogens by phagocytes. Complement Activation -Complement factors also act as opsonins. -Lyses of certain bacteria. ** Antibodies are NOT effective vs. intracellular pathogens ** 1. Neutralization http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/bowers/toxin-endo1.jpg 2. Opsonization http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/bowers/bact1.jpg 3. Complement Activation http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/ bowers/bact-comp.jpg CELL-MEDIATED RESPONSE (TH1) vs. INTRACELLULAR PATHOGENS Intracellular pathogens can reside in; Cytosol -Continuous with nucleus via nuclear pores. -Site of viruses and some bacteria. -Cells harboring pathogens in cytosol are recognized and killed by cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. CELL-MEDIATED RESPONSE (TH1) INTRACELLULAR PATHOGENS Intracellular pathogens can reside in; Vesicular System -Comprises the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, endosomes, lysosomes, and other intracellular vesicles. -Site of bacteria and some parasites. -Cells with pathogens in vesicular system are recognized by helper T cells (TH1), which then release products called cytokines that enable the infected cell to kill the pathogen. Complex Cellular Interactions During Immune Responses Antigens bacterial viral CD4+ WBCs APC; macrophages T-cells B-cells CD4+ Receptors TCR BCR CD4, CD8, MHC Soluble Proteins Cytokines Antibodies CD8+ Antigen Presentation CD4+ CD4+ CD8+ INITIATION OF RESPONSES DETECTION, PROCESSING & PRESENTATION of Antigens TH1 cytokines CD4+ TH2 cytokines CD4+ CD4+ CD8+ Humoral Response (TH2) HUMORAL RESPONSE Response to EXTRACELLULAR PATHOGENS CD4+ Produce Antibodies CD4+ CD4+ Cell-Mediated Response (TH1) CD8+ CELL-MEDIATED RESPONSE INTRACELLULAR PATHOGENS CD4+ CD8+ CYTOKINES “Hormones” of the Immune System The complex interactions among cells of the immune system are mediated by a group of proteins known as cytokines -Also referred to as Lymphokines, Interleukins, and Chemokines. -Cytokines are produced by a wide variety of cells types. -Cytokines can have effects on both nearby cells or throughout the body. CYTOKINES CYTOKINE ACTIONS CYTOKINE-MEDIATED RESPONSES Effects of Cytokines on cells can be: Pleiotropic -Cytokine elicits different biological activities in different cell types. Redundant -Different cytokines can mediate similar responses. Synergistic -The combined effect of two different cytokines greater than the effect of either cytokine alone. Antagonistic -The effect of one cytokine inhibits the effect of another. TYPES OF CYTOKINES Interferons - alpha, beta, and gamma Interleukins - IL-1 through IL-30 Tumor Necrosis Factor - alpha, beta Transforming Growth Factor - alpha, beta Colony Stimulating Factors Chemokines CYTOKINES produced by CD4+ Helper T-cells Cytokine TH1 TH2 Cytokines produced by helper TH1 and TH2 cells regulate immune responses Dominant TH1 Response Strong cell-mediated immunity. Dominant TH2 Response Strong humoral (antibody-mediated) immunity. Cross-regulation TH1 cytokines such as Interferon-gamma inhibit TH2 responses. TH2 cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-10 inhibit TH1 responses. Interferon-gamma and IL-4 provide different signals to helper T-cells: Interferon-gamma acts through Stat-1 which promotes TH1 cell activation. IL-4 acts through Stat 6 which promotes TH2 cell activation. The end result is cytokine induced cross-regulation of helper T-cell function