* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
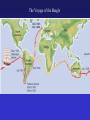
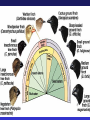
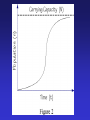
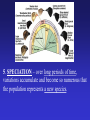
Natural Selection: the mechanism for evolution Charles Darwin (1809 – 1882) I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection. - from The Origin of Species Darwin’s Voyage of Discovery A reconstruction of the HMS Beagle sailing off Patagonia. The Voyage of the Beagle Galapagos Islands http://vimeo.com/17051816 • http://app.discoveryeducation.com/player/vi ew/assetGuid/9E8DE1D4-BCBD-422CB307-E79CA309E95C Natural Selection: Nature acts as the “selecting” agent. Organisms better adapted (most “fit”) to the environment survive and reproduce more successfully. STEPS of Natural Selection: 1. VARIATION - Individuals of a population vary in their characteristics (different color, muscles, eyesight, etc.) HOW DOES THIS OCCUR?????? 2. OVERPOPULATION – A population produces more offspring than can survive 3. COMPETITION – Because of over population, there is competition - “struggle for existence” between organisms for food, space, water, etc. 4. Heredity “DIFFERENTIAL REPRODUCTIVE SUCCESS” Individuals with best suited traits to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce more offspring, passing the helpful variations on in the population. 5. SPECIATION – over long periods of time, variations accumulate and become so numerous that the population represents a new species. Artificial Selection • Humans “select” which organisms breed (humans act as selecting agent instead of nature) Selection Pressures Factors that cause “selection” to occur: • Amount of food available • Water • Shelter • Predation (predators hunting a population) • Disease • Humans…? • Evolution is the progressive change in populations of organisms over time through the process of natural selection. • It explains how biodiversity is achieved. How does evolution really work? Video and Questions: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/cou rse/session4/explore_a.html Evolution of Camouflage Video: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/cou rse/session4/explore_b.html http://app.discoveryeducation.com/player/view/assetGuid/12302FAB-8366-4FCEBF17-7A75F5700B4D