* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
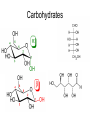
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life Mr. Nagel Meade High School IB Syllabus Statements • 3.2.1 – • 3.2.2 – • Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complementary base pairing and hydrogen bonds. 3.3.5 – • Outline how DNA nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds into a single strand. 3.3.4 – • State the names of the four bases in DNA. 3.3.3 – • Outline DNA nucleotide structure in terms of sugar (deoxyribose), base and phosphate. 3.3.2 – • Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage. 3.3.1 – • State three functions of lipids. 3.2.7 – • Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. 3.2.6 – • State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. 3.2.5 – • List three examples each of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. 3.2.4 – • Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from diagrams showing their structure. 3.2.3 – • Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA. http://click4biology.info/c4b/3/chem3.htm Carbohydrates • CnH2nOn (1:2:1 ratio) • Structure – Rings Chains – α-linkages and β-linkages – Isomers (same formula, different arrangement) • Glucose (cell energy), Galactose (milk), Fructose (fruit) • All are isomers of C6H12O6 • Mono, Di, and Poly – Di • Lactose (Glucose + Galactose) • Sucrose (Fructose + Glucose) • Maltose (Glucose + Glucose) – Poly • Glycogen (Animal sugar storage chain) – α -1,4 Glucose (more branching) • Starch (Plant sugar storage chain) – α -1,4 Glucose (less branching) • Cellulose (Plant cell wall) – β-1,4 Glucose Carbohydrates Lipids • Non-polar Hydrocarbon chains – Lots of C’s and H’s, few O’s – Three functions • Store energy, Cell membranes, Vitamins/Hormones – Fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins • Hydrophobic • Monomer (most): Fatty Acid – hydrophilic head (carboxyl end), hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon) >Saturated – means all Carbons have 2 hydrogen atoms bonded to it. >Unsaturated – means that some Carbons have double bonds (less H atoms) • Three types Triglycerides composed of three molecules of fatty acids and joined to one molecule of glycerol Solid at room temp fats; Liquid at room temp oils Waxes composed of long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain waterproofing (plant leaves) Steroids composed of four carbon rings ex: hormones, nerve tissue, and plant poisons Lipids Amino Acids • Peptide Bond – covalent bond between the amino (NH2) group of one amino acid and the carboxylic group (COOH) of another >Dipeptide – two amino acids bonded together >Polypeptide – 3+ amino acids bonded together • Enzymes – proteins that act as catalysts in intermediary metabolism that are essential for functioning of cell • Substrate – reactant in a chemical reaction that is catalyzed by the enzyme Amino Acids Protein Structure • Primary – Individual Amino Acid ‘Spelling’ • Secondary – Local geography (H bonds) • Alpha helices • Beta pleated sheets • Tertiary – Large geography (protein shape) • Hydrophobic regions • Disulfide bridges • Ionic bonds • Quaternary – Macrostructure (multiple units to make uber protein) Nucleic Acids • Monomer: Nucleotide • Three components • Phosphate group • 5-carbon Sugar • Pentose • • Ribose Deoxyribose • Nitrogenous Base • Two Flavors • DNA • Genetic Information • RNA • Protein manufacturing Organic molecules • Carbon backbone with one or more additional elements – Rings, branched, unbranched, double bonds, triple bonds • Monomers Polymers (macromolecules) • Hydrolysis • Condensation R(x)s Gizmo! • Time to explore how monomers are assembled and disassembled – Enroll in class • We already did this the first week of school, but you may forget your login or may have transferred/switched classes – A2: FNRN6JKZTK – B1: ZKWLDCNKSL – Play around. There are THREE tabs to explore. – Answer the assessment questions (you get one try!) • Mini-Lab grade! (5 points)