* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction of Tumor Immunology
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
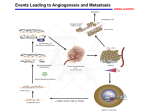
Introduction of Tumor Immunology • Bei-Chang Yang (楊倍昌), Ph.D. Department of Microbiology & Immunology ext 5637; [email protected] • Pin Ling (凌 斌), Ph.D. ext 5632; [email protected] • References: 1. Tumor Immunology and Cancer Vaccines (Samir Khleif, Publisher: Springer; 1st edition 2005) 2. Cancer Immunotherapy-Advances in Immunology, Vol. 90 (James Allison, Glen Dranoff; Publisher: Academic Press 2006) Goals of This Course • Build up the concepts of Tumor Immunology • Learn the current development of Tumor Immunology, including immunotherapy & cancer vaccines. • Not only deliver the knowledge but exercise thinking Outline of Lecture Topics • Discuss the interactions between the immune system and the cancer development, covering the following topics: (1) Basic concepts of tumor immunology (2) Immunosurveillance and immunoediting of cancer (3) Mechanisms of immune evasion by tumors (4) Cancer vaccine development Cancer immunotherapy (5) Inflammation & Cancer, and other topics Lectures & Paper Discussion • Run the class with “Lectures” and “Paper discussion” • Lectures deliver the basic concepts of fields. • Paper discussion focuses on the latest articles related to specific topics. • Research Project discussion - Choose a type of cancer as the topic of cancer immunotherapy - Apply the knowledge from this course to cancer treatment Paper & Project Discussion 1. 4 sections of Paper discussion and 2 sections of Project discussion 2. 2 paper presentations each time for 4 sections (Total 9 students) 3. 2 project presentations each time for 2 sections (Total 4 groups) 4. Each presentation: 40 min talk and 10 min discussion Evaluation 1. Attendance – 60% 2. Paper & Project Presentation – 20 % 3. Class performance – 20% Overview of Tumor Immunology 1. Tumorigenesis 2. Discovery of the protective immune response against tumors. 3. T cells recognize specific antigens on tumors 4. Tumors can escape in many ways 5. Immunotherapy for tumors How does cancer arise? Dysregulated cell growth & proliferation => Transformation A clone of cells expanding indefinitely => A tumor Tumor cells => the body and cause diseases => Cancer How does cancer arise? II Q: What causes dysregulated cell growth & proliferation? • Intrinsic factors - Genetic mutations on Oncogenes & Tumor suppressor genes • Environmental factors – Radiation, Carcinogens • Microbial infections – Viruses (viral oncogenes) Bacteria The Strategies for Cancer Therapy The best scenario – Kill all the tumor cells without destroy others in the body 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Surgery – remove tumor cells & tissues physically Radiotherapy – non-selective, strong side effect Chemotherapy - non-selective, strong side effect Gene therapy – relatively selective Targeted therapy - relatively selective Immunotherapy => manipulate an immune response against tumor cells but not normal cells => quite selective Key Concepts in Tumor immunity 1. Tumors express Ags that are recognized as foreign by the host immune system. 2. Immune responses frequently fail to prevent the growth of tumors. 3. The immune system can be activated by external stimuli to effectively kill tumor cells and eradicate tumors. 4. Various strategies have been developing to enhance the anti-tumor immune responses. Discovery of Immune surveillance of tumors Discovery of Immune surveillance of tumors 1. Immune SurveillanceMacfarlane Burnet in 1950s 2. Use syngeneic mouse strain => Transplantation exp 3. Immunization w/ irradiated tumor X cells protects a syngeneic mouse w/ live X tumor cells but not Y tumor cells. 4. Antigens expressed by tumors, termed tumor antigens. 5. Defense against tumors is mainly mediated by T cells Immune surveillance of tumors-II Identification of tumor Ags by CTLs Examples of tumor antigensI Examples of tumor antigens-II Tumor antigens arise by point mutations in self proteins Tumor antigens arise by reactivated genes or overexpressed genes Induction of T cell responses to tumors Cross-priming (cross-presentation) mediated by APCs, ex. DCs Immune responses to tumors 1. Adaptive immune responses to tumors: a. CD8 CTLs are the key players on the killing effect of tumors. b. CD4 T helper cells => cytokines => CTLs c. Abs => activating complements or Ab-dep cell-med toxicity => preventing oncogenic viruses 2. Innate immune responses to tumors: a. NK cells kill many types of tumor cells that have reduced class-I but express ligands for activating NK cells. b. Macrophages => Ab-med phagocytosis => Cytokines (TNF-a), ROS, & NO Overview of Tumor Immunology 1. Tumorigenesis 2. Discovery of the protective immune response against tumors. 3. T cells recognize specific antigens on tumors 4. Tumors can escape in many ways 5. Immunotherapy for tumors Overview of Tumor Immunology 1. Tumorigenesis 2. Discovery of the protective immune response against tumors. 3. T cells recognize specific antigens on tumors 4. Tumors can escape in many ways 5. Immunotherapy for tumors Q: Why tumors still develop in the body if the immune system has the ability to recognize them? Tumors develop many ways to escape from immune attacks Mechanisms of Tumor evasion Treg infiltrating Tumors w/Fas Tumor loss of MHC-I as a evasion mechanism Immunoediting of Cancer Dunn et al. Nature Reviews Immunology 6, 836–848 (November 2006) | doi:10.1038/nri1961 The progress in Immunology & Molecular Biology in past few decades make possible to manipulate the immune responses against tumors. Enhancing Tumor Immunogenicity Enhancing Anti-Tumor Responses Overview of Tumor Immunology 1. Tumorigenesis 2. Discovery of the protective immune response against tumors. 3. T cells recognize specific antigens on tumors 4. Tumors can escape in many ways 5. Immunotherapy for tumors Tumor vaccines-Targeting DCs Types of Tumor Vaccines Enhancement of tumor immunogenicity Immunotherapy with cytokine gene-transfected tumor cells Systemic cytokine therapy for tumors Passive Immunotherapy for tumors Adoptive cellular therapy Therapy with Anti-tumor Monoclonal Abs Approved Anti-tumor mAb SUMMARY 1. Cancer is a complex and progressive genetic disease. 2. Tumors express Ags that could be recognized by the immune system. But some tumors are weakly immunogenic and the immune system often fails to eradicate them. 3. Cancer from clinical cases usually represents the leading of cancer development over the anti-cancer immune responses. 4. The imperative issue in the field of tumor immunology is to improve the capability of immune defenses to fight cancer. Paper Discussion on March 18 SCIENCE VOL 319 11 JANUARY 2008 Recognition of a Ubiquitous Self Antigen by Prostate Cancer–Infiltrating CD8+ T Lymphocytes Peter A. Savage,1 Keith Vosseller,2 Chulho Kang,3 Kevin Larimore,4 Elyn Riedel,5Kathleen Wojnoonski,1 Achim A. Jungbluth,6 James P. Allison1* Nature. 2007 Jan 4;445(7123):106-10. Epub 2006 Nov 19 A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice. O’Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S, Dick JE. Division of Cell and Molecular Biology, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, M5G 1L7, Canada. The End & Thank you