* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GENETICS AND INHERITANCE
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
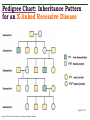
GENETICS AND INHERITANCE CHAPTER 19 Alleles • Different forms of homologous genes: humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • Homozygous: both alleles identical • Heterozygous: alleles different • Genotype: complete set of genes and alleles • Phenotype: observed physical and functional traits Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Punnett Squares Figure 19.2 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Patterns of Genetic Inheritance • Punnett square analysis: predicts patterns of inheritance • Mendel developed basic rules of inheritance • Law of segregation: reproductive cells carry only one copy of each gene • Law of independent assortment: genes for different traits are separated from each other independently during meiosis; applies in most cases Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Allelic Interactions • Genotype and environment affect phenotype • Dominant alleles: gene always expressed, even if heterozygous • Recessive alleles: two copies of gene needed to be expressed, must be homozygous • Incomplete dominance: heterozygote is an intermediate phenotype Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Allelic Interactions (cont.) • Codominance: both phenotypes equally expressed • Polygenic inheritance: multiple genes involved • Linked genes: may be inherited together if close on a chromosome Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Pedigree Chart: Inheritance Pattern for an X-linked Recessive Disease Figure 19.12 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Sex-Linked Inheritance: X and Y Chromosomes • Origin of sex chromosomes • Chance mutations • Y determines sex • Sex-linked genes located on sex chromosomes • Sex linked or X-linked inheritance • Characteristics: mostly males with disease, passed to sons by mother, father cannot pass the gene • Sex influenced traits: affected by presence of testosterone, estrogen Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Genes and Behavior • Mechanism • Product from gene-specific proteins • Proteins have specific functions leading to phenotypes • Protein Functions: hormones, enzymes, structural, neurotransmitters Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings.