* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
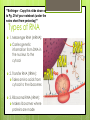
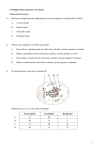
DNA … and Replication DNA DNA is often called the blueprint of life It contains the instructions for making proteins within the cell Full name: deoxyribonucleic acid Why do we study DNA? It’s central importance to life on earth Medical benefits – cures for diseases Better food crops Shape DNA is a very long polymer It’s basic shape is like a twisted ladder or zipper This is called a double helix Nucleotides DNA is a polymer made up of smaller monomers called nucleotides Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogen base Nitrogenous bases DNA has 4 nitrogen bases: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) The bases are specifically paired: Adenine – thymine Guanine – cytosine Base pairings The nitrogen bases are attracted to each other through hydrogen bonds Hydrogen bonds are weak but there are millions of them in a single DNA molecule CHECKPOINT Thumbs up = true, thumbs down = false Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate, nitrogen base and a protein 1 DNA molecule = 1 nucleotide There are 2 strands in each DNA molecule which are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases CHECKPOINT Hold up 1, 2, 3 or 4 fingers: In a DNA molecule, cytosine always pairs with 1- Itself (Cytosine) 2- Guanine 3- Thymine 4- Adenine The Code of Life… The “code” of a gene on a chromosome comes from the specific order of the bases in the gene A T C G T A T G C G G… DNA Replication DNA must be replicated or copied before a cells divides This happens during S (synthesis) phase of interphase The DNA molecule produces 2 identical new complimentary strands following the base pairing rules (A-T & C-G) Each strand of original DNA serves as a template for the new strand Replication process An enzyme called helicase unwinds and separates (unzips) the 2 DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases Replication Another enzyme called DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to each original strand This enzyme initially makes about 1 in 10,000 base pairing errors Other enzymes come through and proof read & correct these errors 1 in 1 billion errors after proofreading http://www.pbs.org/wgb h/aso/tryit/dna/shockwav e.html Replication Semi-conservative theory: The 2 strands of the parental (original) DNA molecule separate and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new complimentary strand Half of the original strand is saved CHECKPOINT What is the name of the enzyme that unzips the DNA molecule? What is the name of the enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the template strand? Why is DNA replication referred to as “semiconservative”? RNA – Ribonucleic acid Responsible for the movement of genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) in the cytoplasm Structure of RNA: Made of repeating nucleotides Single-stranded Differences from DNA: 1. Sugar – ribose 2. Nitrogen base – there is NO thymine, RNA has uracil instead which then pairs with adenine **Bellringer - Copy this slide down on to Pg. 29 of your notebook (under the notes sheet from yesterday)** Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to the cytosol 2. Transfer RNA (tRNA): Takes amino acids from cytosol to the ribosomes 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Makes ribosomes where proteins are made