* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules - Van Buren Public Schools
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
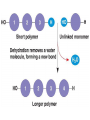
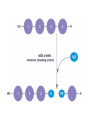
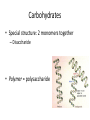
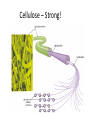
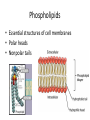
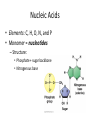
Macromolecules Chemistry of Life Notes Part 3 Remember: Key Elements in Biological Systems C H Carbon Hydrogen N Nitrogen O P S Oxygen Phosphorous Sulfur Biology = Carbon Based Importance of Carbon • Abundant • Versatile • Tetravalent – Forms 4 bonds – Leads to LOTS of variety Macromolecules • Large! • Accomplish all life functions • Types: Carbohydrates, lipids*, proteins, nucleic acids Macromolecules – Building Blocks • Monomer – the repeating subunits of polymers; building blocks • Polymer – long molecule consisting of many similar subunits Building/breaking molecules rely on H2O Polymer Synthesis Term note: Synthesis = to make or form • Dehydration Synthesis – Water is removed – Bonds form between two monomers – One molecule donates –OH and the other molecules donate the –H Put it together = H2O Polymer Breakdown • Term note: Hydro = water; Lysis= to split • Hydrolysis Reactions – Water is added – Break bonds between monomers using water – Allows food to be digested Carbohydrates! Carbohydrates • Other terms: Sugars or starches • Elements: C, O, H • Monomer = monosaccharide – Examples: glucose, fructose Carbohydrates – Monomer Shape DRAW: Carbohydrates • Special structure: 2 monomers together – Disaccharide • Polymer = polysaccharide Polysaccharides – Energy storage • Polysaccharides are great for short term storing of energy • Plants: Energy storage in starch (sugar) molecules • Animals: Energy storage in glycogen molecules Polysaccharides - Structure • Plants: Cellulose is the structure molecule for cell walls • Animals and Fungi: Chitin is the structure molecule (exoskeleton in bugs, cell walls in fungi) Cellulose – Strong! Lipids! Lipids • Other terms: waxes, fats, and oils • Elements: C, H, and O • Monomers: Three major types – Triglyceride (glycerol and fatty acid chains) – Phospholipids – Steroids Fatty acid chains Glycerol Lipids • Key features: – Lipids are nonpolar – Lipids are hydrophobic Hate water! Fats (Triglycerides) • Long term energy storage and insulation • 1 glycerol & 3 fatty acid chains • Types: Saturated and unsaturated (unhealthy) Phospholipids • Essential structures of cell membranes • Polar heads • Nonpolar tails Steroids • Hormones and body functions • Example: Cholesterol Proteins! Proteins • Elements: C, H, O, N, and some S • Monomer: – Amino Acid – 20 types! • Polymer: – Polypeptide chain Label and draw the amino acid! Proteins • Key Features: – Control most functions in humans – Very diverse Proteins Basic Functions • • • • • • Enzymes Structure/support Transport of substances Hormones Cell communication Protection against disease Nucleic Acids! Nucleic Acids • Elements: C, H, O, N, and P • Monomer = nucleotides – Structure: • Phosphate + sugar backbone • Nitrogenous base Nucleic Acids • Polymers: DNA & RNA • Functions: – DNA = genetic material organisms inherit from parents – Blueprint for proteins + information storage molecules RNA vs. DNA