* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate and Weather - AHS * Humanities 11
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
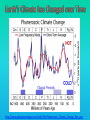
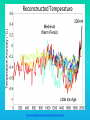
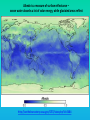
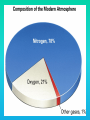
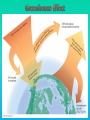
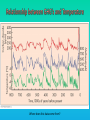
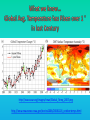
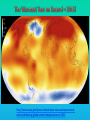
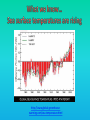
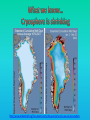
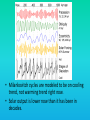
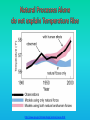
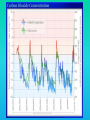
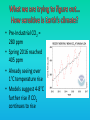
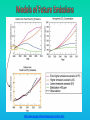
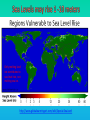
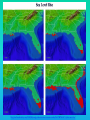
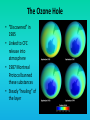
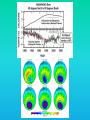
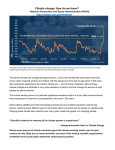
Lauren Heerschap, Fort Lewis College, Spring 2016 • Do you think Earth is cooler or warmer now, compared to past climates? • What are some factors that cause Earth’s climate to change? • How do current changes compare to past changes? http://www.globalwarmingart.com/wiki/File:Phanerozoic_Climate_Change_Rev_png http://www.globalwarmingart.com/wiki/Temperature_Gallery http://www.globalwarmingart.com/wiki/Temperature_Gallery • Paleoclimatology! – Direct Measurements or Records: • Instrumental Record – temperature since about 1860 • Historical Records – written records and archeology, ex: Little Ice Age, Medieval Warm Period – Proxy Data: • Sedimentary Rock Record – rock types and fossils indicate past environments • Tectonic History – distribution of landmasses, mountains, oceans all can affect global climate • Isotopes – oxygen (O-16 vs. O-18) derived from corals and sediments indicates “weight” of seawater and general temperature • Evidence of Glaciation – erosion and deposition by ice leaves record • Ice Cores – trapped gas bubbles show past CO2 and CH4, and also contain ash, pollen, dust that help illustrate climate • Tree Rings – dendrochronology, shows drought vs. wet seasons, fire • Pollen – palynology, tells what plant species were nearby • Tectonics – arrangement of continental masses and areas of high elevation, mountain building • • • • Ocean currents – circulation of cold and warm currents Volcanic activity – release of aerosols, GHGs Atmosphere – amount of GHGs present, methane releases Carbon sequestration or release – times of higher % vegetation, coal formation, limestone formation, weathering • Milankovitch cycles – variations in Earth’s orbit, tilt, and axis wobble • Solar cycles/forcing – variation in Sun’s energy (minor) • Albedo – reflectance of surface leads to feedback loops • Anthropogenic forcing – people! Post-Industrial Revolution increases in greenhouse gases, deforestation, agriculture Ocean currents distribute warm and cold waters throughout the globe Milankovitch Cycles are variations in Earth-Sun geometry that cause glacial fluctuations Albedo is a measure of surface reflectance – ocean water absorbs a lot of solar energy, while glaciated areas reflect http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=5484 Composition of Earth’s Current Atmosphere • • • • • • • Water vapor Carbon dioxide Methane Nitrous oxide Ozone CFC’s Sulfur hexaflouride Earth would be -18 °C on average without these gases! (It’s about 14 °C now…) • These gases trap the Earth’s heat, reduce its heat loss, maintain its temperature – like a greenhouse! That’s 100 ppm higher than past 400,000 years! March 2016 405 http://globalclimatechange.jpl.nasa.gov/ http://globalclimatechange.jpl.nasa.gov/evidence/ Where does this data come from? From www.epa.gov http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/ http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/ http://www.scar.org/images/news/Global_Temp_2007.png http://www.noaanews.noaa.gov/stories2008/20081118_octobertemps.html http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/global/2014/13/supplemental/page-4 RANK 1= WARMEST PERIOD OF RECORD: 1880–2015 YEAR ANOMALY °C ANOMALY °F 1 2015 0.90 1.62 2 2014 0.74 1.33 3 2010 0.70 1.26 4 2013 0.66 1.19 5 2005 0.65 1.17 6 (tie) 1998 0.63 1.13 6 (tie) 2009 0.63 1.13 8 2012 0.62 1.12 9 (tie) 2003 & 2006 0.61 1.10 9 (tie) 2007 1.10 0.61 https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/global/201513 http://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-noaa-analyses-revealrecord-shattering-global-warm-temperatures-in-2015 1880s 1980s These maps show temperatures across the world in the 1880s (left) and the 1980s (right), as compared to average temperatures from 1951 to 1980. This difference from average is called an anomaly. The map on the left shows that it was colder in the 1880's in most places. The map on the right shows it was warmer in the 1980s in most places. Earth's average surface temperature has increased almost 1.5°F during the 20th century. Two-thirds of the warming has occurred since 1975, at a rate of roughly 0.3°F-0.4°F per decade. Source: NASA http://www.global-greenhousewarming.com/sea-temperature.html http://www.columbia.edu/~mhs119/SeaLevel/ http://www.carbonbrief.org/five-reasons-why-the-speed-of-arctic-sea-ice-loss-matters http://www.globalwarmingart.com/images/f/f0/2007_Arctic_Sea_Ice.jpg http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/global/2013/13 http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/service/global/extremes/201313.gif • 2007 report by Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a group of 1200 scientists from 120 countries, concluded that there is 90% probability that observed changes in climate are anthropogenic • Milankovitch cycles are modeled to be on cooling trend, not warming trend right now. • Solar output is lower now than it has been in decades. http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/causes.html http://www.global-warming-and-the-climate.com/images/Manns-hockey-stick.gif • Pre-Industrial CO2 = 280 ppm • Spring 2016 reached 405 ppm • Already seeing over 1C temperature rise • Models suggest 4-8C further rise if CO2 continues to rise http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/future.html http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/future.html • • • • • • • • • Shift in world’s climate zones Extinctions, Loss of Biodiversity Melting Ice: Sea Level Rise, Water Resources Displaced coastal/island communities Droughts, Famines Increased storms, hurricanes, floods, landslides Wildfires Ocean Acidification Feedback Loops • IPCC conclusions: – If temperatures rise 2°C above preindustrial levels, 20-30% of plants and animals may be subject to extinction – If temperatures rise 4°C, 40-70% of species will be at risk Only melting land ice contributes to sea level rise, not melting sea ice. http://www.globalwarmingart.com/wiki/Special:SeaLevel http://earthandindustry.com/2012/08/energy-and-environment-news-roundup-%E2%80%93-8-7-12/sea-level-rise/ http://www.buzzardsbay.org/images /hurricane-frequency-us.gif http://static.icr.org/i/articles/imp/imp406-Hurricane-frequency.jpg Wildfires >250 acres, 1980-2003 http://www.nasa.gov/centers/godda rd/news/topstory/2006/wildfire_thr eat.html • Positive (enhance changes): • Negative (dampen changes): – Water vapor – Natural GHGs – Albedo & Melting Ice – Methane hydrates – CFCs & ozone layer – Aerosols – Black carbon – Cloud cover – Vegetation/Algal Blooms – Cold freshwater influx into oceans Stabilization • Global: – Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) provides information to guide policies – first report in 1990 – United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) began in 1992 at Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro – Kyoto Protocol (1997): GHG emission target limits aiming for below 1990 levels (US did not ratify) – 2014 Agreement with China: https://www.whitehouse.gov/the-pressoffice/2014/11/11/fact-sheet-us-china-joint-announcement-climate-changeand-clean-energy-c – Carbon Cap and Trade, Carbon Offsets, Carbon Tax • National: US is not unified in efforts, many organizations are involved • State: California target of reaching pre-1990 GHG levels by 2020 through renewable electricity sources, carbon trading, strict vehicle emissions standards • Local: grassroots efforts aplenty! • Individual???? The Ozone Hole • “Discovered” in 1985 • Linked to CFC release into atmosphere • 1987 Montreal Protocol banned these substances • Steady “healing” of the layer http://www.theozonehole.com/cfc.htm http://maps.grida.no/library/files/archivetv07_l.gif • What facts support the idea of anthropogenic causes for global warming? • Climate skeptics use what counter-arguments against anthropogenic causes? • How can people look at the same facts but have differing interpretations? • In your opinion, what is the ‘scariest’ consequence of future global warming? • Are there any positive aspects of global warming? • What is the most important thing humans should do NOW to counteract global warming? • Are the environment and the economy inherently at odds with each other? • EPA: http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/ and http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/causes.html • NOAA: http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/climate-information • IPCC: http://www.ipcc.ch/ • NASA: http://climate.nasa.gov/