* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geneticseasy
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
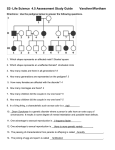
GENETICS • • • • • • • • • Mendel Vocab Practice Mono-crosses Di-crosses Sex crosses Non-Mendel Pedigrees Genetic Engineering Gregor Mendel “Father of Genetics” • • • • Born in Czechoslovakia in 1822 Died in 1884 Studied math and statistics (Biology was a hobby) Entered monastery in Austria at age 21 so he didn’t have to pay for college • Between 1856-1863 he studied over 30,000 pea plants he grew in the monastery garden…(lots of offspring really fast and yummy) • Mendelian Genetics Flower Parts Cross pollination vs. Self pollination Mendel’s Laws • Law of Segregation: random separation of homologous pairs of chromosomes during Anaphase 1 of meiosis. • Law of Independent Assortment (Dihybrid cross): the separation of the alleles of one allelic pair is independent of the segregation of the alleles of another allelic pair • Law of Dominance: One trait trumps another, so, if Dominant trait (capitol letter) is present it will show!!! Basic VOCAB!!!!! Foundation of Genetics • Gene: short segment of DNA, located on a chromosome, that codes for a protein to show a trait. • Trait: a characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring. Ex: blonde hair • Sex-trait: a characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring on sex chromosome (pair #23, X or Y). Ex: blonde hair • Heredity: the passing of traits from parent to offspring. • Genetics: The study of Heredity More vocab!!!! THE IMPORTANT STUFF • Allele: form of a gene…2 alleles per trait – Dominant- stronger, expressed if present, represented by a capitol letter (F) – Recessive- weaker, not expressed if alone, Only expressed if both alleles are recessive, represented by a lower case letter (f) • Genotype: combination of 2 alleles – Homozygous (pure)- (FF or ff)- can be dominant or recessive, both alleles the same – Heterozygous (hybrid)- Ff- the alleles are different • Phenotype: How it physically looks…..ex. Tall, white, short Practice naming and what trait will it show (dominant or recessive) • • • • • RR Tt PP Rr rr Homozygous Dominant--------------- dominant trait Heterozygous-----------------------------dominant trait Homozygous Dominant--------------- dominant trait Heterozygous-----------------------------dominant trait Homozygous recessive--------------- recessive trait Word Problem Steps 1st- Write the two traits 2nd- Figure out which one is dominant and which is recessive 3rd- Pick a letter to use, assign the dominant trait the uppercase of that letter and assign the recessive the lowercase of that letter………… 1 trait = 1 letter 2 traits = 2 letters • A person is heterozygous for curly hair which is the dominant trait over straight hair. What is his genotype? C- curly c- straight Cc • A person has blue skin which is dominant to green. What are the possible genotypes and BB- blue what phenotype will it show? B- blue b- green Bb- blue bb- green • A person has Brown eyes which is dominant to hazel. He is homozygous, what is his genotype? B-brown b- hazel BB • A person has red hair which is recessive to blonde hair. What is his genotype? B-blonde b- red bb Genetic Cross Punnett Square • Punnett Squares are used to solve genetic problems. They show the probability that a certain trait will be inherited by the offspring. MOM’s alleles 25% 25% DAD’s alleles 25% 25% THE BOXES ARE THE POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF THE OFFSPRING Mono Crosses • 1 trait involved in a cross. So only 1 letter, the uppercase and lowercase of it. • Steps: 1st Follow your previous steps for naming 2nd Draw your Punnett Square 3rd Put the parents alleles on the outside 4th Down and over (fill in boxes) • In pea plants, round seeds is dominant and wrinkled is the recessive trait. Show a cross between a homozygous round and a homozygous recessive. What are the possible genotypes and phenotype ratios? • Short fur in rabbits is dominant to long fur. What phenotype ratio and genotype ratio would you expect from a heterozygous female and a male with long fur? • Pink hair in trolls is more powering than green hair. If two heterozygous pink haired trolls made a baby troll, what are the possible genotypes and phenotype ratios? • In guinea pigs, rough hair is dom over straight hair. If two heterozygous pigs are crossed, the largest number of any one genotype of offspring would probably be ? If a yellow heterozygous flower was mated with a white recessive flower, what could the possible outcomes be? THINK!!!!!!! I buy a dog with Red fur. Red is the dominant trait over golden. I wanna know what genotype my dog is for breeding purposes. How would I go about doing that? TEST CROSSES • Test cross = the cross of an organism with an unknown dominant genotype (heterozygous and homozygous dominant) with a (known) genotype (homozygous recessive) So remember, AN ORGANISM WITH A RECESSIVE TRAIT ALWAYS HAS A HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE GENOTYPE (two lowercase letters). • To summarize a little, here are the "Key Points" to remember about a TEST CROSS. LOOK AT THE OFFSPRING!!!!!!!!!!!!! • I buy a dog with Auburn (red) fur. Red is the dominant trait over blue. What are the possible genotypes for this red dog and how would I go about finding out which one he is? I have a brown bunny. For bunnies, brown fur is dominant to white fur. I would like to know which genotype my bunny is. So I mated him with a white bunny and came out with all brown bunnies. What genotype is my bunny? Show the cross to prove it!!!! SEX-linked traits • Carried on the sex chromosomes (mostly on X) X and Y • Still have a dominant and recessive allele that is written as a superscript only on the X chromosome. ex: Xr Xr • Must also specify if a man/ woman – Females XX – Males XY • Males show most sex-linked traits because only has 1 X chromosome • Most diseases carried on the X chromosome • Females can be carriers (heterozygous) Punnett Squares are the same, just have to bring down/over everything Lets practice • Eye color is a sex-linked trait carried on the X chromosome. Red is dominant to white. - Female with white eyes - Female that is heterozygous for red eyes - White eyed male - Red eyed male Cross 1: Cross a White eyed male and a Homozygous red eyed female. Cross 2: Cross a Red-eyed male and a white eyed female. 1) A colorblind man marries a normal, non-carrier woman. Colorblindness is a recessive disorder. What are the chances that they will have a: a. normal son b. colorblind son? c. colorblind daughter? d. daughter who is a carrier? 2) A normal-vision man marries a colorblind woman. What are the chances that they will have a: a. normal son b. colorblind son? c. colorblind daughter? d. daughter who is a carrier? Dihybrid Cross (Mendel’s Rules) • Looking at 2 traits (ex: color and size) so 2 different letters—each with a dominant and recessive allele • Still follows Mendel’s “LAW OF DOMINANCE” Steps to solve a punnett square dihybrid cross 1. Write down the parents genotype (TtHh) (TTHh) 2. Formula : 2n (n = # of heterozygous traits) for each parent gametes 3. to figure out the possible gamete separation, DANCE method 4. Draw a punnett square with correct number of boxes 5. Down and over keeping letters together in box (4 letters per box….2 for each trait) 6. total up phenotypes 25 Question: How many gametes will be produced for the following allele arrangements and what are they? If round is dominant to smooth and Yellow is dominant to blue • Remember: 2n (n = # of heterozygotes) then DANCE • 1. Both parents are heterozygous for each trait RrYy 2n = 22 = 4 gametes • RY 2. • 3. Ry rY ry Homozygous round and heterozygous yellow RRYy Shows both recessive traits rryy 26 If round is dominant to smooth and Yellow is dominant to blue DO STEPS 1-4.....do not complete square, but set it up!!! 1) Parent 1: Homozygous round and blue Parent 2: Heterozygous for both traits 2) Parent1: Shows both recessive traits Parent 2: Smooth and heterozygous for color What r the possible offspring for two parents one of which is heterozygous for height and color hair, and the other shows the recessive trait for height but is heterozygous for color. Tall is dominant to short, and brown in dominant to yellow. • TtBb ttBb TB Tb tB tb tB tb Now put into the Punnett Square How many boxes will we have??? 4 across and 2 down= 8 In trollville, having pink hair for trolls is dominant over yellow hair. Having a green belly ring is dominant over a blue belly ring. If a troll that is pure for pink hair and heterozygous for ring color marries a heterozygous troll for both traits, what possible phenotypes can their children be? Being Blue is a dominant trait to yellow. Being wrinkled is dominant to being smooth. One parent is pure blue and heterozygous for wrinkled. The other parent is yellow and heterozygous for being wrinkled as well. Show the possible offspring and analyze the phenotype ratios. Purple is dominant to yellow in plant color. Starchy plants are dominant to sweet in taste. Cross a heterozygous purple, sweet plant with a yellow, pure starchy plant. White wolves are dominant to black wolves. Brown eyes are dominant to green eyes. Cross a black coated, pure brown eyed wolf with a Heterozygous wolf for both traits 3 Dominance Types • Complete dominance – Only 1 phenotype is shown – Only one letter, dominant and recessive – Ex. – Tall (T) short (t) • Incomplete dominance – – – – Phenotype is blended in Always using dominant allels No recessive Ex. - white flowers mate with red flowers pink flowers • Codominance – – – – – 2 or more phenotypes are shown together Both equally dominant No recessive Ex. – Roan Horse (has patches), calico cats EX- White flower mate with red flower white/red flower Trix to figuring out if an Incomplete or Co-dominant cross 1) 2) 3) 4) Read the question Punnett squares will look the same Look at the possible phenotypes given 2 dominant alleles of different letters: 1 for each trait. 5) Genotype will be homozygous dominant ALWAYS!!!!!!!!! Practice Co-dom or Incomplete Write genotypes • Red flower + white flower= Pink flower – RR + WW= RW • Striped + Spotted = Striped/spotted – SS + TT = ST • Square + round= Oval – SS + RR = SR • Stared eyes + Circle eyes= Star/circled eyes – SS + CC = SC Practice Incomplete dom. • In Oompa loompa’s, hair color is incomplete dominance. Blue-haired oompa crossed with a red-haired oompa. What would the phenotypes be, show your cross. B R B (BR) (BR) (BR) (BR) R So, what would the offspring look like if I crossed 2 purple haired oompas? • A bug that has stripes is mated with a bug that has spots. Stripes and spots are codominant. What would the offspring look like? • A Stripe/spotted bug mates with a striped bug. What would the offspring look like? IB i -type AO,and universal 2 Dominant: B and donor -type: O AB, universal receiver 1 Recessive Blood types: mix on Mendel and Co-dominance BCT Practice 1) Which organisms are chiefly responsible for the recycling of dead matter? a. parasites b. viruses c. decomposers d. producers 2) A characteristic shared by both predators and parasites is that they a. feed on decomposing plant material b. capture and kill animals for food c. live inside their host d. attack a living food source 3) In guinea pigs, rough hair is dominant over straight hair. If two heterozygous pigs are crossed, the largest number of any one genotype of offspring would probably be a. Homozygous straight hair c. Heterozygous straight hair b. Homozygous rough hair d. Heterozygous rough hair 1) In squirrels, the gene for gray fur (G) is dominant over the gene for black fur (g). Fifty % of a large litter of squirrels is gray. Which parental cross most likely produced this litter? a. GG x gg b. GG X GG c. Gg x gg d. gg x gg 2) Compared to that of a body cell, a sperm cell has this many chromosomes? a. The same b. twice c. half d. four times 3) An exact duplication of chromosomes, followed by the separation of these sets into 2 cells is known as a. Meiosis b. mitosis c. fertilization d. differentiation 4) One characteristic of all living organisms is that they a. make food b. live on land c. maintain homeostasis d. move from place to place 5) The basic raw materials of photosynthesis are a. Glucose and CO2 b. Oxygen and water c. Water and CO2 d. oxygen and sugar Practice • A heterozygous parent for blue eyes and brown hair marries a homozygous recessive parent with green eyes and blond hair. What are the possible phenotypes of their children? QUESTION: Pretend that Brad Pitt is homozygous for the type B allele, and Angelina Jolie is heterozygous for type “A.” What are all the possible blood types of their baby? IB IB IA IAIB I AI B i IB i IB i Based on the information in this table, which men can not be the father of the baby? The mother is heterozygous for type A. Justify your answer with Punnett squares showing all possibilities. Het Homo GEORGE Cable Guy I (B) Sammy the Player can not be the babies father. He has blood type O so if he mated with this mother, than all children would have type A. The waiter can also not be the father. The children would either have type A or O. HINT: MAKE a cross between mother and each possible fathers!!!!! "Could a man with type B blood and a woman with type AB produce a child with type O blood?" Practice: • Stewie and his family all have purebreed oval heads which is the dominant trait in Family Guy world. He recently married Ellie, also from Family Guy world, but she has a square head. What are the genotype and phenotype ratios of their possible children for head shape. • A genetic disorder is sex linked and is caused by a recessive allele (e). The allele for the unaffected condition (E) is dominant. A woman who is a carrier of this disorder married an unaffected man. The couple would like to have a child but they are concerned that their child will inherit the disorder. X E X E E XX X E e E XX e Female unaffected Female Carrier Male Unaffected Male affected E Y XY e XY 1) Enzyme molecules are synthesized primarily from a. monosaccharides b. amino acids c. fatty acids d. phopholipids 2) The science of naming and classifying organisms is called a. Ecology b. taxonomy c. synthesis d. homeostasis 3) Cells are to tissues as organs are to a. cells b. genes c. organ system d. organelles 4) The top of a food chain is usually a a. Autotroph b. plant c. herbivore d. carnivore PedigreeA family history of a trait male female married offspring in order of birth, from left to right Individual showing trait being studied Carrier for trait, but does not show it (heterozygous) I, II, III, IV... generation How many women? Diseased women? How many men? Diseased men? How many children did couple 1&2 of generation 2 have? How many children did couple 7&8 of generation 2 have? How many marriages are there? = Huntington’s Disease 1. Which members of the family above are afflicted with Huntington’s Disease? _________________________________ 2. There are no carriers for Huntington’s Disease- you either have it or you don’t. With this in mind, is Huntington’s disease caused by a dominant or recessive trait? ____________________________ 3. How many children did individuals I-1 and I-2 have? _______________________________________________ 4. How many girls did II-1 and II-2 have? ______________ How many have Huntington’s Disease? ________________ 5. How are individuals III-2 and II-4 related? ________________________ I-2 and III-5? _________________________ 12. The pedigree to the right shows a family’s pedigree for colorblindness. Which sex can be carriers of colorblindness and not have it? ______________________ 13. With this in mind, what kind of trait is colorblindness? ______________________ 14. Why does individual IV-7 have colorblindness, show the punnett square? _________________________________________________ 15. Why do all the daughters in generation II carry the colorblind gene? ____________________________________ 16. Name 2 IV generation colorblind males. _________ • Mutations can involve an entire chromosome or a single section of a DNA molecule • Mutations can have a positive effect, a negative effect, or a neutral (no) effect on the organism • MUTATIONS CAUSE EVOLUTION!!!!!!! CHROMOSOME MUTATIONS • Change in structure of chromosome or the loss of entire chromosome – DELETION • Loss of a piece of a chromosome due to breakage…all info carried by missing piece may be lost – INVERSION • Segment breaks off and then reattaches in reverse order to that same chromosome – TRANSLOCATION • A segment breaks off and then reattaches to a different chromosome – NONDISJUNCTION • Alter the # of chromosomes found in the cell • Failure to separate during meiosis • A zygote with 45 Chromosomes …one copy of a particular chromosome= monosomy • three chromosomes on a spot in a karyotype= trisomy…a zygote with 47 chromosomes – Ex: Down Syndrome (trisomy-21)….on chromosome 21 GENE MUTATIONS • May involve large segments of DNA or a single nucleotide within a codon – POINT MUTATIONS • Substitution, addition, or removal of a single nucleotide – SUBSTITUTIONS • One nucleotide is replaced with a different one…can cause problems or may not…What if sub is for a STOP codon….YIKES!!!! – Ex: Sickle Cell Anemia….substi A (adenine) for T (Thymine) – FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS • Since codons are read in threes…..if an addition or deletion occurs….the FRAME OF 3 gets err…..SHIFTED ACGTTA ACTTA ACGTTA ACCTTA DNA Technology Rosalind Franklin • 1950's. • Took X-ray picture of DNA Watson and Crick • Watson and Crick made a model of the DNA molecule and proved that genes determine heredity Genetic code • 1966 • The Genetic code was discovered; scientists are now able to predict characteristics by studying DNA. This leads to genetic engineering, genetic counseling. DNA Fingerprinting • The late 1980's. • An international team of scientists began the project to map the human genome. • The first crime conviction based on DNA fingerprinting, in Portland Oregon. Barbara McClintock • 1983 • Barbara McClintock (1902-1992) of the U.S. was awarded the Nobel Prize for her discovery that genes are able to change position on chromosomes. “crossing-over” Dr. Kary Mullis • 1993 • Dr. Kary Mullis discovered the PCR procedure, for which he was awarded the Nobel prize. Copying DNA • Polymerase Chain Reaction • Also called PCR • A method of making many copies of a piece of DNA Gel Electrophoresis The fragments of DNA cut by restriction enzymes are separated by gel electrophoresis STEPS: a. DNA fragments are loaded at one end of a gel tray b. A current is applied to the gel c. DNA molecules are negatively charged and move toward positive end of gel d. The fragments separate because smaller molecules move faster than larger ones. This results in a pattern of bands e. Photographic film is used to visualize the DNA fragments. This pattern can serve as a person’s DNA fingerprint Cloning Begins • 1997. • Dolly the sheep - the first adult animal clone. Biotechnology Breakthroughs • Potatoes with higher solid content • Garlic that lowers cholesterol • Fruits and vegetables that reduce risks of cancer and heart disease Human Genome Project • Started in 1990 • Research effort to sequence all of our DNA (46 chromosomes) • Over 3.3 billion nucleotides • Mapping every gene location (loci) • Conducted by scientists around the world