* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Muscle and Nervous Tissue ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
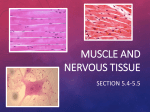
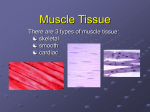
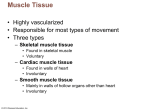
Muscle and Nervous Tissue Muscle Tissue • Muscle Tissue: – Associated with the bones of the skeleton, the heart and in the walls of the hollow organs of the body. • Muscle Tissue Functions: – – – – – Movement Maintains posture Produces heat Pumps blood Peristalsis 3 major types • Skeletal • Smooth • Cardiac Skeletal Muscle Tissue 1. Skeletal muscle is attached to bone and can be controlled by conscious effort (voluntary). 2. The cells (muscle fibers) are long and cylindrical, striated, have many nuclei and contract from nervous impulse. Smooth Muscle Tissue 1. Lacks striations, is uninucleate, and consists of spindle-shaped cells. 2. Involuntary muscle 3. found in the walls of internal organs, and in the digestive tract, blood vessels, and urinary bladder. Cardiac Muscle Tissue 1. Found only in the heart and consists of branching fibers that are connected to each other with intercalated disks. 2. This involuntary muscle has a single nucleus in each cell but appears striated. Muscle Tissue Types Muscle Tissue Types Nervous Tissue • Nervous Tissue: – Main component of the nervous system, ie., brain, spinal cord & nerves. • Nervous Tissue Functions: – Regulates & controls body functions – Generates & transmits nerve impulses – Supports, insulates and protects impulse generating neurons. Nervous Tissue Types of Nervous tissue cells: • Neurons- largest cells, transmit impulses • Neuroglial cells- smaller, more abundant and act as support for neurons