* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Renaissance and Reformation
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
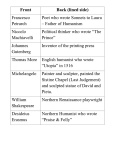
The Middle Ages, Crusades and Renaissance A dangerous time in Europe ► The strong empires of Rome and Greece that protected trade routes and encouraged science and freedom were gone. ► Education died out ► Only the Christian Church kept education alive in monasteries Hand copied books Invaders and Raiders ► Genghis Kahn was the leader of the Mongols Mongols conquered Russia and ruled it for 400 years Russia has been behind the rest of Europe ever since The Vikings ► The Vikings Invaded Europe from 793-1000 ► Came from Scandinavia— modern day Denmark, Sweden, and Norway. ► Raided all across Europe and the Mediterranean ► Great sea farers—traveled to Newfoundland in Canada Feudalism ► Lack of central government for protection leads to rise of Feudalism ► Feudalism: “loosely organized system of government in which local lords governed their own lands but owed military service and other support to a greater lord.” So who is in charge? ► The kings had plenty of land; but he could not control it all ► Lords then gave their land to knights in exchange for protection, loyalty and $. ► Knights let serfs (peasants) work the land and he would protect them. ► Serfs got food and shelter. Problems with Feudalism ► Possible to have allegiances to more than one person ► No strong central government King must ask his lords for knights in time of war King must ask his lords for money to pay for things Lords hold most of the power Lords constantly fighting among themselves. How to keep power ► Goal was to own the most land because More Land = More Crops = More $$$ ► How do you get more land? Conquer it (there was fighting all the time) Marry into it – marry off your daughters for money Make Alliances Empires of the Middle Ages ► Charles the Great – Charlemagne Leader of the Kingdom of Franks ► Pope crowned him emperor of the “Holy Roman Empire” after he chased the barbarians out of Rome ► Revived ► Empire literacy and education declined after he died The Norman Conquest ► In 1066, England was invaded by Normans (Vikings from modern-day France) ► The Battle of Hastings Harold, King of England killed William of Normandy (William the Conqueror) takes over. ► William of Normandy helped make England what it is today and codified feudalism (gave it the force of law). ► 1066 - William I creates Domesday Book for purposes of fair tax collection. The Magna Carta ► English King John was a bad king so his nobles forced him to sign the Magna Carta ► It limited powers of king. ► Signed in 1215 ► Example of Rule of Law The Crusades ► Three major religious groups all claimed Jerusalem in the land of Palestine as their holy land, Christians, Muslims and Jews How the Crusades Started ► The Byzantine Emperor Alexius I asked for help to defeat the Seljuk Turks, who were Muslims. ► Pope Urban II responded to the request by rallying warriors of Europe to liberate Jerusalem and the Holy Land (Palestine) from the Muslims. Turkish Territory Who fought? ► Nobles hoped to add to their personal fortunes and strengthen the power of monarchs. ► For knights, this was a chance to use their fighting skills. They also wanted to defend Jerusalem, the “fief of God”. ► For peasants, this was a chance to escape from their dreary life in the feudal system. ► The pope promised that if they died while fighting a holy crusade, they would automatically be welcomed into heaven. How many crusades were there? ► There were 9+ crusades that are fought over a period of about 200 years (1095-1291 AD). The First Crusade ► 30,000 Europeans left to fight for the holy land ► It took them 2 years to make the trip. ► Eventually they captured Jerusalem ► The Europeans then created 4 feudal “Crusader States” in the Holy Land, each ruled by a European noble. The Second Crusade ► The Crusader States lasted roughly 50 years before falling to the Turks ► The Pope called a 2nd crusade to retake the holy land. ► It was a complete failure. The Third Crusade ► Possibly the most important Crusade of all. ► Led by King Richard (the Lionhearted) of England. ► The Crusaders were defeated by Saladin. ► Despite the defeat, King Richard the Lionhearted negotiated with Saladin to allow Christian pilgrims free access to Jerusalem. More Crusades ► The Fourth Crusade sent Knights back to the Holy Land, however they never made it to Jerusalem. ► Instead attacked the city of Constantinople because they were in desperate need of supplies and funds. More Crusades ► The Children's Crusade in 1212 ► They believed God would protect them because they were children. ► When the ships landed in North Africa, some children were slaughtered and others were sold in to slavery. The Reconquista ► After the Crusades failed European Christians decided to retake Spain from a group of Muslims known as the Moors ► After reconquering Spain the Spanish Inquisition was launched to root out heretics ► Christians in Europe started to persecute the Jews. ► People turned against Jewish populations, the new enemy and the “murderers of Christ”. ► Many Jews were expelled from Europe or just killed altogether. As part of the Inquisition The Effects of the Crusades ► ► The Crusades exposed Europeans to new cultures After the Crusades, there was an increased interest in acquiring new goods from Asia, Africa and the Middle East. ► There was a new European demand for things such as silks, spices, ivory and pearls. This created a demand for trade with the Middle East. ► Increased trade = Increased income for Italian merchants ► Sophisticated Muslim culture, arts and philosophy were introduced to the Europeans – to the Muslims, the Europeans were the Barbarians The Black Death ► 1000-1300 Trade improved and towns grew…until the Black Death hits. ► Spread along trade routes by fleas that lived on rats ► Killed 1/3 of Population in Europe The Renaissance ► Renaissance rebirth ► Trade means cities in Italy grew wealthy due to trade with the Middle East Florence ► Center of art, literature, and culture. ► Florence became wealthy from the manufacturing of wool. ► Later Florence became the banking center of Italy. ► The Medici family were the greatest bankers in Florence. Florence ► The Renaissance started in Florence and spread throughout Europe. ► Competition between the Italian city-states led to advances in literature, architecture, art, music, science, and education. Rome ► Home of the Catholic Church ► Popes commissioned famous artists and architects to beautify Rome. Michelangelo, Raphael, and Botticelli all produced major works in Rome. Venice ► Venice was the wealthiest citystate of the Renaissance. ► It was a port city on the Mediterranean. ► Venice maintained hundreds of merchant ships and warships, and thousands of sailors. Genoa ► Genoa is located on the Mediterranean. ► Genoa was the other major port city in Italy during the Renaissance. ► Dominated trade in the Mediterranean Genoa Harbor ► Milan dominated the inland trade routes because it was the gateway to Italy from the north. ► Milan is the site of Santa Maria delle Grazie, the cathedral where Leonardo da Vinci painted The Last Supper. Milan The Intellectual and Artistic Renaissance Niccolo Machiavelli ► Philosopher, diplomat, poet, musician, playwright. ► Best known for The Prince – realist politics Rulers should behave like a lion (aggressive and powerful) and at other times like a fox (cunning and practical) “The Ends Justify the Means” “It was better to be feared than to be loved” All this done to keep peace and stabilize power Italian Renaissance & Humanism ► Stressed that man was the center of the universe and had dignity and value ► Humanism – intellectual movement based on the ► Vernacular Literature – written in common classics Study – grammar, rhetoric (debate), poetry, philosophy & history (the Humanities) language Petrarch: “Father of Humanism” ► Petrarch was a scholar and poet who was responsible for the recovery of manuscripts and works of Greek and Roman writers that had been lost in monastery libraries. ► Petrarch, like other writers of the time, wrote in Latin. Francesco Petrarch Dante Alighieri ► “Father of the Italian Language” ► Wrote The Divine Comedy. ► Dante was first to write in the vernacular. Until his time, all European literature was written in Latin. Dante Alighieri New Artistic Techniques ► Fresco – watercolor on fresh plaster ► Law of Perspective ► Study of human anatomy ► GOAL – imitate nature From Michelangelo’s Sketch Book Leonardo da Vinci ► Master of realism & perspective ► Studied human anatomy (cadavers) to be as accurate as possible ► Sculptor, painter, astronomer, inventor – a true “Renaissance Man” Leonardo da Vinci The Last Supper A page from one of da Vinci’s notebooks, he “coded” his work by writing backwards. He could read it, but most other people would need a mirror to read it. Raphael Santi ►1 of the top Renaissance painters ► Especially known for his “Madonna's” – paintings of Mary the mother of Jesus ► A major artist in the Vatican Madonna of the Meadows Madonna del Granduca Raphael Santi School of Athens fresco in the Apostolic Palace in the Vatican. Thought to be Raphael’s masterpiece . Michelangelo Buonarroti ► Painter, sculptor and architect ► Most famous for work in Vatican City Vatican City St. Peter’s Bascillica (large domed building) – designed by Michelangelo (St. Peter’s Square – designed by Bernini) Michelangelo Well known for his frescoes in the Sistine Chapel. The ceiling illustrates the stories of the Book of Genesis The Creation of Adam The Last Judgement On the Alter Wall of the Sistine Chapel. Michelangelo, the sculptor The Pieta – marble statue of a crucified Jesus being held by his mother Mary. In St. Peter’s Basilica. David – carved from one piece of marble from 1501 to 1504. Said to be proportionally perfect, though David is 17 feet tall Northern Renaissance ► Centered in Low Countries – Belgium and the Netherlands ► Due to weather- few frescoes Stained glass, wooden panels, canvas ► Jan van Eyck – Flemish, perfected use of oil paints Oils allow greater variety of color & detail Portrait of a Man in a Turban , probably a self-portrait, painted 1433 Albrecht Durer ► German ►1 of greatest Northern Renaissance artists ► Revolutionized ► Studied woodcuts in Italy on several different occasions Architecture ► Architectural design returns to the classical styles of Rome and Greece. ► Public buildings, homes and villas are designed using Greek and Roman architectural styles. ► Renaissance buildings feature columns, domes, and vaulted ceilings. The Printing Press ► Johannes Gutenberg was a German goldsmith and printer. ► Gutenberg was the first to develop movable type. This allowed for mass production of books. ► Gutenberg was the key figure in spreading the Renaissance. ► His invention of movable type is still considered the most important invention in history. IMPACT ► Much easier to publish books ► Increased literacy ► 1450-1500, 20 million books printed covering 35,000 topics Miguel de Cervantes ► Cervantes was a Spanish novelist, poet, painter, and playwright. wrote the novel Don Quixote, the most influential work of literature to come out of the Spanish Golden Age. ► Cervantes got the idea for Don Quixote while serving one of two prison terms for irregularities in his bookkeeping as a tax collector and purchasing agent. ► Cervantes William Shakespeare ► Shakespeare is considered the greatest writer and dramatist of all time. ► Shakespeare wrote Romeo and Juliet, Julius Caesar, A Midsummer’s Night Dream, Hamlet and more. “All the world’s a stage, and all the men and women merely players there, they have their exits and their entrances, and one man in his time plays many parts….” William Shakespeare ► Shakespeare wrote 38 plays, 154 sonnets, two narrative poems, and other poems.