* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lec 12: Fatty acid biosynthesis
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis of doxorubicin wikipedia , lookup
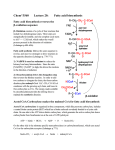
Lec 12: Fatty acid biosynthesis Reference material Biochemistry 4th edition, Mathews, Van Holde, Appling, Anthony‐Cahill. Pearson ISBN:978‐0‐13‐800464‐4 Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 4th edition, David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox. W. H. Freeman ISBN:978‐0716743392 Sugars FATS TAG storage 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 Breakdown to acetyl‐CoA 1 Coordinated regulation of Fatty acid metabolism Malonyl‐CoA (the activated form of acetyl‐CoA) is a key repressor for fatty acid degradation (because it inhibits fatty acid transport to mitochondria for degradation). Malonyl‐CoA is also the building block intermediate for fatty acid biosynthesis.. So think about the relationship between carbohydrates and fats… Overview of Fatty acid biosynthesis • Animals readily convert carbohydrate to fat, but cannot carry out net conversion of fat to carbohydrate. • Fatty acid synthesis occurs through intermediates similar to those of fatty acid oxidation, but with differences in electron carriers, carboxyl group activation, stereochemistry, acyl‐carrier, and cellular location. • Electron carrier: NADPH instead of NADH and FADH2 • Carboxyl group activation: malonyl‐CoA (carboxylated form of acetyl‐CoA) is used as carbon addition unit instead of acetyl‐CoA. • Acyl‐carrier: Acyl‐carrier protein (ACP) is used instead of coenzyme A • Stereochemistry: R‐3‐hydroxyl‐acyl‐ACP instead of S‐3‐hydroxyl‐acyl‐CoA • Cellular location: Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in cytosol instead of mitochondria 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 2 Cellular localization of lipid metabolism Bacterial cells have no localization since they don’t have organelles Acetyl‐CoA is transported out of mitochondria via citrate shuttle • For most nonphotosynthetic eukaryotes, nearly all acetyl‐CoA is generated in the mitochondria. • However, acetyl‐CoA cannot come out of mitochondria directly… therefore a indirect method of transport is used. This is the citrate shuttle. 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 3 Chemical reactions related to citrate shuttle 1. Acetyl‐CoA react with OAA to form citrate 2. Citrate can leave mitochondria because it has a transporter 3. Once in cytosol, enzyme Citrate lyase utilizes ATP to split citrate into Acetyl‐CoA & OAA. 4. OAA cannot directly return to mitochondria because of no transporter. OAA is transformed into either Pyruvate or malate, which can be transported into mitochondria Acetyl‐CoA activation into malonyl‐CoA As previously mentioned, 3‐ketoacyl‐CoA thiolase reaction is very thermodynamically favorable, therefore, its direct reversal would be very thermodynamically unfavorable! Keq ≈ 105 The reversal…. Keq ≈ 10‐5 Evolution made it such that this reaction can become much more favorable: o + CO2 ‐o Keq ≈ 0.25 Malonyl‐CoA Where do you get this malonyl‐CoA? ADP + Pi + HCO3‐ Keq ≈ 5 ATP 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 4 Acetyl‐CoA carboxylase Carboxylation of acetyl‐CoA by Acetyl‐CoA carboxylase (ACCase) is the committed step for fatty acid biosynthesis. This is often believed to be the limiting step of fatty acid biosynthesis ACCase is a multifunctional enzyme with 3 enzymatic activities: • Bacterial ACCase is complex of 3 proteins (one of them is complex of 2 polypeptides). For example: E. coli ACCase is coded by genes accABCD • Higher organisms such as animal cell ACCase is a large single multifunctional polypeptide. • The 3 proteins are: • Biotin carrier protein • Biotin carboxylase • Transcarboxylase Biotin is a cofactor for ACCase Biotin (Vitamin B7) 3 proteins/domains of ACCase #2 #3 #1 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 5 Electron moving mechanism of ACCase Fatty acid biosynthesis enzymes are different between bacteria and eukaryotes • In bacteria, each enzyme of the fatty acid biosynthesis pathway is its own individual enzyme • However, in eukaryotes, these enzymes are merged into a single MEGA enzyme complex called fatty acid synthase 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 6 Fatty acid biosynthesis: Loading • Malonyl/acetyl‐CoA‐ACP transacylase (AT) loads malonyl‐ or acetyl‐ to the ACP. • The acetyl‐ACP “primer” is then loaded to KS (3‐Keto‐ACP synthase) Acyl‐carrier for fatty acid biosynthesis is ACP (Acyl‐carrier protein) ACP and Coenzyme A, both contain phosphopantetheine moiety (which has –SH group). The difference is that ACP is a small protein (77 residues in E. coli) or a small domain in fatty acid synthase of eurkaryotes. HS‐ is the important part here Recall that phosphopantetheine is derived from Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 7 Fatty acid biosynthesis overview Malonyl‐ACP condenses with the acetyl‐ primer on KS. Result is that acetyl‐ primer is elongated to 4 carbon (3‐keto acyl‐ ACP) and liberated from KS. 3‐Keto acyl‐ACP is reduced using NADPH by KR (3‐ketoacyl‐ACP reductase) 3‐hydroxy acyl‐ACP is dehydrated by DH (3‐hydroxyacyl‐ACP dehydratase) Fatty acid biosynthesis overview Enoyl‐ACP is reduced with NADPH by ER (enoyl‐ACP reductase). The result is now saturated acyl‐ACP, which can be loaded into KS again This process continues until chain length reaches around 16 carbons, which a thioesterase will hydrolyze the thioester bond between the acyl‐ group and ACP 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 8 Comparing Fatty acid degradation vs. synthesis +ATP Fatty acid synthase 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 9 Fatty acid synthase NADPH + H+ NADP+ NADP+ NADPH H2O Unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis Unsaturated lipids are important for various cellular functions. In particular, they increase the fluidity of cellular membrane. How are these unsaturation (alkene units) made? Oleic acid (18:1cΔ9): formed from stearoyl‐CoA 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 Palmitoleic acid (16:1cΔ9): formed from palmitoyl‐CoA 10 Pathway for synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in plants and animals: Mammalian endoplasmic reticulum contains Δ5 and Δ6 desaturase, which uses the same mechanism as the Δ9 desaturase we saw. Animals CANNOT introduce C=C double bond beyond Δ9, whereas plants CAN. Plants can do Δ12 and Δ15 desaturation, forming the omega‐6 and omega‐3 fatty acids which are essential fatty acids for animals. Observation showed that increasing consumption of omega‐3 fatty acids depresses levels of serum cholesterol. Fish is an excellent source of omega‐3. Linoleic acids are used to make arachidonate, which is used for making eicosanoids Eicosanoids Eicosanoids (C20) include diverse compounds of prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes Participates in various complex physiological responses such as immflamation/immunity 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 11 Some metabolic functions of eicosanoids http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eicosanoid COX1 and COX2 and inflammation • COX‐1 is constitutively expressed in most tissues, and is responsible for the physiological production of prostaglandins. • COX‐2 is induced by cytokines, mitogens, and endotoxins in inflammatory cells and is responsible for the elevated production of prostaglandins during inflammation. • Both isoforms are covalently modified, and hence inactivated, by reaction with aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). • As shown, aspirin acetylates a specific serine residue, which in turn blocks access of the fatty acid substrate to the cyclooxygenase active site. 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 12 Regulation of fatty acid synthesis in animal cells: • The rate‐limiting enzyme, acetyl‐CoA carboxylase (ACC), is controlled by both allosteric (citrate↑and long‐chain fa y acids↓) and covalent modification mechanisms. • Phosphorylation by AMP‐activated protein kinase (AMPK) or cyclic AMP–dependent protein kinase (PKA) inactivates ACC. • Insulin stimulates fatty acid synthesis by increasing glucose uptake and increasing flux through pyruvate dehydrogenase to produce acetyl‐CoA. Formation of triacylglycerol (TAG) Recall that the “glycerol” part of TAG is made from DHAP or from glycerol. Subsequently, each acyl‐ group (in the form of acyl‐CoA) is added onto the “glycerol”. branching point for production of TAG or membrane lipid To make membrane lipids, a polar head group is attached to the phosphate of phosphatidic acid. 國立交通大學生物科技學系 蘭宜錚老師 13