* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download digestive,excretory systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
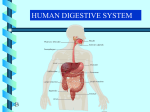
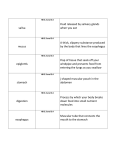
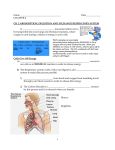
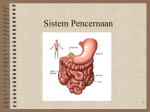
The Digestive System 35.1 Notes Pg. 124 E.Q. – How does absorption happen in the small intestine? What are the structures and functions of the digestive system? structures of the digestive system • Structures: – – – – – – – Mouth Esophagus Stomach Pancreas Liver (Gallbladder) Small Intestine Large Intestine • (colon) functions of the digestive system • Functions: – Ingestion – taking food in – Digestion – breaking food down – Absorption – taking nutrients in to the circulatory system – Elimination – getting rid of waste Lets start in the Esophagus & intestines • Ingestion and the beginning of Digestion. • #1 -Digestion begins in the mouth. The food is ground up and moistened (mechanical digestion) • #2 -Saliva contains enzymes (salivary amylase), which start breaking down carbohydrates into sugars. (chemical digestion) • #3 -Once swallowed, muscular contractions of the esophagus (peristalsis) massage the ball of food (bolus) down into the stomach. What happens in the Stomach? • 3 mechanical tasks • 2 chemical tasks What happens in the Stomach? • MECHANICAL TASKS – Stores the swallowed food and liquid. – Grinds up the food, liquid, and digestive juice produced by the stomach. (chyme) – Empties its contents slowly into the small intestine. • CHEMICAL TASKS – HCl – digests everything – Pepsin – digests proteins #1 #2 #3 We’re in the small intestine! • Absorption!! – The food is mixed with more digestive enzymes (chemical) and it moves into the lower parts of the small intestine: the jejunum and the ileum. – Nutrients are absorbed (mechanical) from the ileum, by projections called villi. – Each villus is connected to a mesh of capillaries. This is how nutrients pass into the bloodstream. On to the large intestine! We’re in the large intestine! • Absorption and Elimination – Minerals and vitamins and water are absorbed. – Waste can then be eliminated from the body through the anus. – This waste is called feces. What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? • Protease – Breaks down proteins into amino acids – Secreted from the stomach and pancreas What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? • Amylase – Breaks down carbohydrates (starches) into glucose – Secreted from: the mouth (in saliva), pancreas, and small intestine What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? • Lipases: – Breaks down lipids into mono, di and triglycerides – Secreted from the pancreas and small intestine What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? What is the name, function and place of secretion of this enzyme? • Nuclease: – Breaks down nucleic acids (DNA) into nucleotides – Secreted from the small intestine and pancreas This is not an enzyme – What is its name, function and place of secretion? This is not an enzyme – What is its name, function and place of secretion? • Bile – Breaks down fat globules into small droplets – Secreted from the liver and stored in the gallbladder Digestive REView pg. 123 complete sentence explained answers!! 1. Identify/explain three functions of the digestive system. 2. Explain the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion.(give example of each) 3. What is peristalsis? Where does it happen? 4. Food is called ____ once it enter the stomach. 5. Write a 2-3 sentence explanation of what happens in the small intestine. (villi,capillary) 6. Explain the difference between the small / large intestines. The Excretory System 34.3 Notes (pg. 138) E.Q. – Identify/explain the three functions of the Excretory system. structures and functions of the Excretory System Structures and functions of the Excretory System • Structures: – Skin (sweat glands) – Kidneys (nephron) – Liver – Lungs – Urinary Bladder • Functions: – Get Rid of Wastes (other than digestive) – Keep the blood clean – Maintain Homeostasis (balance) Kidneys & homeostasis Kidneys and homeostasis Function: - Removes wastes from the blood. • Homeostasis: – maintaining water balance and pH – excreting urine – filtering wastecarrying blood. A closer look at Kidneys • NEPHRONS – – – – Filtration Re-absorption Secretion Formation of Urine Your kidneys in action! • 1 – Filtration – Urea (formed in the liver) is • • • filtered through the Bowman’s capsule of the nephron. 2 – Re-absorption – Water is re-absorbed from the filtrate back into the blood in the loop of Henle 3 – Secretion – In the distal convoluted tubule, toxins are secreted by the blood and absorbed into the filtrate. 4 – Formation of Urine – Once the filtrate enters the collecting duct it is called urine. The urine travels through the ureter to the urinary bladder where it is stored. How do the kidneys work? What is the function of the liver? How does the liver maintain homeostasis? The Liver and homeostasis • Function: – stores glycogen – breaks down toxic substances (alcohol) – secretes bile. – Filters blood to form urea. • Homeostasis: – glucose balance and blood detoxification Your skin and homeostasis • Function: – PROTECTION!!! • Homeostasis: – The skin excretes water and salt (sweat) from the body Your lungs and homeostasis • Function: – Intake Oxygen and expel Carbon Dioxide. • Homeostasis: – The lungs excrete carbon dioxide from the burning of glucose through respiration. The End Of notes Turn to pg. 137 for review questions. Excretory Review pg. 137 (copy/fill in # 1) 1. Kidneys and the Liver both filter your _______ 2. Arrange the following in correct order & explain each step Formation of Urine, Filtration, Secretion, Reabsorption. 3. Identify two structures of the Excretory system that are also parts of other systems & explain their function. 4. Explain how the Excretory system helps maintain homeostasis. (two examples) 5. Identify one kidney disorder, explain symptoms, causes, and treatments. (pg. 1008)