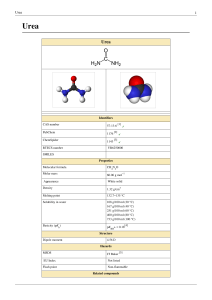
Urea - Rebound Health
... solutions (in combination with ammonium nitrate: UAN), e.g., in 'foliar feed' fertilizers. For fertilizer use, granules are preferred over prills because of their narrower particle size distribution which is an advantage for mechanical application. The most common impurity of synthetic urea is biure ...
... solutions (in combination with ammonium nitrate: UAN), e.g., in 'foliar feed' fertilizers. For fertilizer use, granules are preferred over prills because of their narrower particle size distribution which is an advantage for mechanical application. The most common impurity of synthetic urea is biure ...
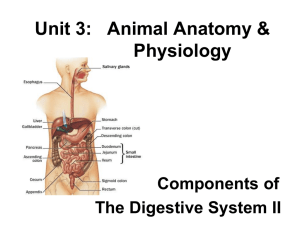
Digestive System_lecture III - Medical
... small intestine and lies between the duodenum and the ileum. In adult humans, it is usually between 2-8m (06' 07"-26' 03") long. The pH in the jejunum is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly alkaline). The jejunum and the ileum are suspended by mesentery which gives the bowel great mobility ...
... small intestine and lies between the duodenum and the ileum. In adult humans, it is usually between 2-8m (06' 07"-26' 03") long. The pH in the jejunum is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly alkaline). The jejunum and the ileum are suspended by mesentery which gives the bowel great mobility ...
Colonics Training Manual
... hydrotherapy is about promoting the wellbeing of clients, encouraging clients to improve their own lifestyle by more exercise; nutritional improvements; advice on supplements; other beneficial complementary treatments; plus emotional support. When the colon is out of balance it is necessary to clean ...
... hydrotherapy is about promoting the wellbeing of clients, encouraging clients to improve their own lifestyle by more exercise; nutritional improvements; advice on supplements; other beneficial complementary treatments; plus emotional support. When the colon is out of balance it is necessary to clean ...
Lecture 2
... eventual fate of ingested minerals. § Mineral availability in body depends on its chemical form. § Generally body does not absorb minerals very well (% ingested) § Heme Fe ~15%, non-heme Fe 2-10% § Ca2+ not often > 35% (males > females) § Mg 20-30% § Zn 14-40% § Chromium < 2% 6 Factors affect ...
... eventual fate of ingested minerals. § Mineral availability in body depends on its chemical form. § Generally body does not absorb minerals very well (% ingested) § Heme Fe ~15%, non-heme Fe 2-10% § Ca2+ not often > 35% (males > females) § Mg 20-30% § Zn 14-40% § Chromium < 2% 6 Factors affect ...
Nitrogen losses from the human small bowel
... g/day.7 It is assumed that this is a mixture of endogenous nitrogen and dietary residues. The relative contributions from the two sources, and the form in which they enter the large bowel are not known. There are also few data available on the influence of dietary factors on small bowel nitrogen los ...
... g/day.7 It is assumed that this is a mixture of endogenous nitrogen and dietary residues. The relative contributions from the two sources, and the form in which they enter the large bowel are not known. There are also few data available on the influence of dietary factors on small bowel nitrogen los ...
The physiology of colonic hydrotherapy - E
... lungs eliminate the carbon dioxide and help maintain acid–base balance. The liver and the reticulo-endothelial system neutralize circulating toxins from food and the body and unwanted matter in circulation and secrete them into the gastrointestinal tract or excrete them via the kidney. The kidney el ...
... lungs eliminate the carbon dioxide and help maintain acid–base balance. The liver and the reticulo-endothelial system neutralize circulating toxins from food and the body and unwanted matter in circulation and secrete them into the gastrointestinal tract or excrete them via the kidney. The kidney el ...
The Water-Soluble Vitamins
... • Grains are an important source of many Bvitamins. However, when grains are milled, the seeds are crushed and the germ, bran, and husk layers are removed. This refining process leaves just the starch-containing endosperm, which is the only portion of the grain used to make white flour, as well as m ...
... • Grains are an important source of many Bvitamins. However, when grains are milled, the seeds are crushed and the germ, bran, and husk layers are removed. This refining process leaves just the starch-containing endosperm, which is the only portion of the grain used to make white flour, as well as m ...
Exploring Digestive and Excretory Systems
... 63. This is an example of mechanical digestion and results in the physical breakdown of food. 64. Food is chemically digested in the stomach as well when it mixes with hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and mucus secreted by glands located in the walls of the stomach. 65. While liquids pass through the stom ...
... 63. This is an example of mechanical digestion and results in the physical breakdown of food. 64. Food is chemically digested in the stomach as well when it mixes with hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and mucus secreted by glands located in the walls of the stomach. 65. While liquids pass through the stom ...
Unit 1: Nutrients & Digestion
... protein, energy and other nutrients required for structural growth ...
... protein, energy and other nutrients required for structural growth ...
Assignment MSWord - Technical Learning College
... If you’ve paid on the Internet, please write your Customer#______________ Please invoice me, my PO#_________________________________________ Please pay with your credit card on our website under Bookstore or Buy Now. Or call us and provide your credit card information. We will stop mailing the certi ...
... If you’ve paid on the Internet, please write your Customer#______________ Please invoice me, my PO#_________________________________________ Please pay with your credit card on our website under Bookstore or Buy Now. Or call us and provide your credit card information. We will stop mailing the certi ...
The Digestive System
... Circular muscles push it back and forth while food stays in same place. Figure 10.16 ...
... Circular muscles push it back and forth while food stays in same place. Figure 10.16 ...
Full Text
... Chemical Characteristics of E. cottonii: The water content of E. cottonii was 16.3±12:23%. A high water content of the substrate enhances the growth of microorganisms under degradation [20]. The ash content was 14.39±0.035% (Table 1). According to Matanjun et al. [21] this species has a fairly high ...
... Chemical Characteristics of E. cottonii: The water content of E. cottonii was 16.3±12:23%. A high water content of the substrate enhances the growth of microorganisms under degradation [20]. The ash content was 14.39±0.035% (Table 1). According to Matanjun et al. [21] this species has a fairly high ...
What are Biosolids? What About Pathogens in Biosolids? What do
... fertilizer pellets. Class A biosolids products are sometimes ingredients in soil amendments, potting soils, and slow-release fertilizers. Class B: Class B biosolids undergo a "Process to Significantly Reduce Pathogens (PSRP)." This means that while pathogens are significantly reduced to levels which ...
... fertilizer pellets. Class A biosolids products are sometimes ingredients in soil amendments, potting soils, and slow-release fertilizers. Class B: Class B biosolids undergo a "Process to Significantly Reduce Pathogens (PSRP)." This means that while pathogens are significantly reduced to levels which ...
large intestine
... • It is derived from two sources 1. Swallowed air [up to 500ml of air may be swallowed during a meal]. 2. Gas produced by bacterial fermentation in the colon. Most gas in the colon is due to result of bacterial activity, but the quantity and the nature of gas produced depend on the type of food eate ...
... • It is derived from two sources 1. Swallowed air [up to 500ml of air may be swallowed during a meal]. 2. Gas produced by bacterial fermentation in the colon. Most gas in the colon is due to result of bacterial activity, but the quantity and the nature of gas produced depend on the type of food eate ...
Title: The Large Intestine
... the large intestine. These bacteria ferment any remaining CHO’s into carbon dioxide, hydrogen and methane gas. Thes contribute to flatus or gas in the colon. 2- Bilirubin is broken down into stercobilin 3- Vitamin K produced by the bacteria is absorbed into the blood. ...
... the large intestine. These bacteria ferment any remaining CHO’s into carbon dioxide, hydrogen and methane gas. Thes contribute to flatus or gas in the colon. 2- Bilirubin is broken down into stercobilin 3- Vitamin K produced by the bacteria is absorbed into the blood. ...
The Physiology of the Kidney and Body Fluids EDUCATIONAL
... (juxtaglomerular apparatus). When fluid delivery and NaCl transport at MD increase (as with increased GFR or decreased PT reabsorption), there are increases in cell Na and Ca and release of arachidonic acid metabolites and adenosine that act on vascular smooth muscle cells of the afferent arteriole, ...
... (juxtaglomerular apparatus). When fluid delivery and NaCl transport at MD increase (as with increased GFR or decreased PT reabsorption), there are increases in cell Na and Ca and release of arachidonic acid metabolites and adenosine that act on vascular smooth muscle cells of the afferent arteriole, ...
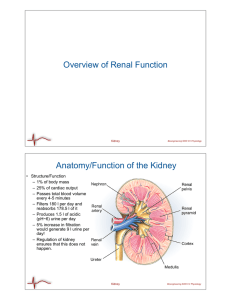
Overview of Renal Function Anatomy/Function of the Kidney
... 1) Active transport of salt • Increased osmolarity • Lower water permeability 2) Osmotic passive transport of water • Low NaCl, urea permeability 3) Passive diffusion of urea • Only place with high urea permeability 4) Osmotic diffusion of water • Produces high osmolarity filtrate and bottom of loop ...
... 1) Active transport of salt • Increased osmolarity • Lower water permeability 2) Osmotic passive transport of water • Low NaCl, urea permeability 3) Passive diffusion of urea • Only place with high urea permeability 4) Osmotic diffusion of water • Produces high osmolarity filtrate and bottom of loop ...
The Large Intestine - Avery County Schools
... inflamed. Then the feces are loose and watery because food residues have moved through the large intestine too quickly to absorb the excess water. The opposite condition, of course, is constipation. This happens when the food residues moved too slowly and too much water has been absorbed. The feces ...
... inflamed. Then the feces are loose and watery because food residues have moved through the large intestine too quickly to absorb the excess water. The opposite condition, of course, is constipation. This happens when the food residues moved too slowly and too much water has been absorbed. The feces ...
Disturbances in Bilirubin Metabolism
... the enzymes heme oxygenase and biliverdin reductase. In the liver, unconjugated bilirubin which is insoluble in water is conjugated with glucuronic acid by the enzyme UGT to form the soluble (conjugated) bilirubin. Bilirubin is converted to microbial enzymes into urobilinogen and oxidized to stercob ...
... the enzymes heme oxygenase and biliverdin reductase. In the liver, unconjugated bilirubin which is insoluble in water is conjugated with glucuronic acid by the enzyme UGT to form the soluble (conjugated) bilirubin. Bilirubin is converted to microbial enzymes into urobilinogen and oxidized to stercob ...
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION 1.1 Heavy metals pollution in
... can disturb natural processes on land and in the water. Heavy metals contain in the wastes from the illegal dumping activities can leach to the environment and not only pollute the environment but also can cause serious health hazards. Heavy metals tend to bioaccumulate in plants and animals, biocon ...
... can disturb natural processes on land and in the water. Heavy metals contain in the wastes from the illegal dumping activities can leach to the environment and not only pollute the environment but also can cause serious health hazards. Heavy metals tend to bioaccumulate in plants and animals, biocon ...
Digestive System CH 49 PPT
... • Lipids are nonpolar molecules that are insoluble in water and can be found in fats, oils, and waxes. • Lipids are used to make cell membranes and hormones and to store energy. • The most common fat is called a triglyceride. Triglycerides can be used for energy and to build membranes and other cell ...
... • Lipids are nonpolar molecules that are insoluble in water and can be found in fats, oils, and waxes. • Lipids are used to make cell membranes and hormones and to store energy. • The most common fat is called a triglyceride. Triglycerides can be used for energy and to build membranes and other cell ...
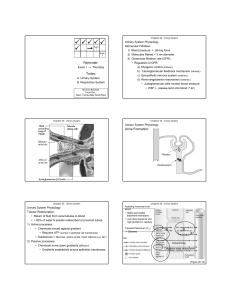
Page 1 Exam I Exam II Today: A. Urinary System B. Respiratory
... • Juxtaglomerular cells monitor blood pressure • If BP ↓, release renin into blood (↑ BP) ...
... • Juxtaglomerular cells monitor blood pressure • If BP ↓, release renin into blood (↑ BP) ...
Teacher`s Guide for “The Digestive Tract” CT State Standards
... pancreas, intestinal juice is released. At the same time, villi lining the small intestine absorb nutrients released form the food as digestion occurs. e. Large Intestine – Water is reabsorbed here and bacteria work on the remaining chyme turning it into the waste product feces which then passe ...
... pancreas, intestinal juice is released. At the same time, villi lining the small intestine absorb nutrients released form the food as digestion occurs. e. Large Intestine – Water is reabsorbed here and bacteria work on the remaining chyme turning it into the waste product feces which then passe ...
Biogas – Green Energy Process, Design, Energy
... At the end of the 1950s, development nearly stopped, however, due to the cheapness of the fossil fuels oil and gas. The interest in biogas was not reawakened until the mid 1970s following the oil crisis in 1973. The Danish state initiated a research and development programme with the aim of testin ...
... At the end of the 1950s, development nearly stopped, however, due to the cheapness of the fossil fuels oil and gas. The interest in biogas was not reawakened until the mid 1970s following the oil crisis in 1973. The Danish state initiated a research and development programme with the aim of testin ...
File
... major site of chemical digestion. Frogs swallow their meals whole. Follow the stomach to where it turns into the small intestine. The pyloric sphincter valve regulates the exit of digested food from the stomach to the small intestine. Small Intestine--Leading from the stomach. The first straight por ...
... major site of chemical digestion. Frogs swallow their meals whole. Follow the stomach to where it turns into the small intestine. The pyloric sphincter valve regulates the exit of digested food from the stomach to the small intestine. Small Intestine--Leading from the stomach. The first straight por ...
Reuse of excreta

Reuse of excreta (alternative spelling: re-use) refers to the safe, beneficial use of animal or human excreta, i.e. feces (or faeces in British English) and urine. Such beneficial use can be as a soil conditioner or fertilizer in agriculture, gardening, aquaculture or ornamental activities. Other possible uses include use as building material, fuel source or protein production. An alternative term is also ""use of excreta"" rather than ""reuse"" as strictly speaking it is the first use of excreta, not the second time that it is used.Reuse of excreta is one example of resource recovery of the resources contained in excreta, mainly the plant-available nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium as well as micronutrients such as sulphur and organic matter. These resources which are contained in wastewater, excreta and greywater have traditionally been reused in agriculture in many countries and are still being reused in agriculture to this day, but the practice is often carried out in an unregulated and unsafe manner for example in many developing countries (e.g. Mexico, India, Bangladesh, Ghana). The WHO Guidelines from 2006 have set up a framework how this reuse can be done safely by following a multiple barrier approach.Excreta-based fertilisers vary in their general properties and fertilising characteristics and include the following types: urine, dried feces, composted feces, faecal sludge (septage), municipal wastewater, sewage sludge and animal manure. Reuse of sanitised excreta in agriculture has also been called a ""closing the loop"" approach for sanitation and agriculture and is central to the ecological sanitation approach.Reuse of excreta is the final step of the sanitation chain which starts with collection of excreta (by use of toilets) and continues with transport and treatment (wastewater treatment is one example) all the way to either disposal or reuse.