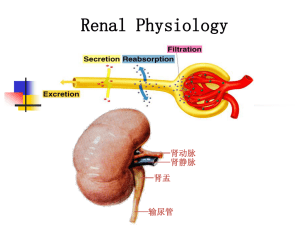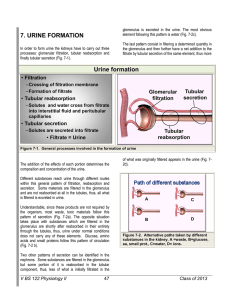
7. URINE FORMATION Urine formation
... multiplying by 1.44 (Number of minutes in one day/1000 mL) (Fig 7-16). Thus, this animal produces 1.04 mL/min X 1.44 = 1.4976 L/day ...
... multiplying by 1.44 (Number of minutes in one day/1000 mL) (Fig 7-16). Thus, this animal produces 1.04 mL/min X 1.44 = 1.4976 L/day ...
Disorders of the Kidneys, Bladder and Urinary Organs
... and the primary urine collected. A filter membrane that retains red and white blood cells, blood platelets, large molecules (e.g., proteins) in healthy humans is also found there.The highly concentrated secondary urine develops in the tubular apparatus through recovery of water.This is further enric ...
... and the primary urine collected. A filter membrane that retains red and white blood cells, blood platelets, large molecules (e.g., proteins) in healthy humans is also found there.The highly concentrated secondary urine develops in the tubular apparatus through recovery of water.This is further enric ...
8、kidney organ
... Overview of kidney function • Excretion - the body substances of metabolic end products and do not need to or surplus material excreted process • The kidneys process the plasma portion of blood by removing waste materials that are either ingested or produced by metabolism. • In so doing, they perf ...
... Overview of kidney function • Excretion - the body substances of metabolic end products and do not need to or surplus material excreted process • The kidneys process the plasma portion of blood by removing waste materials that are either ingested or produced by metabolism. • In so doing, they perf ...
lec#30 by salsabeel khreem
... , if these binding sites are completely saturated, we call this Tmax , transport maximum, or Vmax. We cannot exceed this. *Km is for affinity, Vmax or Tmax are for capacity. *If concentration of glucose in filtrate < Vmax, then all glucose is reabsorbed. If concentration of glucose in filtrate > Vma ...
... , if these binding sites are completely saturated, we call this Tmax , transport maximum, or Vmax. We cannot exceed this. *Km is for affinity, Vmax or Tmax are for capacity. *If concentration of glucose in filtrate < Vmax, then all glucose is reabsorbed. If concentration of glucose in filtrate > Vma ...
30.3 The Digestive System
... Lesson 30.3 • Workbook A • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Lesson 30.3 • Workbook A • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
digestive system - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... The large intestine is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract, and it is composed of three parts: cecum, colon, rectum. Its functions are to: • absorb water, salts and vitamins; • collect waste materials and eliminate them as feces. ...
... The large intestine is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract, and it is composed of three parts: cecum, colon, rectum. Its functions are to: • absorb water, salts and vitamins; • collect waste materials and eliminate them as feces. ...
Chapter 5: Point and Nonpoint Source Reductions
... application of state and federal regulations. It is anticipated that biological chemical removal technologies will be used at these wastewater facilities. Some facilities might add effluent filters to achieve effluent limits less than 0.6 mg/l phosphorus consistently. In the past, wastewater treatme ...
... application of state and federal regulations. It is anticipated that biological chemical removal technologies will be used at these wastewater facilities. Some facilities might add effluent filters to achieve effluent limits less than 0.6 mg/l phosphorus consistently. In the past, wastewater treatme ...
Nutrient Cycling - Region 11 Math and Science Teacher Academy
... More Fun Facts About Soil Twenty thousand species of nematodes have been described, but it is thought that 500,000 species may exist. Every time you take a step in a mature forest, your foot is being supported on the backs of 16,000 invertebrates held up by an average total of 120,000 legs. There is ...
... More Fun Facts About Soil Twenty thousand species of nematodes have been described, but it is thought that 500,000 species may exist. Every time you take a step in a mature forest, your foot is being supported on the backs of 16,000 invertebrates held up by an average total of 120,000 legs. There is ...
NORMAL NUTRITION NURP 102 ANDERSON
... Pylorus: sphincter muscle between stomach and small intestine Small Intestine: Enzymes from gall bladder, pancreas plus intestine completes digestion of Carbohydrates, Fats, & Protein Bile: emulsifier produced in liver that emulsifies fat—stored in gall bladder Large Intestine: Reabsorbs water and s ...
... Pylorus: sphincter muscle between stomach and small intestine Small Intestine: Enzymes from gall bladder, pancreas plus intestine completes digestion of Carbohydrates, Fats, & Protein Bile: emulsifier produced in liver that emulsifies fat—stored in gall bladder Large Intestine: Reabsorbs water and s ...
Understanding Soil Phosphorus - Integrated Pest and Crop
... between the SP and PP proportion of the total P in runoff varies as a function of erosion rates (Fig. 3). As erosion rates increase, the PP fraction of total P content increases while the SP fraction decreases significantly (Pote et al., 1996). Once eroded sediment has reached a lake, it eventually ...
... between the SP and PP proportion of the total P in runoff varies as a function of erosion rates (Fig. 3). As erosion rates increase, the PP fraction of total P content increases while the SP fraction decreases significantly (Pote et al., 1996). Once eroded sediment has reached a lake, it eventually ...
C H A P T E R 2 8
... from the distal tubule and cortical collecting tubule further raises the tubular fluid concentration of urea. And as this urea flows into the inner medullary collecting duct, the high tubular fluid concentration of urea and specific urea transporters cause urea to diffuse into the medullary intersti ...
... from the distal tubule and cortical collecting tubule further raises the tubular fluid concentration of urea. And as this urea flows into the inner medullary collecting duct, the high tubular fluid concentration of urea and specific urea transporters cause urea to diffuse into the medullary intersti ...
Digestive System Guided Notes
... Digestive System Guided Notes To be used with Digestive System PowerPoint ...
... Digestive System Guided Notes To be used with Digestive System PowerPoint ...
The Digestive System
... Role of Saliva – the first chemical digestion site! To moisten the food and contains enzymes (salivary amylase) that begins digestion of starch (glycogen into small polysaccharides, or disaccharides) into smaller ...
... Role of Saliva – the first chemical digestion site! To moisten the food and contains enzymes (salivary amylase) that begins digestion of starch (glycogen into small polysaccharides, or disaccharides) into smaller ...
Review of the Advantages and Disadvantages of
... of a crop nutrient management plan with applications of inorganic fertilisers adjusted to take account of the nutrient content of the organic fertiliser. 2.2 Nutrient Retention Virtually all animal wastes are spread on the land in some form or other. Undigested material used as fertiliser suffers fr ...
... of a crop nutrient management plan with applications of inorganic fertilisers adjusted to take account of the nutrient content of the organic fertiliser. 2.2 Nutrient Retention Virtually all animal wastes are spread on the land in some form or other. Undigested material used as fertiliser suffers fr ...
The Large Intestine Questions
... !iiiddd yyyooouuu kkknnnooowww ttthhhaaattt ttthhheee lllaaarrrgggeee iiinnnttteeessstttiiinnneee cccooouuulllddd aaabbbsssooorrrbbb aaabbbooouuuttt 111...666 gggaaallllllooonnnsss ooofff wwwaaattteeerrr aaa dddaaayyy??? ...
... !iiiddd yyyooouuu kkknnnooowww ttthhhaaattt ttthhheee lllaaarrrgggeee iiinnnttteeessstttiiinnneee cccooouuulllddd aaabbbsssooorrrbbb aaabbbooouuuttt 111...666 gggaaallllllooonnnsss ooofff wwwaaattteeerrr aaa dddaaayyy??? ...
Circular Economy of Phosphorus Flow
... The production process of phosphate rock into phosphate products causes a significant amount of loss as well, especially phosphorus that is extracted in the form of the by-product phosphogypsum, that also causes severe environmental impacts because of its radioactivity. (Prud’homme 2010) With some i ...
... The production process of phosphate rock into phosphate products causes a significant amount of loss as well, especially phosphorus that is extracted in the form of the by-product phosphogypsum, that also causes severe environmental impacts because of its radioactivity. (Prud’homme 2010) With some i ...
Geotube® Dewatering Technology
... out by a specialised contractor or service provider. The sludge is pumped from the septic tanks into sludge transportation tankers and taken to a centralised location with sand drying bed facility for dewatering. The TenCate Geotube® dewatering system is ideal for dewatering septic tank sludge. The ...
... out by a specialised contractor or service provider. The sludge is pumped from the septic tanks into sludge transportation tankers and taken to a centralised location with sand drying bed facility for dewatering. The TenCate Geotube® dewatering system is ideal for dewatering septic tank sludge. The ...
introduction - Alberta Agriculture and Forestry
... cent of the body’s mass and is the sixth most abundant element in the human body following oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and calcium. Phosphorus is a component of every living cell, and cannot be replaced by any other element. It occurs in many complicated compounds such as genetic molecules (D ...
... cent of the body’s mass and is the sixth most abundant element in the human body following oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and calcium. Phosphorus is a component of every living cell, and cannot be replaced by any other element. It occurs in many complicated compounds such as genetic molecules (D ...
Why Study Nutrition?
... Comprise approximately 60% of annual cow costs in cow-calf operations 50-75% in other species ...
... Comprise approximately 60% of annual cow costs in cow-calf operations 50-75% in other species ...
Document
... It is found worldwide especially in tropical and subtropical areas. This occurs more frequently under poor sanitation conditions. There is a 3-14 day incubation period. There are no known organism vectors or reservoirs of Isosporiasis. Infection occurs in immunodepressed individuals. ...
... It is found worldwide especially in tropical and subtropical areas. This occurs more frequently under poor sanitation conditions. There is a 3-14 day incubation period. There are no known organism vectors or reservoirs of Isosporiasis. Infection occurs in immunodepressed individuals. ...
File
... ______ 4. Organ that mixes food in the mouth. ______ 5. Common passage for food and air. ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes ...
... ______ 4. Organ that mixes food in the mouth. ______ 5. Common passage for food and air. ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes ...
Digestive_System_organs
... Part 3: Using the key choices below, match the description given with the structure in the alimentary canal that it describes. Choices may be used more than once. ...
... Part 3: Using the key choices below, match the description given with the structure in the alimentary canal that it describes. Choices may be used more than once. ...
Digestive System Worksheet Name
... ______ 4. Organ that mixes food in the mouth. ______ 5. Common passage for food and air. ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes ...
... ______ 4. Organ that mixes food in the mouth. ______ 5. Common passage for food and air. ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes ...
Digestive and Excretory Systems Pretest
... 39. What type of digestion doesn't chemically change food but is the physical manipulation of solid foods called? This type of digestion occurs first by the tongue and the teeth in the oral cavity ...
... 39. What type of digestion doesn't chemically change food but is the physical manipulation of solid foods called? This type of digestion occurs first by the tongue and the teeth in the oral cavity ...
Giardia: Description
... countries and twice that in developing countries. • Overall U.S prevalence ~ 0.3%, but in day care center children it is 6-54%. • Estimated concentration in raw sewage is about 104/L. • Concentrations of 10s to 1000s/L in 2o treated sewage • Oocyst concentrations in fecally contaminated water vary b ...
... countries and twice that in developing countries. • Overall U.S prevalence ~ 0.3%, but in day care center children it is 6-54%. • Estimated concentration in raw sewage is about 104/L. • Concentrations of 10s to 1000s/L in 2o treated sewage • Oocyst concentrations in fecally contaminated water vary b ...
Reuse of excreta

Reuse of excreta (alternative spelling: re-use) refers to the safe, beneficial use of animal or human excreta, i.e. feces (or faeces in British English) and urine. Such beneficial use can be as a soil conditioner or fertilizer in agriculture, gardening, aquaculture or ornamental activities. Other possible uses include use as building material, fuel source or protein production. An alternative term is also ""use of excreta"" rather than ""reuse"" as strictly speaking it is the first use of excreta, not the second time that it is used.Reuse of excreta is one example of resource recovery of the resources contained in excreta, mainly the plant-available nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium as well as micronutrients such as sulphur and organic matter. These resources which are contained in wastewater, excreta and greywater have traditionally been reused in agriculture in many countries and are still being reused in agriculture to this day, but the practice is often carried out in an unregulated and unsafe manner for example in many developing countries (e.g. Mexico, India, Bangladesh, Ghana). The WHO Guidelines from 2006 have set up a framework how this reuse can be done safely by following a multiple barrier approach.Excreta-based fertilisers vary in their general properties and fertilising characteristics and include the following types: urine, dried feces, composted feces, faecal sludge (septage), municipal wastewater, sewage sludge and animal manure. Reuse of sanitised excreta in agriculture has also been called a ""closing the loop"" approach for sanitation and agriculture and is central to the ecological sanitation approach.Reuse of excreta is the final step of the sanitation chain which starts with collection of excreta (by use of toilets) and continues with transport and treatment (wastewater treatment is one example) all the way to either disposal or reuse.