Chapter 5 - Digestion and Absorption
... 25. Which of the following organs is the primary source of digestive enzymes? a. pancreas b. gallbladder c. stomach d. liver 26. After the pancreatic juices have mixed with chyme in the intestine, the resulting mixture is: a. very acidic. b. slightly acidic. c. strongly alkaline. d. slightly alkalin ...
... 25. Which of the following organs is the primary source of digestive enzymes? a. pancreas b. gallbladder c. stomach d. liver 26. After the pancreatic juices have mixed with chyme in the intestine, the resulting mixture is: a. very acidic. b. slightly acidic. c. strongly alkaline. d. slightly alkalin ...
Steen and Arnosti 2011 enzyme lifetime
... sea salts S9883, 35.0 g L−1). Sigma-Aldrich confirmed that no secondary enzymes (e.g. proteases) were added to the purified enzymes as part of the production process (pers. comm). Final enzyme concentrations were 3 ng phosphatase mL−1, 2 μg β-glucosidase mL−1, and 12 μg leucine aminopeptidase mL −1 . ...
... sea salts S9883, 35.0 g L−1). Sigma-Aldrich confirmed that no secondary enzymes (e.g. proteases) were added to the purified enzymes as part of the production process (pers. comm). Final enzyme concentrations were 3 ng phosphatase mL−1, 2 μg β-glucosidase mL−1, and 12 μg leucine aminopeptidase mL −1 . ...
Understanding the Gastrointestinal, Drug and Dosage Form
... Chauret, N., A. Gauthier, J. Martin and D. A. Nicoll-Griffith (1997). "In Vitro Comparison of Cytochrome P450-Mediated Metabolic Activities in Human, Dog, Cat, and Horse." Drug Metabolism and Disposition 25(10): 1130-1136. Straw, J. A., T. L. Loo, C. C. deVera, P. D. Nelson, W. A. Tompkins and S. A. ...
... Chauret, N., A. Gauthier, J. Martin and D. A. Nicoll-Griffith (1997). "In Vitro Comparison of Cytochrome P450-Mediated Metabolic Activities in Human, Dog, Cat, and Horse." Drug Metabolism and Disposition 25(10): 1130-1136. Straw, J. A., T. L. Loo, C. C. deVera, P. D. Nelson, W. A. Tompkins and S. A. ...
8 I PUC – Biology Chapter - 16 Digestion and Absorption One Mark
... 47. In which part of the small intestine does digestion take place? Ans: Duodenum 48. What controls the reflex of vomiting? Ans: The reflex of vomiting is controlled by the vomit centre in the modulla. 49. What is the function of HCl in the stomach? Ans: HCl provides the acidic PH [PH – 1.8] require ...
... 47. In which part of the small intestine does digestion take place? Ans: Duodenum 48. What controls the reflex of vomiting? Ans: The reflex of vomiting is controlled by the vomit centre in the modulla. 49. What is the function of HCl in the stomach? Ans: HCl provides the acidic PH [PH – 1.8] require ...
Chapter 24 Digestion
... Water especially if it is cold Electrolytes Some drugs (especially aspirin) & alcohol Fat content in the stomach slows the passage of alcohol to the intestine where absorption is more rapid • Gastric mucosal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase that converts some alcohol to acetaldehyde-----more of t ...
... Water especially if it is cold Electrolytes Some drugs (especially aspirin) & alcohol Fat content in the stomach slows the passage of alcohol to the intestine where absorption is more rapid • Gastric mucosal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase that converts some alcohol to acetaldehyde-----more of t ...
Chemical digestion
... •Jaundice - yellow pigmentation of the skin caused by increased levels of bilirubin in the blood. •Hepatitis - inflammation of the liver caused by viruses. •Cirrhosis - damage of tissues leading to loss of liver functions. •Liver cancer. ...
... •Jaundice - yellow pigmentation of the skin caused by increased levels of bilirubin in the blood. •Hepatitis - inflammation of the liver caused by viruses. •Cirrhosis - damage of tissues leading to loss of liver functions. •Liver cancer. ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... Gastric glands—found below level of the pits; secrete most of gastric juice • Chief cells—secretory cells found in gastric glands; secrete the enzymes of gastric juice • Parietal cells—secretory cells found in gastric glands; secrete hydrochloric acid; thought to produce intrinsic factor needed for ...
... Gastric glands—found below level of the pits; secrete most of gastric juice • Chief cells—secretory cells found in gastric glands; secrete the enzymes of gastric juice • Parietal cells—secretory cells found in gastric glands; secrete hydrochloric acid; thought to produce intrinsic factor needed for ...
book - MUK Publications
... Oesophageal diseases consist of a spectrum of disorders affecting the oesophagus. The most common condition of the oesophagus in Western countries is gastroesophageal reflux disease, which in chronic forms is thought to result in changes to the epithelium of the oesophagus, known as Barrett’s oesoph ...
... Oesophageal diseases consist of a spectrum of disorders affecting the oesophagus. The most common condition of the oesophagus in Western countries is gastroesophageal reflux disease, which in chronic forms is thought to result in changes to the epithelium of the oesophagus, known as Barrett’s oesoph ...
GIT 323 Block Educational Framework (Week 1)
... MCQs: Multiple choice questions; SAQs: Short answer questions; OSPE: Objective structured practical examination; SDL: Self Directed Learning ...
... MCQs: Multiple choice questions; SAQs: Short answer questions; OSPE: Objective structured practical examination; SDL: Self Directed Learning ...
“Advanced Viscera-Bowel Physiology and Pathomechanisms”
... these concepts available in modern and classical Chinese texts. Unfortunately, this denies the Englishlanguage CM community the opportunity to develop a more mature and more clinically viable understanding of CM physiology and pathomechanisms on their own terms. Through his translations of modern an ...
... these concepts available in modern and classical Chinese texts. Unfortunately, this denies the Englishlanguage CM community the opportunity to develop a more mature and more clinically viable understanding of CM physiology and pathomechanisms on their own terms. Through his translations of modern an ...
The Digestive System
... Typically, the epithelium of the mucosa is a simple columnar epithelium rich in mucus-secreting cells. The slippery mucus it produces protects certain digestive organs from being digested themselves by enzymes working within their cavities and eases food passage along the tract. In the stomach and s ...
... Typically, the epithelium of the mucosa is a simple columnar epithelium rich in mucus-secreting cells. The slippery mucus it produces protects certain digestive organs from being digested themselves by enzymes working within their cavities and eases food passage along the tract. In the stomach and s ...
chapter 8 - Mrs. Aymami`s Class
... • Teeth in front of mouth bite, tear, or cut food into small pieces; include incisors and cuspids or canines; see . Figure 8.3 • Posterior teeth grind and crush food into even finer pieces; include bicuspids, or pre-molars, and molars • Tooth subdivided into crown and root; crown is part of tooth vi ...
... • Teeth in front of mouth bite, tear, or cut food into small pieces; include incisors and cuspids or canines; see . Figure 8.3 • Posterior teeth grind and crush food into even finer pieces; include bicuspids, or pre-molars, and molars • Tooth subdivided into crown and root; crown is part of tooth vi ...
Gallbladder and Bile Duct Surgery (Cholecystectomy and Common
... of the gallbladder and make their way down the bile duct into the intestine. As long as these stones do not get caught in the bile duct this is not a problem. If these stones do get caught in one of the bile ducts, this can cause a very severe infection or severe inflammation of the pancreas. This w ...
... of the gallbladder and make their way down the bile duct into the intestine. As long as these stones do not get caught in the bile duct this is not a problem. If these stones do get caught in one of the bile ducts, this can cause a very severe infection or severe inflammation of the pancreas. This w ...
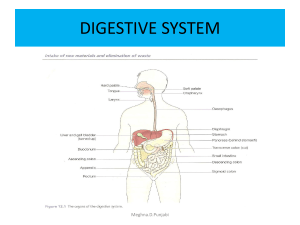
Digestive System
... 5) phagocytosis of RBC a) results in the production of bilirubin 6) synthesis of bile salts 7) produces bile a) yellow-green, alkaline solution containing bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, lecithin & and a number of electrolytes b) involved with lipid catabolism & absorption ...
... 5) phagocytosis of RBC a) results in the production of bilirubin 6) synthesis of bile salts 7) produces bile a) yellow-green, alkaline solution containing bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, lecithin & and a number of electrolytes b) involved with lipid catabolism & absorption ...
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... List the four major organic macromolecules that we ingest, and explain how each is broken down by various enzymes within the alimentary canal. Be sure to include enzyme names, the location of enzyme action, and the breakdown products that result from the enzymatic action, and explain any hormonal co ...
... List the four major organic macromolecules that we ingest, and explain how each is broken down by various enzymes within the alimentary canal. Be sure to include enzyme names, the location of enzyme action, and the breakdown products that result from the enzymatic action, and explain any hormonal co ...
Digestion © 2009 Cengage - Wadsworth
... Stomach action Stomach has the thickest walls & strongest muscles of all of the GI tract organs Circular, longitudinal & diagonal muscles churn food into semiliquid chyme ...
... Stomach action Stomach has the thickest walls & strongest muscles of all of the GI tract organs Circular, longitudinal & diagonal muscles churn food into semiliquid chyme ...
7-OMENTUM-2016-Final
... • It is the communication between the greater and lesser sacs . • It is bounded by; • In front by the free border of the lesser omentum, with its contents ; hepatic artery, common bile duct, and portal vein between its two layers. • Behind by the peritoneum covering the inferior vena cava. • Above ( ...
... • It is the communication between the greater and lesser sacs . • It is bounded by; • In front by the free border of the lesser omentum, with its contents ; hepatic artery, common bile duct, and portal vein between its two layers. • Behind by the peritoneum covering the inferior vena cava. • Above ( ...
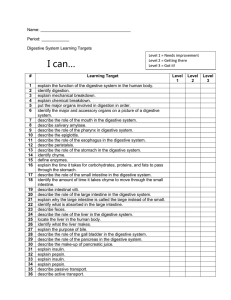
Digestive System Learning Targets
... define enzymes. explain the time it takes for carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to pass through the stomach. describe the role of the small intestine in the digestive system. identify the amount of time it takes chyme to move through the small intestine. describe intestinal villi. describe the role ...
... define enzymes. explain the time it takes for carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to pass through the stomach. describe the role of the small intestine in the digestive system. identify the amount of time it takes chyme to move through the small intestine. describe intestinal villi. describe the role ...
Hepatotoxicity

Hepatotoxicity (from hepatic toxicity) implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure the organ. Other chemical agents, such as those used in laboratories and industries, natural chemicals (e.g., microcystins) and herbal remedies can also induce hepatotoxicity. Chemicals that cause liver injury are called hepatotoxins.More than 900 drugs have been implicated in causing liver injury and it is the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market. Hepatotoxicity and drug-induced liver injury also account for a substantial number of compound failures, highlighting the need for drug screening assays, such as stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells, that are capable of detecting toxicity early in the drug development process. Chemicals often cause subclinical injury to the liver, which manifests only as abnormal liver enzyme tests. Drug-induced liver injury is responsible for 5% of all hospital admissions and 50% of all acute liver failures.