Other Digestive Organs
... • attached behind the liver • stores bile (which aids in physical digestion of fats/oils in the small intestine) • a.k.a emulsification (doesn’t change composition of fats, just breaks them down) ...
... • attached behind the liver • stores bile (which aids in physical digestion of fats/oils in the small intestine) • a.k.a emulsification (doesn’t change composition of fats, just breaks them down) ...
Esophagus
... triggered by aroma, taste, sight, thought – Gastric phase – lasts 3–4 hours; ⅔ gastric juice released • Stimulated by distension, peptides, low acidity, gastrin (major stimulus) • Enteroendocrine G cells stimulated by caffeine, peptides, rising pH gastrin ...
... triggered by aroma, taste, sight, thought – Gastric phase – lasts 3–4 hours; ⅔ gastric juice released • Stimulated by distension, peptides, low acidity, gastrin (major stimulus) • Enteroendocrine G cells stimulated by caffeine, peptides, rising pH gastrin ...
Lecture Chpt. 41 Digestion
... Quick question: Whose genes matter most to you? Your mom's? Your dad's? Or genes inside the trillions of bacteria living in your intestine, your mouth, your nasal passages and a lot of places we'd rather not mention? The answer: Obviously, your parents' genes matter, but it turns out we humans have ...
... Quick question: Whose genes matter most to you? Your mom's? Your dad's? Or genes inside the trillions of bacteria living in your intestine, your mouth, your nasal passages and a lot of places we'd rather not mention? The answer: Obviously, your parents' genes matter, but it turns out we humans have ...
Chapter 24
... local and autonomic reflexes to control intestinal secretion and different types of motility that facilitate breakdown and absorption of food molecules. Physiology of Absorption in the Small Intestine 71. Describe the end products of chemical digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Absorpt ...
... local and autonomic reflexes to control intestinal secretion and different types of motility that facilitate breakdown and absorption of food molecules. Physiology of Absorption in the Small Intestine 71. Describe the end products of chemical digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Absorpt ...
physiologicoanatomical features of the digestive system in children
... The teeth are inspected for number in each dental arch, hygiene, and occlusion or bite. The general rule for estimating the number of temporary teeth in children who are 2 years of age or younger is: the child's age in months minus 6 months equals the number of teeth. Discoloration of tooth enamel w ...
... The teeth are inspected for number in each dental arch, hygiene, and occlusion or bite. The general rule for estimating the number of temporary teeth in children who are 2 years of age or younger is: the child's age in months minus 6 months equals the number of teeth. Discoloration of tooth enamel w ...
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... Well over half of the people who seek medical attention have gastrointestinal complaints. This striking fact is a tribute to the complexity, diversity, and conspicuous impact of digestive system function and dysfunction. The clinical problems highlight many of the key structures and processes found ...
... Well over half of the people who seek medical attention have gastrointestinal complaints. This striking fact is a tribute to the complexity, diversity, and conspicuous impact of digestive system function and dysfunction. The clinical problems highlight many of the key structures and processes found ...
Stomach
... Digestive Processes in the Stomach • Lipid-soluble alcohol and aspirin absorbed into blood • Only stomach function essential to life – Secretes intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption • B12 needed mature red blood cells • Lack of intrinsic factor causes pernicious anemia • Treated with B12 in ...
... Digestive Processes in the Stomach • Lipid-soluble alcohol and aspirin absorbed into blood • Only stomach function essential to life – Secretes intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption • B12 needed mature red blood cells • Lack of intrinsic factor causes pernicious anemia • Treated with B12 in ...
The Digestive system includes - Websupport1
... Anatomy of the stomach • Cardia – superior, medial portion (portion of the stomach that connects to the esofagous) • Fundus – portion superior to stomachesophageal junction • Body – area between the fundus and the curve of the J • Pylorus – antrum and pyloric canal adjacent to the duodenum (portion ...
... Anatomy of the stomach • Cardia – superior, medial portion (portion of the stomach that connects to the esofagous) • Fundus – portion superior to stomachesophageal junction • Body – area between the fundus and the curve of the J • Pylorus – antrum and pyloric canal adjacent to the duodenum (portion ...
The Digestive System What are the organs of the digestive system
... Narrow band of smooth muscle and elastic fibers in lamina propria Smooth muscle cells arranged in 2 ...
... Narrow band of smooth muscle and elastic fibers in lamina propria Smooth muscle cells arranged in 2 ...
Worksheet Chapter 8
... 3. The organ that produces bile is the a. gallbladder. b. pancreas. c. liver. d. small intestine. 4. The pathological condition characterized by twisting of the intestine on itself is called a. polyp. b. intussusception. ...
... 3. The organ that produces bile is the a. gallbladder. b. pancreas. c. liver. d. small intestine. 4. The pathological condition characterized by twisting of the intestine on itself is called a. polyp. b. intussusception. ...
Foregut is a source for development of: Stomach, small intestine
... On level of 11 th rib, right to medial clavicular (collar) line* On level of 9 th rib, left to medial clavicular (collar) line On level of 12 th rib, left to breast bone (2.5-3 cm) 83. Name structures that belong to gastric mucosa only: Mucosal folds and lymph follicles Villi, folds and glands ...
... On level of 11 th rib, right to medial clavicular (collar) line* On level of 9 th rib, left to medial clavicular (collar) line On level of 12 th rib, left to breast bone (2.5-3 cm) 83. Name structures that belong to gastric mucosa only: Mucosal folds and lymph follicles Villi, folds and glands ...
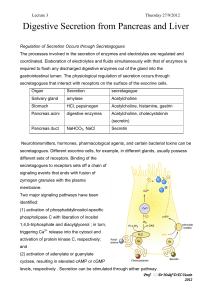
The Pancreas
... The pancreas, not the stomach, is the major organ that synthesizes and secretes the large amounts of enzymes needed for digestion. Thus the pancreas plays a vital role in accomplishing the followings: • Acid must be quickly and efficiently neutralized to prevent damage to the duodenal mucosa • Macro ...
... The pancreas, not the stomach, is the major organ that synthesizes and secretes the large amounts of enzymes needed for digestion. Thus the pancreas plays a vital role in accomplishing the followings: • Acid must be quickly and efficiently neutralized to prevent damage to the duodenal mucosa • Macro ...
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Taste and
... In this chapter, Bobbie’s fiber and fluid intakes are listed, as both are important for a healthy GI tract. The following questions could be asked at the close of the chapter in a small group setting: 1. Is there anything else Bobbie can do to boost her fluid intake? 2. Could Bobbie be at risk for d ...
... In this chapter, Bobbie’s fiber and fluid intakes are listed, as both are important for a healthy GI tract. The following questions could be asked at the close of the chapter in a small group setting: 1. Is there anything else Bobbie can do to boost her fluid intake? 2. Could Bobbie be at risk for d ...
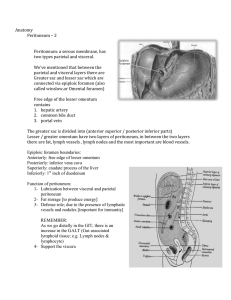
Anatomy Peritoneum – 2 Peritoneum: a serous membrane, has two
... connected to the posterior abdominal wall… these 2 ends are a MUST in the mesentery]] Between the two layers there are blood vessels, lymphatics, lymph nodes & ...
... connected to the posterior abdominal wall… these 2 ends are a MUST in the mesentery]] Between the two layers there are blood vessels, lymphatics, lymph nodes & ...
the digestive system
... the tongue, and most of them contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae (least numerous), 10 to 12 in number, are arranged in the form of an inverted V on the posterior surface of the tongue, and all of them contain taste buds. Although the tip of the tongue reacts to all four primary taste sensatio ...
... the tongue, and most of them contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae (least numerous), 10 to 12 in number, are arranged in the form of an inverted V on the posterior surface of the tongue, and all of them contain taste buds. Although the tip of the tongue reacts to all four primary taste sensatio ...
Let`s Eat! – The Gastrointestinal System
... b. Feces collects in the large bowel and exits through the anus ...
... b. Feces collects in the large bowel and exits through the anus ...
ST120 Digestive System_BB
... Esophagogastroduodenoscopy: visualization of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum Colonoscopy: visualization of the inner surface of the entire colon from the rectum to the cecum. Sigmoidoscopy: visualization of the sigmoid colon Capsule endoscopy: a tiny video camera in a capsule that the pt. swall ...
... Esophagogastroduodenoscopy: visualization of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum Colonoscopy: visualization of the inner surface of the entire colon from the rectum to the cecum. Sigmoidoscopy: visualization of the sigmoid colon Capsule endoscopy: a tiny video camera in a capsule that the pt. swall ...
Chapter 24: Digestive System
... • Surface area increased 600X by: – Plicae (transverse folds) – Villi with microvilli ...
... • Surface area increased 600X by: – Plicae (transverse folds) – Villi with microvilli ...
The Gallbladder: A Change in Physiology The gallbladder is a
... duodenum of the small intestine. Under normal conditions the liver produces bile, which is a yellowish-green liquid composed mainly of cholesterol, bile acids, lecithin, and water that emulsifies dietary fat in the small intestine, and releases it into the duodenum when fat is present. When bile is ...
... duodenum of the small intestine. Under normal conditions the liver produces bile, which is a yellowish-green liquid composed mainly of cholesterol, bile acids, lecithin, and water that emulsifies dietary fat in the small intestine, and releases it into the duodenum when fat is present. When bile is ...
bio 241 – spring 2003 – examination #1
... It is able to continue its digestive function until the food is converted to chyme and passed into the duodenum. D. It actively works to breakdown carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, as long as it remains in the mouth. E. All of the above are true statements. ...
... It is able to continue its digestive function until the food is converted to chyme and passed into the duodenum. D. It actively works to breakdown carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, as long as it remains in the mouth. E. All of the above are true statements. ...
Hepatotoxicity

Hepatotoxicity (from hepatic toxicity) implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure the organ. Other chemical agents, such as those used in laboratories and industries, natural chemicals (e.g., microcystins) and herbal remedies can also induce hepatotoxicity. Chemicals that cause liver injury are called hepatotoxins.More than 900 drugs have been implicated in causing liver injury and it is the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market. Hepatotoxicity and drug-induced liver injury also account for a substantial number of compound failures, highlighting the need for drug screening assays, such as stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells, that are capable of detecting toxicity early in the drug development process. Chemicals often cause subclinical injury to the liver, which manifests only as abnormal liver enzyme tests. Drug-induced liver injury is responsible for 5% of all hospital admissions and 50% of all acute liver failures.