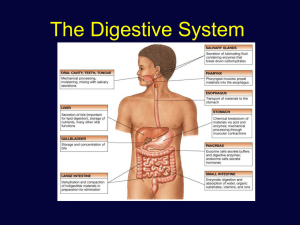
The Digestive System
... (sodium bicarbonate) and liver (bile) When chyme enters the small intestine the carbs and proteins are only partially digested, digestion finishes here Villi (singular- villus) are small folds in the lining of the small intestine that increase the surface area to absorb more nutrients ...
... (sodium bicarbonate) and liver (bile) When chyme enters the small intestine the carbs and proteins are only partially digested, digestion finishes here Villi (singular- villus) are small folds in the lining of the small intestine that increase the surface area to absorb more nutrients ...
1 ppt Digestive system - Liberty Union High School District
... • secretion of intrinsic factor is the only indispensable function of the stomach – digestion can continue if stomach is removed (gastrectomy), but B12 supplements will be needed ...
... • secretion of intrinsic factor is the only indispensable function of the stomach – digestion can continue if stomach is removed (gastrectomy), but B12 supplements will be needed ...
ch24 outline
... The epithelium consists of a protective layer of non-keratinized stratified squamous cells in the mouth, pharynx and esophagus and simple columnar cells for secretion and absorption in the stomach and inntestines. Other cells include mucus secreting cells as well as some enteroendocrine cells that s ...
... The epithelium consists of a protective layer of non-keratinized stratified squamous cells in the mouth, pharynx and esophagus and simple columnar cells for secretion and absorption in the stomach and inntestines. Other cells include mucus secreting cells as well as some enteroendocrine cells that s ...
4/19
... Why is bicarbonate generated in so many different places around the duodenum? What does the intestinal wall look like at the microscopic level? How does the intestine move chyme with peristaltic waves of smooth muscle cell contraction? VIP!! What enzymes degrade protein, carbohydrates and fat? Can p ...
... Why is bicarbonate generated in so many different places around the duodenum? What does the intestinal wall look like at the microscopic level? How does the intestine move chyme with peristaltic waves of smooth muscle cell contraction? VIP!! What enzymes degrade protein, carbohydrates and fat? Can p ...
notes - Main
... proteins into peptides by pepsin, an enzyme that is most effective in the very acidic environment (pH 2) of the stomach. The acid (HCl) is secreted by the stomach’s parietal cells (Figure 24.13). b. Gastric lipase splits certain molecules in butterfat of milk into fatty acids and monoglycerides and ...
... proteins into peptides by pepsin, an enzyme that is most effective in the very acidic environment (pH 2) of the stomach. The acid (HCl) is secreted by the stomach’s parietal cells (Figure 24.13). b. Gastric lipase splits certain molecules in butterfat of milk into fatty acids and monoglycerides and ...
ch24 Digestive System
... proteins into peptides by pepsin, an enzyme that is most effective in the very acidic environment (pH 2) of the stomach. The acid (HCl) is secreted by the stomach’s parietal cells (Figure 24.13). b. Gastric lipase splits certain molecules in butterfat of milk into fatty acids and monoglycerides and ...
... proteins into peptides by pepsin, an enzyme that is most effective in the very acidic environment (pH 2) of the stomach. The acid (HCl) is secreted by the stomach’s parietal cells (Figure 24.13). b. Gastric lipase splits certain molecules in butterfat of milk into fatty acids and monoglycerides and ...
The Digestive System
... Liver 5) It stores glucose as glycogen; breaks down glycogen to maintain constant blood glucose concentration. – Blood vessels from large and small intestines lead to liver as hepatic portal vein. – Liver maintains blood glucose level at 0.1% by removing glucose from hepatic portal vein to store as ...
... Liver 5) It stores glucose as glycogen; breaks down glycogen to maintain constant blood glucose concentration. – Blood vessels from large and small intestines lead to liver as hepatic portal vein. – Liver maintains blood glucose level at 0.1% by removing glucose from hepatic portal vein to store as ...
Digestive System
... Liquids and carbohydrates pass through fairly quickly. Proteins takes a little more time, and fats takes even longer, usually between 4 to 6 hours. Secretes gastric acid and enzymes, which mixes with food, chemical digestion. Absorb small amounts of water and substances on a limited bases,although a ...
... Liquids and carbohydrates pass through fairly quickly. Proteins takes a little more time, and fats takes even longer, usually between 4 to 6 hours. Secretes gastric acid and enzymes, which mixes with food, chemical digestion. Absorb small amounts of water and substances on a limited bases,although a ...
Chapter 24
... blood from aorta hepatic portal vein deoxygenated blood from intestine w/ newly absorbed nutrients ...
... blood from aorta hepatic portal vein deoxygenated blood from intestine w/ newly absorbed nutrients ...
The Digestive System
... • Exocrine functions - majority of pancreatic secretions, pancreatic juice secreted into small intestine ...
... • Exocrine functions - majority of pancreatic secretions, pancreatic juice secreted into small intestine ...
HUMAN DIGESTION
... bicarbonate ion into the small intestine where it will neutralize the acidic chyme and raise the pH from 2.5 to 9.0. This inactivates the pepsin. ...
... bicarbonate ion into the small intestine where it will neutralize the acidic chyme and raise the pH from 2.5 to 9.0. This inactivates the pepsin. ...
32.2 Digestive System
... digestive process by tying foods to string, putting them into the stomach, and observing how the food was digested ...
... digestive process by tying foods to string, putting them into the stomach, and observing how the food was digested ...
Intestines/Digestive System Directions
... 2. Find the tube-like esophagus which joins the mouth and the stomach. Food moves down the esophagus by muscular contractions after being softened by saliva in the mouth. Follow the esophagus and locate the soft, sac-like stomach beneath the liver. 3. With scissors, cut along the outer curve of the ...
... 2. Find the tube-like esophagus which joins the mouth and the stomach. Food moves down the esophagus by muscular contractions after being softened by saliva in the mouth. Follow the esophagus and locate the soft, sac-like stomach beneath the liver. 3. With scissors, cut along the outer curve of the ...
nutrition-for-health-and-health-care-4th-edition-whitney-test-bank
... 36. Which of the following foods would result in the slowest rate of digestion? a. a piece of toast with strawberry jam b. a grilled steak c. a green salad with low-fat salad dressing d. a cup of green beans ...
... 36. Which of the following foods would result in the slowest rate of digestion? a. a piece of toast with strawberry jam b. a grilled steak c. a green salad with low-fat salad dressing d. a cup of green beans ...
digestion part 3.pptx
... 2) How is the inner lining of the small intestine special and why is this important to digestion? 3) What three substances does the small intestine contain and which organs or cells are responsible for secreting each of these substances? 4) What 3 nutrients are digested in the small intestine and ...
... 2) How is the inner lining of the small intestine special and why is this important to digestion? 3) What three substances does the small intestine contain and which organs or cells are responsible for secreting each of these substances? 4) What 3 nutrients are digested in the small intestine and ...
Functions of the Digestive System
... Common cause = Virus Symps – diarrhea and vomiting for 24-36 hours Complication = dehydration ...
... Common cause = Virus Symps – diarrhea and vomiting for 24-36 hours Complication = dehydration ...
Hepatotoxicity

Hepatotoxicity (from hepatic toxicity) implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure the organ. Other chemical agents, such as those used in laboratories and industries, natural chemicals (e.g., microcystins) and herbal remedies can also induce hepatotoxicity. Chemicals that cause liver injury are called hepatotoxins.More than 900 drugs have been implicated in causing liver injury and it is the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market. Hepatotoxicity and drug-induced liver injury also account for a substantial number of compound failures, highlighting the need for drug screening assays, such as stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells, that are capable of detecting toxicity early in the drug development process. Chemicals often cause subclinical injury to the liver, which manifests only as abnormal liver enzyme tests. Drug-induced liver injury is responsible for 5% of all hospital admissions and 50% of all acute liver failures.