analysis and prediction of absorption profile including hepatic first
... the observed bioavailability was only 39.0%. The in vitro metabolism study clarified that NMT is metabolized in the liver, but not in the small-intestinal mucosa. With the hepatic intrinsic clearance value (2.0 liters/h) calculated from the rate of metabolism in vitro, the hepatic availability was e ...
... the observed bioavailability was only 39.0%. The in vitro metabolism study clarified that NMT is metabolized in the liver, but not in the small-intestinal mucosa. With the hepatic intrinsic clearance value (2.0 liters/h) calculated from the rate of metabolism in vitro, the hepatic availability was e ...
Objectives Derivatives of the yolk sac,
... • Insulin secretion begins at about 10th wk of IUL • Glucagon secretion = at about 15thwk of IUL • Pancreatic tissue may be located in the Meckel’s diverticulum • Reversed rotation of Ventral bud can produce anular pancreas ...
... • Insulin secretion begins at about 10th wk of IUL • Glucagon secretion = at about 15thwk of IUL • Pancreatic tissue may be located in the Meckel’s diverticulum • Reversed rotation of Ventral bud can produce anular pancreas ...
Chapter 17 Abdomen Abdominal examination is performed: As part
... Pancreatic buds, liver, and gallbladder all begin to form during week 4 of gestation. Intestine already exists as a single tube. Meconium, an end product of fetal metabolism, is produced at about 17 weeks. By 36 to 38 weeks of gestation, the gastrointestinal tract is capable of adapting to extrauter ...
... Pancreatic buds, liver, and gallbladder all begin to form during week 4 of gestation. Intestine already exists as a single tube. Meconium, an end product of fetal metabolism, is produced at about 17 weeks. By 36 to 38 weeks of gestation, the gastrointestinal tract is capable of adapting to extrauter ...
Game Board
... This is the process of making glucose from non-carbohydrate substances like fats and proteins. ...
... This is the process of making glucose from non-carbohydrate substances like fats and proteins. ...
chap 23b - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... Digestive Processes in the Stomach • Lipid-soluble alcohol and aspirin absorbed into blood • Only stomach function essential to life – Secretes intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption • B12 needed mature red blood cells • Lack of intrinsic factor causes pernicious anemia • Treated with B12 in ...
... Digestive Processes in the Stomach • Lipid-soluble alcohol and aspirin absorbed into blood • Only stomach function essential to life – Secretes intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption • B12 needed mature red blood cells • Lack of intrinsic factor causes pernicious anemia • Treated with B12 in ...
Ch11 - ISpatula
... adjective endocrine indicates that a particular gland’s secretions are internal, e The rather than external; that is, secretions are not expelled through a duct. Glands that do expel their secretions through a duct are called exocrine glands. You will learn more about the endocrine system in Chapter ...
... adjective endocrine indicates that a particular gland’s secretions are internal, e The rather than external; that is, secretions are not expelled through a duct. Glands that do expel their secretions through a duct are called exocrine glands. You will learn more about the endocrine system in Chapter ...
Stomach - Anatomy and Physiology
... triggered by aroma, taste, sight, thought – Gastric phase – lasts 3–4 hours; ⅔ gastric juice released • Stimulated by distension, peptides, low acidity, gastrin (major stimulus) • Enteroendocrine G cells stimulated by caffeine, peptides, rising pH gastrin ...
... triggered by aroma, taste, sight, thought – Gastric phase – lasts 3–4 hours; ⅔ gastric juice released • Stimulated by distension, peptides, low acidity, gastrin (major stimulus) • Enteroendocrine G cells stimulated by caffeine, peptides, rising pH gastrin ...
Powerpoint 23 Digestion
... 2. Intestinal juice and brush border enzymes 3. Physiology of digestion in the small intestine a. Mechanical digestion b. Chemical digestion 4. Regulation of intestinal secretion and motility 5. Physiology of absorption ...
... 2. Intestinal juice and brush border enzymes 3. Physiology of digestion in the small intestine a. Mechanical digestion b. Chemical digestion 4. Regulation of intestinal secretion and motility 5. Physiology of absorption ...
Digestion PPT - Wilson`s Web Page
... The digestive system is involved in the ingestion and digestion of food and elimination of indigestible material. • Digestion takes place within the digestive tract, which begins with the mouth and ends with the anus. • Digestion involves mechanical and chemical digestion. o Mechanical digestion: ch ...
... The digestive system is involved in the ingestion and digestion of food and elimination of indigestible material. • Digestion takes place within the digestive tract, which begins with the mouth and ends with the anus. • Digestion involves mechanical and chemical digestion. o Mechanical digestion: ch ...
Digestion and the Digestive System
... The small intestine is approximately 3 m long. Like the stomach, it contains numerous ridges and furrows. In addition, there are numerous projections called villi that function to increase the surface area of the intestine. Individual villus cells have microvilli which greatly increase absorptive su ...
... The small intestine is approximately 3 m long. Like the stomach, it contains numerous ridges and furrows. In addition, there are numerous projections called villi that function to increase the surface area of the intestine. Individual villus cells have microvilli which greatly increase absorptive su ...
The digestive system – Apparatus digestorius
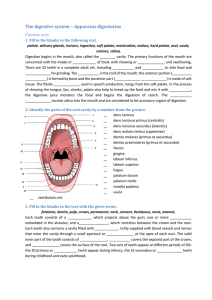
... The _____________ glands, which secrete into the mouth, are the first accessory organs to act on food. They secrete an enzyme (salivary amylase) that begins the digestion of starch. The remainder of the accessory organs is in the abdomen and secrete into the duodenum. The_________ is a large gland w ...
... The _____________ glands, which secrete into the mouth, are the first accessory organs to act on food. They secrete an enzyme (salivary amylase) that begins the digestion of starch. The remainder of the accessory organs is in the abdomen and secrete into the duodenum. The_________ is a large gland w ...
Digestive System - Austin Community College
... Human Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System; Ziser Lecture Notes, 2014.4 ...
... Human Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System; Ziser Lecture Notes, 2014.4 ...
Chapter 38
... Histology Lobules • Structural and functional units of the liver • They have cords of hepatocytes running away from the central vein • Hexagonal shape Central vein ...
... Histology Lobules • Structural and functional units of the liver • They have cords of hepatocytes running away from the central vein • Hexagonal shape Central vein ...
Digestion Review 2016 • Mechanical Digestion • Chemical
... 1. Describe how to test to determine if a food contains starch. 2. Describe how to test to determine if a food contains sugar. L4 – Digestion in the Mouth 1. What enzyme in your saliva is important for digestion? 2. Describe chemical digestion in the mouth. 3. Describe mechanical digestion in the mo ...
... 1. Describe how to test to determine if a food contains starch. 2. Describe how to test to determine if a food contains sugar. L4 – Digestion in the Mouth 1. What enzyme in your saliva is important for digestion? 2. Describe chemical digestion in the mouth. 3. Describe mechanical digestion in the mo ...
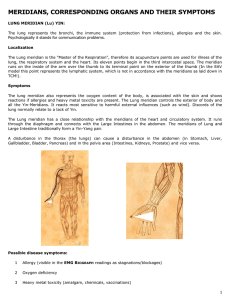
meridians, corresponding organs and their symptoms
... and electro-smog should be considered and checked. Simultaneous hypo-function of SP and Lv (sometimes also GB) very often are an indication of a toxic overload (heavy metal toxicity, exposure to chemical poisons such as glues, paints, solvents and wood sealers). Disturbances within SP are caused by ...
... and electro-smog should be considered and checked. Simultaneous hypo-function of SP and Lv (sometimes also GB) very often are an indication of a toxic overload (heavy metal toxicity, exposure to chemical poisons such as glues, paints, solvents and wood sealers). Disturbances within SP are caused by ...
the digestive system - People Server at UNCW
... to lubricate food so that it can be easily swallowed and to facilitate speech. ...
... to lubricate food so that it can be easily swallowed and to facilitate speech. ...
Hepatotoxicity

Hepatotoxicity (from hepatic toxicity) implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure the organ. Other chemical agents, such as those used in laboratories and industries, natural chemicals (e.g., microcystins) and herbal remedies can also induce hepatotoxicity. Chemicals that cause liver injury are called hepatotoxins.More than 900 drugs have been implicated in causing liver injury and it is the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market. Hepatotoxicity and drug-induced liver injury also account for a substantial number of compound failures, highlighting the need for drug screening assays, such as stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells, that are capable of detecting toxicity early in the drug development process. Chemicals often cause subclinical injury to the liver, which manifests only as abnormal liver enzyme tests. Drug-induced liver injury is responsible for 5% of all hospital admissions and 50% of all acute liver failures.