* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwinian Evolution
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
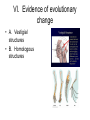
Darwinian evolution I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Introduction Influences on young Darwin Definition of evolution Mechanism Example Pieces of evidence supporting theory I. Intro to Darwinian evolution • Unifying principle of biology • Helps to explain how change has occurred over time • Nothing magical about how it occurs Influences on a young Charles Darwin II. Influences on a young Darwin A. Family Background • 1. religious family • 2. professions considered • 3. naturalist B. Voyage of the Beagle C. Galapagos Islands • • • • 1. Tortoises 2. Iguanas 3. Finches 4. Adaptive radiation D. Thomas Malthus • 1. Economist • 2. Malthusian Principle • 3. Introduced the concept of struggle E. Artificial selection • 1. man’s selection of breeding pairs to produce desired “phenotype” • 2. examples • 3. significance III. Definition of evolution • A. Slow and gradual change over time in organisms appearance in response to environmental change • B. Organisms living today appear different than their ancestors • C. Living organisms share common ancestors IV. Mechanism of Change/Natural Selection • A. Variation exists in all populations • B. Reproductive potential • C. Variable fitness • D. Environmental carrying capacity • Differential reproduction • Slow gradual change in phenotype V. Example of evolutionary change • Size of beagle ears • Environment changes • Results VI. Evidence of evolutionary change • A. Vestigial structures • B. Homologous structures Evidence cont. • C. Common embryology Evidence cont. • C. Common embryology • D. Fossil record – 1. Missing links Evidence cont. • C. Common embryology • D. Fossil record – 1. Missing links – 2. Phylogenies