* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT4 - Ycmou
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
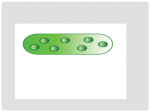
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Online Counseling Resource YCMOU ELearning Drive… School of Architecture, Science and Technology Yashwantrao Chavan Maharashtra Open University, Nashik – 422222, India OC-SEP041-CP01-04 Introduction Programmes and Courses SEP – SBT041 – Unit 01 SEP – SBI041 – Unit 01 SEP – SGS041 – Unit 01 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Credits Academic Inputs by Mrs. Rasika Bhore M.sc (Microbiology) [email protected] © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 3 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… How to Use This Resource Counselor at each study center should use this presentation to deliver lecture of 40-60 minutes during Face-To-Face counseling. Discussion about students difficulties or tutorial with assignments should follow the lecture for about 40-60 minutes. Handouts (with 6 slides on each A4 size page) of this presentation should be provided to each student. Each student should discuss on the discussion forum all the terms which could not be understood. This will improve his writing skills and enhance knowledge level about topics, which shall be immensely useful for end exam. Appear several times, for all the Self-Tests, available for this course. Student can use handouts for last minutes preparation just before end exam. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 4 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Learning Objectives After studying this module, you should be able to: Discuss the content of cytoplasm of bacteria. Describe the bacterial genome. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 5 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Introduction The cytoplasm of bacterial cells consists of an aqueous solution of three groups of molecules: Macromolecules such as proteins (enzymes). mRNA and tRNA. Small molecules that are energy sources, precursors of macromolecules, metabolites or vitamins; and various inorganic ions and cofactors. The primary structural components found in the cytoplasm are the nucleoid and ribosomes, and possibly some type of inclusion. The cytoplasm of prokaryotes is more gel-like than that of eukaryotes. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 6 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Contents Of Cytoplasm © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 7 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Ribosomes The distinct granular appearance of prokaryotic cytoplasm is due to the presence and distribution of ribosomes. Ribosomes are composed of proteins and RNA. The ribosomes of prokaryotes are smaller than cytoplasmic ribosomes of eukaryotes. Prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S in size, being composed of 30S and 50S subunits. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 8 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Function Of Ribosomes Ribosomes are involved in the process of translation (protein synthesis), but some of their activities differ in eukaryotes, bacteria and archaea. Ribosomes do this by catalyzing the assembly of individual amino acids into polypeptide chains; this involves binding a messenger RNA and then using this as a template to join together the correct sequence of amino acids. This reaction uses adapters called transfer RNA molecules, which read the sequence of the messenger RNA and are attached to the amino acids. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 9 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Effect of Antibiotics On Ribosomes The differences between the bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes are exploited to create antibiotics that can destroy a bacterial infection without harming the cells of the infected person. Due to the differences in their structures, the bacterial 70S ribosomes are vulnerable to these antibiotics while the eukaryotic 80S ribosomes are not. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 10 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Bacterial Chromosome The bacterial chromosome (nucleoid) is typically one large circular molecule of DNA, more or less free in the cytoplasm, although coiled and supercoiled and anchored by proteins. The total DNA content of a prokaryote is referred to as the cell genome. The cell chromosome is the genetic control center of the cell which determines all the properties and functions of the bacterium. During cell growth and division, the prokaryotic chromosome is replicated in a semiconservative fashion to make an exact copy of the molecule for distribution to progeny cells. Replication and segregation of prokaryotic DNA is coordinated by the membrane and various proteins in the cytoplasm. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 11 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Function of Bacterial Chromosome The nucleoid is the genetic material of the bacterium. Genes located along the DNA are transcribed into RNA that, in the case of mRNA, is then translated into protein at the ribosomes. In other words, DNA determines what proteins and enzymes an organism can synthesize and, therefore, what chemical reactions it is able to carry out. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 12 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Genome In Defense Mechanism In order to protect against infection, the body must detect the presence of microorganisms. The body does this by recognizing molecules unique to microorganisms that are not associated with human cells. These unique molecules are called pathogen-associated molecular patterns or PAMPS. Bacterial and viral genomes contain a high frequency of unmethylated cytosine-guanine dinucleotide sequences. Mammalian DNA has a low frequency of cytosine-guanine dinucleotides and most are methylated. These unmethylated cytosine-guanine dinucleotide sequences in bacterial DNA are PAMPS that bind to pattern-recognition receptors on a variety of defense cells of the body and triggers innate immune defenses such as inflammation, fever, and phagocytosis. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 13 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Plasmids Many bacteria possess extrachromosomal DNA known as plasmids, which exist and replicate independently of the chromosome. They are 2- to 30 times smaller than chromosome, but their structure is same. Plasmids have relatively few genes (fewer than 30). The genetic information of the plasmid is usually not essential to survival of the host bacteria. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 14 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… ‘F’ Plasmid A special plasmid called a fertility (F) factor plays an important role in conjugation. The F factor contains genes that encourage cellular attachment during conjugation and accelerate plasmid transfer between conjugating bacterial cells. Those cells contributing DNA are called F+ (donor) cells , while those receiving DNA are the F(recipient) cells. The F factor can exist outside the bacterial chromosome or may be integrated into the chromosome. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 15 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… ‘R’ Plasmid Plasmids that encode enzymes that make a bacterium resistant to antibiotics are called R (resistance) factors. Some R factors confers resistance to only a single antibiotic, other to several antibiotics. Strains that carry R factors have multiple drug resistance. Genes that encode a series of bacteriocins are also found on plasmids. Bacteriocins are bacterial proteins capable of destroying other bacteria. Still other plasmids increase the pathogenicity of their host bacteria because the plasmid contains genes for toxin synthesis. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 16 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… What We Learn…… Cytoplasm is a complex water solution consists of nucleoid & ribosomes. Ribosomes are 70s type made up of 30s & 50s subunits. Ribosomes functions in protein synthesis. Bacterial chromosome is one long, single molecule of double stranded, helical, supercoiled DNA. It decides which proteins & enzymes should synthesize in cell. Plasmid is extrachromosomal DNA not necessary for cell functioning. ‘F’ plasmid acts in conjugation while ‘R’ plasmid act as antibiotic resistant marker. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 17 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Critical Thinking Questions 1. How can we produce the penicillin resistant strain of E.coli? 2. Mitochondria of eukaryotes possess same 70s ribosome as that found in prokaryotes. Does it affected by antibiotics? How? © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 18 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Tips For Critical Thinking Questions 1. By transferring R plasmids. 2. No it is not affected, because of the double membrane covering of mitochondria, antibiotics can not enter. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Study Tips Lipps G (editor). (2008). Plasmids: Current Research and Future Trends. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-90445535-6. Russell, David W.; Sambrook, Joseph (2001). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. LEDERBERG J (1952). "Cell genetics and hereditary symbiosis". Physiol. Rev. 32 (4): 403–30. Kandavelou K; Chandrasegaran S (2008). "Plasmids for Gene Therapy", Plasmids: Current Research and Future Trends. Caister Academic Press. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 20 School of Science and Technology, Online Counseling Resource… Study Tips www.en.wikipedia.org Plasmids www.cliffsnotes.com Bacterial chromosome & plasmid www.students.ccbcmd.edu Bacterial chromosome © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. 21 End of the Presentation Thank You !