* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes
Targeted temperature management wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
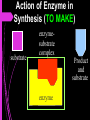
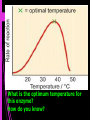
Control METABOLISM Metabolic reactions can be controlled and sped up by enzymes • metabolic reactions would be too slow to occur if no enzymes were present! • End in “ase” Properties of Enzymes 1. Proteins 2. Catalysts 3. Reusable Properties of Enzymes 4. Substrate specific 5. Sensitive to temperature 6. Sensitive to pH Enzymes Remain Unchanged! Enzymes are not used up; Reaction ends when there is NO MORE SUBSTRATE!! Before After Mechanism of Enzyme Action • THE ACTIVE SITE is the place where the substrate binds with the enzyme substrate substrate active site enzyme Action of Enzyme in Synthesis (TO MAKE) substrate enzymesubstrate complex Product and substrate enzyme Action of Enzyme in Decomposition (TO BREAK DOWN) enzymesubstrate complex product substrate enzyme Lock and Key Hypothesis Enzyme Substrate Lock and Key Hypothesis Lock & Key Model ONE enzyme for every substrate Unique fit Enzyme Substrate Enzymes are Temperature Dependent…... Most work BEST at body temperature 37oC DENATURE (change shape) at high temperatures Inactive (doesn’t work that well) at LOW temperature What is the optimum temperature for this enzyme? How do you know? What is pH? Used to determine the acidity or alkalinity (base) of a solution on a scale on which 7 is neutral, lower values are more acid, and higher values more alkaline (basic) Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity -If pH of the substrate is higher or lower than optimum pH (highest enzyme activity) denaturation happens; enzyme becomes ineffective. -Different enzymes may have different optimum pH’s What pH does pepsin work best? What pH does pancreatic lipase work?