* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
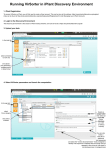
Download iplant collaborative
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Bridging the gap between models and crops A systems approach to understand biological mechanism LHY/ CCA1 PRR7/ PRR9 Y (GI) Rapid method to identify the mutated gene responsible for a trait High throughput sequencing to develop next generation genetic tool for crops TOC1 X Prof Anthony Hall Iplant UK • £2M BBSRC funded project with TGAC, Warwick, Nottingham and Liverpool- Funded as a capital investment • Putting the Iplant system on top of TGAC Hardware, providing community access • Work with the community to ensure take up of the system and develop resources around imaging, systems biology and NGS Liverpool 2 X 18month post-docs, £135K to build iplant node • Liverpool developing workflows NGS around wheat and Arabidopsis • In addition to develop community led workflow around NGS Iplant UK-TGAC-hardware TGAC 2 X 18month post-docs, £1M to build iplant storage and memory node with high speed connection Rob Davey, Erik van den Bergh, Tim Stitt • Build iplant on top of UK infra structure • Assist with building test nodes at regional sites Iplant UK-Liverpool-NGS Liverpool 2 X 18month post-docs, £135K to build iplant node Anthony Hall, Ryan Johnson, Ritesh Kreshna • Update and maintain existing NGS workflows • Liverpool developing workflows NGS around wheat and Arabidopsis. Mapping-by-sequencing; RNA-seq for wheat; de novo assemble for pan-genome and non-reference assembly • In addition to develop community led workflows around NGS Iplant UK-Warwick-System biology Warwick- 2 X 18month post-docs, £135K to build iplant node David Wild, Sam Mason • Converting code to run effectively in iplant ie. Matlab code. • Build systems biology software packages in the iplant environment • Network analysis; promoter analysis tools Iplant UK-Nottingham-image analysis Nottingham - 2 X 18month post-docs, £135K to build iplant node Tony Pridmore • Build root imaging analysis work flows in iPlant • Root phenotyping tool bench Iplant UK-GARNET GARNet- Jim Murray, Ruth Bastow, Geraint Parry • Host future iplant workshops • Produce iplant blog • Articles about using iPlant in GARNISH • Advertise and promote iPlant • Current have 952 registered UK users Diverse collection of germplasm iPlant collaborative Across site/community access to data, data analysis workflows and storage. • • • • • Biomass diversity panel Primary synthetic diversity panel BREAD wheat diversity panel Watkins core collection Mapping populations Transfer x DBW10 and Seri / Babax LIV LAN Epigenetic variation (EWAS) Genome wide Epigenetic variation (INTREPID project) across the Watkins collection will be correlated with phenotypic variation in Photosynthetic efficiency. Output: association of epitype with PS phenotypes PROJECT IMPACT • Informatics tools and a complete dataset in the hands of crop breeders and physiologists • Molecular (KASP-assays) and phenotypic markers for breeding programs • Potentially, genes/pathways as new targets for research and engineering USING NEXT GENERATION GENETIC APPROACHES TO EXPLOIT PHENOTYPIC VARIATION IN PHOTOSYNTHETIC EFFICIENCY TO INCREASE WHEAT YIELD LIV Field phenotypinggenotyping-GWAS • Field phenotyping of 1500 lines using spectral indices and canopy temperature • Genotyping using 12Mb exome capture • GWAS Outputs: ID genomic regions, tail panel conferring enhanced PS LIV LAN Fine phenotyping and BSA • Fine phenotyping of phenotypic tails in the greenhouse and field. • DNA from tails pooled to identify potential genes/marks underlying trait. Output: Physiological description of enhanced P/sin cultivar; identification of linked markers or genes LIV Mapping-by-sequencing Screen mapping populations for specific enhanced PS traits Mapping-by-sequencing pools to identify genes/ markers associated with enhanced PS Output: identification of linked markers or genes