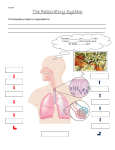
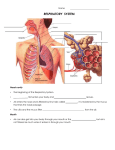
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory
Hemodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Biofluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Alveolar macrophage wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Acute respiratory distress syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Physiology of decompression wikipedia , lookup
Common raven physiology wikipedia , lookup
Circulatory system wikipedia , lookup
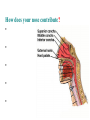
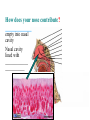
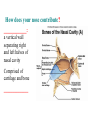
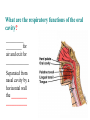
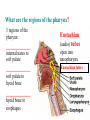
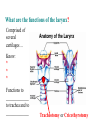
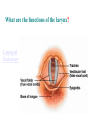
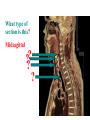
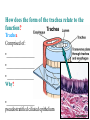
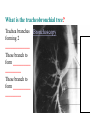
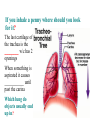
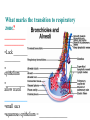
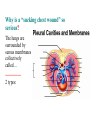
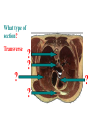
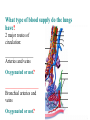
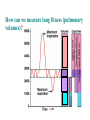
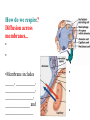
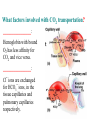
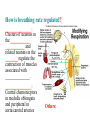
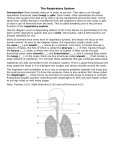
BIOL 2030 Human Anatomy & Physiology II What are the functions of the respiratory system? Major: ________________: •Bring air in and out •Allow gas exchange CO2 O2 N2 Others The mechanical process of moving air in and out ________________: 4 steps… 1) 2) 3) 4) Minor: ____________________ How do we get there from here (anatomy)? * * * * * * * * * Upper Respiratory Tract Lower Respiratory Tract How does your nose contribute? • • • • • How does your nose contribute? _______________ empty into nasal cavity Nasal cavity lined with _____________ ___________ How does your nose contribute? _____________: a vertical wall separating right and left halves of nasal cavity Comprised of cartilage and bone ______________ How does your nose contribute? ___________ Cavities or spaces in bones of skull, empty into the nasal cavity. _________ inflammation of membranes lining sinus cavities What are the respiratory functions of the oral cavity? __________ _________ for air and exit for _____________ Separated from nasal cavity by a horizontal wall the _________ ____________ What are the regions of the pharynx? 3 regions of the pharynx: ______________ internal nares to soft palate ______________ soft palate to hyoid bone ______________ hyoid bone to esophagus Eustachian (audio) tubes open into nasopharynx Eustachian tubes What are the functions of the larynx? Comprised of several cartilages… Know: * * * Functions to _____________ to trachea and to _____________ Tracheotomy or Cricothyrotomy What are the functions of the larynx? Laryngeal Endoscopy What type of section is this? Midsagittal ? ?? ? How does the form of the trachea relate to the function? Trachea Comprised of: •________________ •________________ • _______________ Why? •________________ pseudostratified ciliated epithelium What is the tracheobronchial tree? Trachea branches Bronchoscopy forming 2 ______________ These branch to form __________ _________ These branch to form __________ _________ If you inhale a penny where should you look for it? The last cartilage of the trachea is the _______ w/c has 2 openings When something is aspirated it causes ___________ until past the carina Which lung do objects usually end up in? What marks the transition to respiratory zone? ____________ ___________ •Lack ________ _________ •_____________ epithelium •___________ allow recoil _____________ •small sacs •squamous epithelium = ________________ Are both lungs identical? 2 lungs ___________ larger and 3 lobes ___________ smaller and 2 lobes Each has an: ________ = superior tip ________ = entrance of bronchi, vessels ________ = all the structures entering/exiting the hilum Why is a “sucking chest wound” so serious? The lungs are surrounded by serous membranes collectively called… _________ 2 types: What type of section? Transverse ? ? ? ? ? What type of blood supply do the lungs have? 2 major routes of circulation: ________________ Arteries and veins Oxygenated or not? ___________________ Bronchial arteries and veins Oxygenated or not? How do we ventilate (physics)? General Gas Law: •___________ •___________ •Pleural pressure and ____________ •_________ _________ = volume change necessary to generate pressure How can we measure lung fitness? ____________________ = volume during normal inspiration or expiration ____________________ = forceful inspiration after tidal inspiration ____________________ = forceful expiration after tidal expiration ____________________ = air still remaining after forceful expiration ________________ = sum of tidal, and both reserves ________________ = sum of all volumes How can we measure lung fitness (pulmonary volumes)? How do we respire? Diffusion across membranes... • • •Membrane includes _____, ___________, _________________, ________________, ______________ and ________________ • • • How do we respire? Dalton’s Law… Partial Pressure of gases: The pressure each gas in a mixture of gases contributes to the ______________. 760mmHg (1ATM) mixed = Soda water! What factors affect hemoglobin O2 saturation? •Partial Pressure of O2 PO2 at lungs ~ 104mmHg… usually ~____________ PO2 at tissues ~ 40mmHg… usually ~ ____________ •pH: H+ cause “globins” to change shape… ____________ >pH = _________________ <pH = _________________ Oxygen/Hemoglobin dissociation at rest... Soda water! What factors affect hemoglobin O2 saturation? •Partial Pressure of CO2 also affects because of CO2 becoming H2CO3 >PCO2 = ______________ •Temperature: >temp = ________ •______ produced by erythrocytes as they metabolize glucose binds to hemoglobin… ________________ Oxygen/Hemoglobin dissociation shifting the curve... What factors involved with CO2 transportation? ________________: Hemoglobin with bound O2 has less affinity for CO2 and vice versa. ________________: Cl- ions are exchanged for HCO - ions, in the 3 tissue capillaries and pulmonary capillaries respectively. What effects does CO2 have on respiratory rate? How does this relate to snorkeling? How is breathing rate regulated? _______________: Clusters of neurons in the ___________ ___________ and related neurons in the _______ regulate the contraction of muscles associated with ______________. _______________: Central chemorecptors in medulla oblongata and peripheral in aorta/carotid arteries Others: What is the big picture? *Air moves into respiratory tract via… *Gases are exchanged across the respiratory membrane… How? Where? Why? *O2 in the blood is transported via… Why does it bind in lungs and release in tissues? What affects its transport (saturation)? *CO2 is transported via… Why does it leave the cells (tissues) and enter the blood? Why does it leave the blood and enter the lungs? *Air moves out of the respiratory tract via... What diseases affect the respiratory system? • •Common Cold •Emphysema • • •Whooping cough •Cystic fibrosis • • •Pneumonia •Lung CA • • •Flu •Strep throat • • •Pneumothorax