* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The respiratory system – structure and function
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
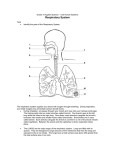
The respiratory system – structure and function • Every cell in our body needs a constant supply of oxygen (O2) and food to maintain life and keep the body operating effectively. • The human respiratory system plays a significant role in human movement. Whether it is short, sharp movements over a limited period of time or repeated movements over a long period of time, the human lungs will have a role to play. • The respiratory system supplies the blood with oxygen through the breathing process. When humans breathe, oxygen (O2) is inhaled and carbon dioxide (CO2) is exhaled. This exchange of gases is the respiratory systems means of getting O2 to the blood. The human respiratory system 1. When we breathe in (inhale) O2 enters the respiratory system through the mouth & nose. 2. The pharynx (throat) is the common passage for the air to the trachea (windpipe) or food pipe (oesophagus). It leads from the nasal cavity to the larynx (voice box). 3. The trachea is a hollow tube kept opened by rings of cartilage. After entering the chest cavity (thorax) the trachea divides into right and left bronchus which lead to the right and left lungs. 4. The bronchus divides further into bronchial tubes which divide into smaller tubes (bronchial) which connect to tiny air sacs (alveoli). The inner lining of the air passages produce mucus to catch and hold dirt and germs. Microscopic hairs (cilia) remove dirt, irritants and mucus through steady, rhythmic movements. Cont. 5. There are 600+ million sponge-like alveoli whose with very thin walls and this is where O2 exchange takes place. Oxygen inhaled into the lung passes through the thin wall of the alveoli and into the blood stream. At the same time poisonous CO2 passes back into the lung through the wall of the alveoli. 6. Control of the breathing action is done by the diaphragm whose job is to help pump CO2 out of the lungs and create space to allow the O2 to flow into the lungs. The efficiency of the respiratory system has a big impact on human performance. Those athletes who display highly efficient lung function will often perform well in endurance sports such as triathlon, soccer, ocean swimming. Circulatory system • What is the role of water in the circulatory system (included with plasma) • Water controls body heat through sweating. If sweating is extreme excessive loss of water from plasma and tissues can decrease blood volume making frequent hydration (replacement of water) necessary.