A Global Model for the Cardiovascular and Respiratory System
... relation which takes into account the initial anaerobic energy supply. Moreover, metabolic autoregulation of the blood vessels is considered by assuming that the systemic vessel resistance depends on the oxygen concentration in venous blood. A dilatation of the pulmonary blood vessels during exercis ...
... relation which takes into account the initial anaerobic energy supply. Moreover, metabolic autoregulation of the blood vessels is considered by assuming that the systemic vessel resistance depends on the oxygen concentration in venous blood. A dilatation of the pulmonary blood vessels during exercis ...
RCP 112 Basic Concepts
... 1. Frictional forces seen with ventilation are due to the anatomical structure of the conductive airways and the tissue viscous resistance of the lungs and adjacent tissues and organs. 2. When the lungs and thorax move during ventilation, the movement and displacement of the lungs, abdominal organs ...
... 1. Frictional forces seen with ventilation are due to the anatomical structure of the conductive airways and the tissue viscous resistance of the lungs and adjacent tissues and organs. 2. When the lungs and thorax move during ventilation, the movement and displacement of the lungs, abdominal organs ...
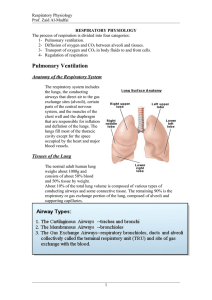
Respiratory physiology
... blood flow. However, the lack of arterioles also compromises the ability of the lung to readily control the distribution of blood flow. Blood flow in the upright lung is distributed preferentially to the lung base because of the influence of gravity. However, the base also receives a greater proport ...
... blood flow. However, the lack of arterioles also compromises the ability of the lung to readily control the distribution of blood flow. Blood flow in the upright lung is distributed preferentially to the lung base because of the influence of gravity. However, the base also receives a greater proport ...
11 Respiratory physiology
... • Pressure and volume are inversely related (if other variables are kept constant.) ...
... • Pressure and volume are inversely related (if other variables are kept constant.) ...
CHAPTER 1 Anatomy and physiology of the human respiratory system
... Number of Alveoli (millions) ...
... Number of Alveoli (millions) ...
Respiratory Physiology
... Thoracic compliance curve transmural pressure cmH2O Large slope of curve middle section, big compliance and small resistance; When lung volume is justo major or justo minor, curve slope become smaller and elastic resistance larger. When lung volume is 67% of total lung capacity, transmural press ...
... Thoracic compliance curve transmural pressure cmH2O Large slope of curve middle section, big compliance and small resistance; When lung volume is justo major or justo minor, curve slope become smaller and elastic resistance larger. When lung volume is 67% of total lung capacity, transmural press ...
O 2
... produce CO2 O2 diffuses from blood to cells; CO2 diffuses from cells to blood Actual amount of O2 and CO2 that is exchanged in any given vascular bed depends on metabolic activity of tissue rate of metabolism exchange All venous blood returns to right atrium 右心房 and mixes together befo ...
... produce CO2 O2 diffuses from blood to cells; CO2 diffuses from cells to blood Actual amount of O2 and CO2 that is exchanged in any given vascular bed depends on metabolic activity of tissue rate of metabolism exchange All venous blood returns to right atrium 右心房 and mixes together befo ...
Respiratory Physio Detailed File
... Basic Properties of Gases: Henry’s Law • When a mixture of gases is in contact with a liquid, each gas will dissolve in the liquid in proportion to its partial pressure • At equilibrium, the partial pressures in the two phases will be equal • The amount of gas that will dissolve in a liquid also de ...
... Basic Properties of Gases: Henry’s Law • When a mixture of gases is in contact with a liquid, each gas will dissolve in the liquid in proportion to its partial pressure • At equilibrium, the partial pressures in the two phases will be equal • The amount of gas that will dissolve in a liquid also de ...
Respiration
... Pulmonary ventilation Gas Diffusion across the respiratory membrane The storage and transport of O2 and CO2. The exchange of dissolved gases ...
... Pulmonary ventilation Gas Diffusion across the respiratory membrane The storage and transport of O2 and CO2. The exchange of dissolved gases ...
B. True or False/Edit
... IV. GAS EXCHANGE IN THE LUNGS Gas exchange between the alveolar air and the blood in pulmonary capillaries results in an increased oxygen concentration and a decreased carbon dioxide concentration in the blood leaving the lungs. This blood enters the systemic arteries, where blood gas measurements a ...
... IV. GAS EXCHANGE IN THE LUNGS Gas exchange between the alveolar air and the blood in pulmonary capillaries results in an increased oxygen concentration and a decreased carbon dioxide concentration in the blood leaving the lungs. This blood enters the systemic arteries, where blood gas measurements a ...
Dear Notetaker:
... - Goal is to provide oxygen to the tissues and to remove carbon dioxide - Four major functions o 1. Pulmonary ventilation (air lungs) o 2. Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between alveoli and blood o 3. Transport of O2 and CO2 in blood to and from cells Focus on this! o 4. Regulation of ventilation Gas T ...
... - Goal is to provide oxygen to the tissues and to remove carbon dioxide - Four major functions o 1. Pulmonary ventilation (air lungs) o 2. Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between alveoli and blood o 3. Transport of O2 and CO2 in blood to and from cells Focus on this! o 4. Regulation of ventilation Gas T ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... ii. Attached to the arytenoid cartilages’ upper ends is a pair of little horns, the corniculate cartilages; the arytenoid and corniculate cartilages function in speech. iii. A pair of cuneiform cartilages supports the soft tissues between the arytenoids and the epiglottis. 5. A group of fibrous liga ...
... ii. Attached to the arytenoid cartilages’ upper ends is a pair of little horns, the corniculate cartilages; the arytenoid and corniculate cartilages function in speech. iii. A pair of cuneiform cartilages supports the soft tissues between the arytenoids and the epiglottis. 5. A group of fibrous liga ...
2002 - reptile respiration and controlled ventilation during anesthesia
... during anesthesia. Traditionally this is accomplished by temporarily occluding the outflow from a T-piece or similar circuit, or by manually compressing a rebreathing bag, resulting in positive pressure ventilation of the patient. Depending on the extent of this intervention, these manual techniques ...
... during anesthesia. Traditionally this is accomplished by temporarily occluding the outflow from a T-piece or similar circuit, or by manually compressing a rebreathing bag, resulting in positive pressure ventilation of the patient. Depending on the extent of this intervention, these manual techniques ...
anatomy and physiology of nitrous oxide
... Concentration effect - higher concentrations cause more rapid uptake of N2O Second gas effect - a second anesthetic gas will also be taken up more rapidly than usual when added to N2O ...
... Concentration effect - higher concentrations cause more rapid uptake of N2O Second gas effect - a second anesthetic gas will also be taken up more rapidly than usual when added to N2O ...
Chapter 16 - Dr. Dorena Rode
... IV. GAS EXCHANGE IN THE LUNGS Gas exchange between the alveolar air and the blood in pulmonary capillaries results in an increased oxygen concentration and a decreased carbon dioxide concentration in the blood leaving the lungs. This blood enters the systemic arteries, where blood gas measurements a ...
... IV. GAS EXCHANGE IN THE LUNGS Gas exchange between the alveolar air and the blood in pulmonary capillaries results in an increased oxygen concentration and a decreased carbon dioxide concentration in the blood leaving the lungs. This blood enters the systemic arteries, where blood gas measurements a ...
Mechanical Ventilation
... lungs – due to physiological shunt (some blood passing through lungs without encountering an air space) ...
... lungs – due to physiological shunt (some blood passing through lungs without encountering an air space) ...
Respiratory - GEOCITIES.ws
... 2. Partial pressure (P) of a gas in air reflects number of molecules present Air contains: ~ 79% N2, ~ 21 % O2 ~ 0.03 % CO2 ~ 0.5 % H2O The partial pressure (= tension) of any gas in air is PBarometric x FIA Diffusion of gases is passive, down partial pressure gradient 3. Partial pressures of gases ...
... 2. Partial pressure (P) of a gas in air reflects number of molecules present Air contains: ~ 79% N2, ~ 21 % O2 ~ 0.03 % CO2 ~ 0.5 % H2O The partial pressure (= tension) of any gas in air is PBarometric x FIA Diffusion of gases is passive, down partial pressure gradient 3. Partial pressures of gases ...
Lab_respiration - Ping Pong
... Note: These factors have been calculated for barometric pressure of 760 mmHg. Since factors at 22oC for example are 1.0904, 1.0910 and 1.0915, respectively, at barometric pressures 770, 760 and 750 mmHg. It is unnecessary to correct for small deviations from standard barometric pressure. ...
... Note: These factors have been calculated for barometric pressure of 760 mmHg. Since factors at 22oC for example are 1.0904, 1.0910 and 1.0915, respectively, at barometric pressures 770, 760 and 750 mmHg. It is unnecessary to correct for small deviations from standard barometric pressure. ...
3. Respiration - Ping Pong
... Note: These factors have been calculated for barometric pressure of 760 mmHg. Since factors at 22oC for example are 1.0904, 1.0910 and 1.0915, respectively, at barometric pressures 770, 760 and 750 mmHg. It is unnecessary to correct for small deviations from standard barometric pressure. ...
... Note: These factors have been calculated for barometric pressure of 760 mmHg. Since factors at 22oC for example are 1.0904, 1.0910 and 1.0915, respectively, at barometric pressures 770, 760 and 750 mmHg. It is unnecessary to correct for small deviations from standard barometric pressure. ...
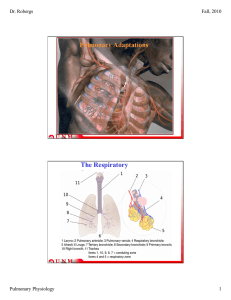
Pulmonary Adaptations The Respiratory System
... The factors that govern the directionality and magnitude of gas diffusion are? ...
... The factors that govern the directionality and magnitude of gas diffusion are? ...
Burns Pulm Lect 1 Physiol 2017
... Gas Exchange • Occurs across “respiratory membrane” • Oxygen and carbon dioxide move between air (gas) and blood (liquid) by simple diffusion • Driving force is partial pressure difference • Dalton’s Law: “Total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of individual partial pressures” ...
... Gas Exchange • Occurs across “respiratory membrane” • Oxygen and carbon dioxide move between air (gas) and blood (liquid) by simple diffusion • Driving force is partial pressure difference • Dalton’s Law: “Total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of individual partial pressures” ...
Respiratory
... ____________________ = forceful expiration after tidal expiration ____________________ = air still remaining after forceful expiration ...
... ____________________ = forceful expiration after tidal expiration ____________________ = air still remaining after forceful expiration ...
2672aLec16
... no cell is more than 2-3 cell diameters from a tracheole Tissues with high metabolism (e.g. flight muscle) may have at least one terminal tracheole penetrating each cell (!) On-tap oxygen in every cell! ...
... no cell is more than 2-3 cell diameters from a tracheole Tissues with high metabolism (e.g. flight muscle) may have at least one terminal tracheole penetrating each cell (!) On-tap oxygen in every cell! ...
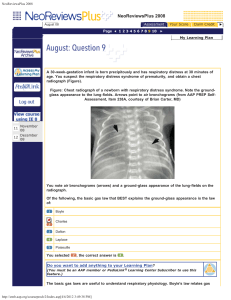
NeoReviewsPlus 2008 - American Academy of Pediatrics
... high surface tension pulling on its surface will close at a higher air pressure than a similar small airway with a low surface tension, as expected by the Laplace law. Pulmonary surfactant serves to lower the surface tension of small airways and keep them patent at low air pressures. A lack of surfa ...
... high surface tension pulling on its surface will close at a higher air pressure than a similar small airway with a low surface tension, as expected by the Laplace law. Pulmonary surfactant serves to lower the surface tension of small airways and keep them patent at low air pressures. A lack of surfa ...