Elementary Steps, the Role of Chemisorbed Oxygen, and the Effects
... (O*) much faster than CH4 with reactive collision probability ratios for CO and CH4 proportional to O2/CO ratios via a constant exceeding 500. Thus, even if CO desorbed before forming CO2, it would oxidize via reactions with O* at any reactor residence time required for detectable CH4 conversion, ma ...
... (O*) much faster than CH4 with reactive collision probability ratios for CO and CH4 proportional to O2/CO ratios via a constant exceeding 500. Thus, even if CO desorbed before forming CO2, it would oxidize via reactions with O* at any reactor residence time required for detectable CH4 conversion, ma ...
ARTICLE Hierarchy of orofacial rhythms revealed through whisking and breathing
... (Fig. 1b). To test whether whisking can also occur without breathing, we applied a puff of ammonia to the snout, which inactivates the central inspiratory drive19 (Supplementary Fig. 1) and temporarily inhibits respiration. Critically, rats can whisk during such a disruption in breathing (Fig. 1b), ...
... (Fig. 1b). To test whether whisking can also occur without breathing, we applied a puff of ammonia to the snout, which inactivates the central inspiratory drive19 (Supplementary Fig. 1) and temporarily inhibits respiration. Critically, rats can whisk during such a disruption in breathing (Fig. 1b), ...
A Global Model for the Cardiovascular and Respiratory System
... this type see, e.g., Noordergraaf [50] or Swan [66]. A comprehensive discussion of the control mechanisms in the human cardiovascular system is given in Guyton [17] or Rowell [60]. Models dealing with the regulation of breathing date back to the beginning of this century (Haldane and Priestley [18]) ...
... this type see, e.g., Noordergraaf [50] or Swan [66]. A comprehensive discussion of the control mechanisms in the human cardiovascular system is given in Guyton [17] or Rowell [60]. Models dealing with the regulation of breathing date back to the beginning of this century (Haldane and Priestley [18]) ...
Physiology Ch 19 p213-228 [4-25
... of accepted normal pressure -a mean arterial pressure of >110mmHg (normal is 90mmHg) is considered hypertensive -this level of mean pressure occurs when diastolic is >90 and systolic is >135mmHg -in SEVERE hypertension, mean arterial pressure can rise to 150-170mmHg with diastolic as high as 130mmHg ...
... of accepted normal pressure -a mean arterial pressure of >110mmHg (normal is 90mmHg) is considered hypertensive -this level of mean pressure occurs when diastolic is >90 and systolic is >135mmHg -in SEVERE hypertension, mean arterial pressure can rise to 150-170mmHg with diastolic as high as 130mmHg ...
Diffusion, Blood O2, CO2 Content and Transport
... the hemoglobin-oxygen saturation and thus the O2 blood content is influenced by the blood PCO2/pH. The Haldane effect on the other hand (or the other Hb hand) states that the CO2 content in blood is affected by the amount of oxygen dissolved in blood or the PO2. Carbon dioxide physiologically is mor ...
... the hemoglobin-oxygen saturation and thus the O2 blood content is influenced by the blood PCO2/pH. The Haldane effect on the other hand (or the other Hb hand) states that the CO2 content in blood is affected by the amount of oxygen dissolved in blood or the PO2. Carbon dioxide physiologically is mor ...
Oxygen transport through La,_,Sr,FeO,_, membranes. I. Permeation
... Oxygen diffusion through the bulk may be modelled using Wagner theory [El, provided that sufficient literature data are available on the defect chemistry or conductivity parameters of the material under consideration. The La, _ .Sr,FeO, _ s solid solution system (0 G x G 1) has been studied extensiv ...
... Oxygen diffusion through the bulk may be modelled using Wagner theory [El, provided that sufficient literature data are available on the defect chemistry or conductivity parameters of the material under consideration. The La, _ .Sr,FeO, _ s solid solution system (0 G x G 1) has been studied extensiv ...
HYPOXIA (Dombrovský P., Rácz O.
... The basic symptom of chronically developing hypoxia is cyanosis. It is a term for blue or bluish colouring of skin, mucosae or even of the inner organs. It occurs when the concentration of reduced hemoglobin in capillary blood reaches 50 g/l. One can observe it most conveniently on the nail bed, on ...
... The basic symptom of chronically developing hypoxia is cyanosis. It is a term for blue or bluish colouring of skin, mucosae or even of the inner organs. It occurs when the concentration of reduced hemoglobin in capillary blood reaches 50 g/l. One can observe it most conveniently on the nail bed, on ...
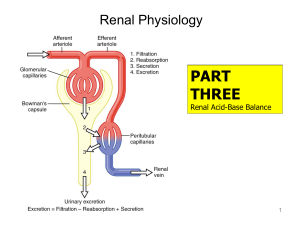
18 Renal Acid-Base Balance
... carbon dioxide back in after breathing it out. • For severe cases, need to replace the water and electrolytes (sodium and potassium). ...
... carbon dioxide back in after breathing it out. • For severe cases, need to replace the water and electrolytes (sodium and potassium). ...
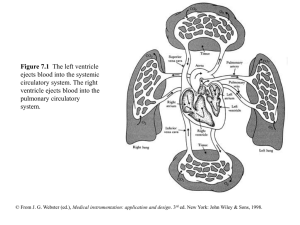
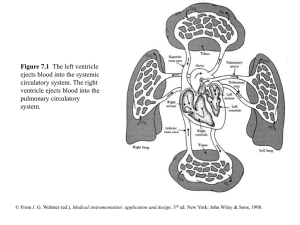
chapter07
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
Figure 1.1 Generalized instrumentation system The sensor
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
Chapter 14 Regulation of Breathing
... inhibitory signals to DRG, stopping further inspiration. • In adults active only on large VT (>800 ml) • Regulates rate and depth of breathing during moderate to strenuous exercise ...
... inhibitory signals to DRG, stopping further inspiration. • In adults active only on large VT (>800 ml) • Regulates rate and depth of breathing during moderate to strenuous exercise ...
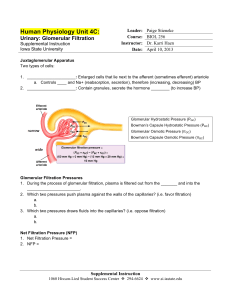
Bio 256 Unit 4C - Iowa State University
... Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Two types of cells: 1. _____________________: Enlarged cells that lie next to the afferent (sometimes efferent) arteriole a. Controls ____ and Na+ (reabsorption, secretion), therefore (increasing, decreasing) BP 2. _____________________: Contain granules, secrete the hormon ...
... Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Two types of cells: 1. _____________________: Enlarged cells that lie next to the afferent (sometimes efferent) arteriole a. Controls ____ and Na+ (reabsorption, secretion), therefore (increasing, decreasing) BP 2. _____________________: Contain granules, secrete the hormon ...
Control of Respiration - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... 30. (Page 8.) In each of these blanks, put "increase(s)" or "decrease(s)": If the arterial PCO2 increases, there is a(an) a. _______ in the PCO2 in the fourth ventricle. This causes a(an) b. ________ in hydrogen ions in the cerebrospinal fluid, which c. ___________ the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid. ...
... 30. (Page 8.) In each of these blanks, put "increase(s)" or "decrease(s)": If the arterial PCO2 increases, there is a(an) a. _______ in the PCO2 in the fourth ventricle. This causes a(an) b. ________ in hydrogen ions in the cerebrospinal fluid, which c. ___________ the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid. ...
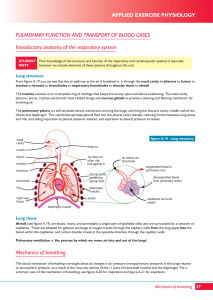
AQAAS_ch2 Resp.system
... Lung structure From figure A.19 you can see that the air pathway as the air is breathed in, is through the nasal cavity to pharynx to larynx to trachea to bronchi to bronchioles to respiratory bronchioles to alveolar ducts to alveoli. The trachea consists of an incomplete ring of cartilage that keep ...
... Lung structure From figure A.19 you can see that the air pathway as the air is breathed in, is through the nasal cavity to pharynx to larynx to trachea to bronchi to bronchioles to respiratory bronchioles to alveolar ducts to alveoli. The trachea consists of an incomplete ring of cartilage that keep ...
Blood Pressure and Pulse BIOL 204, Section 550 Lab Report By
... also able to recover faster than the poor conditioned subject, showing a lower heart rate and blood pressure after two minutes (from 92 bpm and 130/80 mmHg immediately following exercise to 75 bpm and 100/68 mmHg two minutes after exercise). The poorly conditioned subject’s heart rate took the full ...
... also able to recover faster than the poor conditioned subject, showing a lower heart rate and blood pressure after two minutes (from 92 bpm and 130/80 mmHg immediately following exercise to 75 bpm and 100/68 mmHg two minutes after exercise). The poorly conditioned subject’s heart rate took the full ...
Respiratory System
... This affects the way that the immune systems in today's young children develop during very early childhood, and it may increase their risk for atopy and asthma. This is especially true for children who have close family members with one or both of these conditions. ...
... This affects the way that the immune systems in today's young children develop during very early childhood, and it may increase their risk for atopy and asthma. This is especially true for children who have close family members with one or both of these conditions. ...
1 FORM W KEY deducted if you fail to do this!!!!!!
... 18. Reabsoprtion of water in the proximal tubules a) Is a Na+ dependent passive process b) Is a Na+ dependent active process c) Occurs because water osmotically follows Na+ from the tubule to the interstitial fluid d) Both a and c are true e) Both b and c are true 19. Anakin Skywalker, from the pla ...
... 18. Reabsoprtion of water in the proximal tubules a) Is a Na+ dependent passive process b) Is a Na+ dependent active process c) Occurs because water osmotically follows Na+ from the tubule to the interstitial fluid d) Both a and c are true e) Both b and c are true 19. Anakin Skywalker, from the pla ...
Gases - HCC Learning Web
... • Temperature is related to their average kinetic. • Individual molecules can have different speeds of motion. • The figure shows three different speeds: ump is the most probable speed (most molecules are this fast). uav is the average speed of the molecules. urms, the root-mean-square speed, ...
... • Temperature is related to their average kinetic. • Individual molecules can have different speeds of motion. • The figure shows three different speeds: ump is the most probable speed (most molecules are this fast). uav is the average speed of the molecules. urms, the root-mean-square speed, ...
Materials
... release some bubbles and rise with them. If you watch carefully, you can see them expand as the pressure decreases. Exercises Two water pipes, of the same diameter, go from the top of a building to the bottom. One is zig-zag while the other is straight. When filled, which one will have higher wate ...
... release some bubbles and rise with them. If you watch carefully, you can see them expand as the pressure decreases. Exercises Two water pipes, of the same diameter, go from the top of a building to the bottom. One is zig-zag while the other is straight. When filled, which one will have higher wate ...
Developer Notes
... Blood in your body works the same way. Since the pressure in a fluid varies with depth, blood in the lower body has a higher pressure than in the upper body. Blood pressure is usually measured at the same level as the heart in order to measure the pressure of the blood leaving the heart. Many other ...
... Blood in your body works the same way. Since the pressure in a fluid varies with depth, blood in the lower body has a higher pressure than in the upper body. Blood pressure is usually measured at the same level as the heart in order to measure the pressure of the blood leaving the heart. Many other ...
Diastolic pressure
... • Caused by suspended blood proteins that are too large to cross capillary walls ...
... • Caused by suspended blood proteins that are too large to cross capillary walls ...
01 Mills
... which stimulates the central chemoreceptors. If PaCO2 is maintained at abnormal values for several days, CSF pH is restored to normal by changes in CSF bicarbonate. Sleep affects the changes which would normally be produced by the action of the chemoreceptors on the medulla, allowing PaCO2 to rise b ...
... which stimulates the central chemoreceptors. If PaCO2 is maintained at abnormal values for several days, CSF pH is restored to normal by changes in CSF bicarbonate. Sleep affects the changes which would normally be produced by the action of the chemoreceptors on the medulla, allowing PaCO2 to rise b ...
19 Comp Review 3b
... The alveoli have broken, leaving spaces where gas exchange cannot take place. Compliance decreases, so It is difficult to expel the air in the lungs. Each inhalation is a forced inspiration also. When the ribs are continually raised with each breath, they eventually remain in the upright position, c ...
... The alveoli have broken, leaving spaces where gas exchange cannot take place. Compliance decreases, so It is difficult to expel the air in the lungs. Each inhalation is a forced inspiration also. When the ribs are continually raised with each breath, they eventually remain in the upright position, c ...