* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Study Guide
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
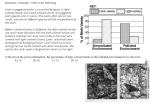
Final Exam Study Guide Be able to answer the following question: 1. From which labeled structure in the figure above is structure D made? A 2. Identify what structure D is in the figure above. mRNA 3. Predict what would happen to structure F if structure C was deleted. The base sequence of the codon would change from GCU to GUG 4. Predict what effect the deletion of structure C would have on the process that occurs during step Y. A frameshift mutation would occur, causing the amino acids after the deletion to change 5. DNA can best be compared to a(n)? A twisted ladder 6. The order of nitrogen bases in DNA determines the order of ________ in proteins? Amino acids 7. Genes are a segment of ____ that code for ____? DNA/trait 8. What are the nucleotides found in DNA? Deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine 9. The overall structure of DNA can be described as? Double helix or two strands that are twisted 10. Explain the process of translation. The ribosomes use information from mRNA to produce proteins 11. Why is crossing over an important event in meiosis? It creates new combinations of genes 12. Explain why it is important for gametes to have half the number of regular chromosomes. Gametes only have ½ of the number of chromosomes so when two gametes come together the new organism has the exact number of chromosmes needed for the new organism’s genetic makeup 13. Crossing a snapdragon that has red flowers with one that has white flowers produces a snapdragon that has pink flowers. The trait for flower color exhibits? Incomplete dominance 14. Understand the difference between homozygous and heterozygous and be able to do punnet squares and answer questions about them. 15. Cancer is a disease in which some cells lose the ability to control their? Rate of division 16. What does a cell do to prepare to divide? Replicate all of its DNA 17. The traits of populations in the forest ecosystem have changed over time. What caused the traits to change? Natural selection 18. Which scientific evidence would show that two species of birds are closely related? The two bird species have similar DNA sequences 19. What is a major concept included in Lamarck’s theory of evolution? Body structure can change according to the actions of the organism 20. Directional selection occurs when? The organisms on one extreme of the population have a better chance to survive than those on the other extremes 21. Greater than 2 cm or less than 2 cm 22. Directional, stabilizing and disruptive 23. Survive, reproduce and pass on genes 24. Possession of inherited adaptations that maximize fitness 25. Fossils, homologous structures, vestigial structures 26. Graph 27. Light 28. Dark 29. The percent of light colored moths captured dropped significantly from ~ 100 moths to almost zero moths, while the dark colored moths increased from near zero to ~ 100 percent 30. Dark moths 31. The moth population changed from light to dark moths because the dark moths were able to blend into the environment and therefore survive and reproduce passing on its genes to the next generation 32. Any living thing. 33. Ex: plants, animals, micro bacteria 34. Any non-living thing 35. Ex: water, wind, sunlight, soil 36. The study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment 37. Habitat 38. Population 39. Polar zone, temperate zone, and tropical zone\ 40. A land oriented biome (tropical rainforest, desert, temperate deciduous forest) 41. A water oriented biome (oceans, estuaries, and rivers) 42. Organisms living in the same community competing for limited recourses 43. An organism that eats another organism 44. The organism that gets eaten by the predator 45. Producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer 46. Decomposers 47. Picture 48. Blank 49. Disk soaked in distilled water 50. Some antibiotics are more effective at controlling one species of bacteria than another 51. Antibiotic 2