* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download kexborough primary school - Wilthorpe Primary School
Survey
Document related concepts
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
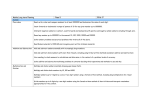
Town Centre Collaboration Primary Long Term Maths Planning Foundation Stage 2 to Year 6 TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Foundation Stage Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Number Recognise some numerals of personal significance Count forwards and backwards to at least 10. Begin to count forwards and backwards beyond 10. Recognise and name numbers to at least 10. Place numbers in order, 0 – 10 Accurately count out number groups to at least 10 Count actions or objects that can’t be moved to at least 10 Begin to count out irregular arrangements of objects to at least 5. Begin to estimate and check by counting groups to at least 10. In practical activities (counting, number rhymes and songs) and discussion begin to use the vocabulary used in addition and subtraction. To begin to record using marks they can interpret and explain. Measurement and Geometry To describe their relative position such as ‘behind’ or next to’ To use everyday language to talk about size, compare objects and solve related problems Number Count forwards and backwards to 20. Begin to recognise numbers to 20. Begin to order numbers 0 to 20 To begin to use the language of more, fewer and the same when comparing sets of objects. To begin to say which number is 1 more, 1 less than a given number up to at least 5. To find one more or one less from a group of at least 5 objects. In practical activities (counting, number rhymes and songs) and discussion begin to use the vocabulary used in addition and subtraction. To begin to record using marks they can interpret and explain. Measurement and Geometry To use everyday language related to time and money TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Foundation Stage Spring 1 Number Count forwards and backwards to 20 and beyond. Begin to recognise numbers to 20 and beyond. Begin to order numbers 0 to 20 and beyond. To use the language of more, fewer and the same when comparing sets of objects. To say which number is 1 more, 1 less than a given number up to at least 5. To find one more or one less from a group of at least 10 objects. To begin to find the total number of items in 2 groups by counting all of them. In practical activities (counting, number rhymes and songs) and discussion begin to use the vocabulary used in addition and subtraction. To begin to record using marks they can interpret and explain. Measurement and Geometry To begin to use mathematical names for ‘Flat 2D shapes’ and ‘Solid 3D shapes’ To use mathematical terms and describe shapes. To select a particular named shape Children to use everyday language to talk about size and weight, to compare objects and to solve problems. Spring 2 Number To consolidate knowledge and understanding of numbers 0 to 20 by: Counting forwards and backwards to 20 and beyond. Recognising numbers to 20 and beyond. Ordering numbers 0 to 20 and beyond. Using the language of more, fewer and the same when comparing sets of objects. Saying which number is at least 1 more, 1 less than a given number up to at least 5. Finding at least one more or one less from a group of at least 10 objects. Finding the total number of items in 2 groups by counting all of them. In practical activities (counting, number rhymes and songs) and discussion begin to use the vocabulary used in addition and subtraction. To begin to record using marks they can interpret and explain. Measurement and Geometry To use familiar objects and common shapes to create and recreate patterns and build models. To use everyday language related to time. To measure short periods of time in simple ways. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Foundation Stage Summer 1 Number To count forwards to 100 and beyond. To begin to count in 2s, 5, and 10s To recognise numbers to 20 and beyond. Ordering numbers 0 to 20 and beyond. To begin to add and subtract 2 single digit numbers and count on or back to find the answer. To use everyday language to compare quantities and objects and solve practical problems. To identify own mathematical problems based on interest and fascination. In practical activities (counting, number rhymes and songs) and discussion begin to use the vocabulary used in addition and subtraction. To begin to record using marks they can interpret and explain. Measurement and Geometry To use every language related to time. To measure short periods of time in simple ways. Summer 2 Number: To consolidate all the following: To count forwards to 100 and beyond. To begin to count in 2s, 5, and 10s To recognise numbers to 20 and beyond. Ordering numbers 0 to 20 and beyond. To begin to add and subtract 2 single digit numbers and count on or back to find the answer. To use everyday language to compare quantities and objects and solve practical problems. To identify own mathematical problems based on interest and fascination. In practical activities (counting, number rhymes and songs) and discussion begin to use the vocabulary used in addition and subtraction. To begin to record using marks they can interpret and explain. Measurement and Geometry To use everyday language related to money. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 1 Autumn 1 Count reliably at least 20 objects. Estimate a number of objects that can be checked by counting. Read & write 0-20 & beyond, use knowledge of place value to position on a number line. Counting on or back in 1s, 2s & 10s. Introduce to odds & evens, doubles & halves. Say a number that is 1 more or less than any given number. Relate addition to counting on and subtraction to counting back. Use practical & informal written methods for addition of 1-digit numbers. Practical & informal oral methods to subtract a 1-digit number from a 2-digit number. Begin to use the vocabulary related to addition & subtraction and begin to use +, -, = to describe & record number sentences. Recognise & recall number bonds to 10. Derive & recall pairs of numbers to 5+5 & corresponding subtraction facts. Eg 2+3=5, 5-3=2. Solving problems involving counting, adding & doubling in the context of money. Distinguish between & use ordinal & cardinal numbers (used daily in context. Eg lining up). ICT Link Answering a question by recording information in lists & tables & presenting using pictures, block graphs or pictograms. Length vocabulary: non-standard measures. Autumn 2 Addition & subtraction factors to 5. Compare describe and solve practical problems for length (long, short, longer, shorter, tall, short, double, half) weight (heavy, light, heavier than, lighter than) & capacity (full, empty, more than, less than, half, half full, quarter)using non-standard methods. Use diagrams to sort objects into groups, record to given criteria. Recognise and know the value of different denominations of coins and notes. Counting, adding, subtracting in the context of money to ‘pay’ & measures. Addition patterns – revision of number bonds. Use the vocabulary of halves & quarters in context. Revise doubling & introduce halving of numbers & shape. Time sequencing events chronologically: o’clock & introduce to half past. Draw the hands on a clock face to show these times. Recognise and use language relating to dates, including days of the week, weeks, months and years. Recognise and name common 2D and 3D shapes including 2D shapes e.g. rectangles, squares, circles, triangles 3D shapes e.g. cubes, cuboids, pyramids and spheres Use positional language e.g. on top of, left, right, below TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 1 Spring 1 Relate addition to counting on in the context of 3, 1-digit numbers. Use practical & informal written methods. Introduce 2-digit numbers. Place value – missing numbers, blank number tracks (partitioning TU). Identify and represent numbers using objects and pictorial representations including the number line, and use language of equal to, more than, less than, fewer, most least Say the number 1 more or 1 less, recap & relate to subtraction of a 1 or 2-digit number from a 1 or 2-digit number. Use formal written method (number sentence). Add and subtract 1 digit and 2 digit numbers to 20 including zero. Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. Repeat with 10 more/less. Represent and use number bonds and related subtraction facts within 20. Solve one-step problems involving counting, adding & subtracting using concrete objects and pictorial representations and missing number problems such as 7 = ( ) - 5 Doubling in the context of number & money, for example to pay & give change (number bonds to 20 & 100). ICT Link: Data handling – sorting objects into groups according to given criteria & representing as pictograms & block graphs. Spring 2 Measure and begin to record the following: lengths and heights; mass and weight; capacity and volume. Find different ways of making at least 10p. Use different coins to make different amounts up to 20p. Give change from at least 10p/20p. Money – extend to 15p & 20p using least amount of coins. Relate to money using addition & subtraction to ‘pay’ & ‘give change’. Doubles & near doubles. Revisit fractions of shapes to include ¼ & ¾. Use vocabulary of halves & quarters. Sharing in a practical context into groups of 2s, 3s, 5s. Revise doubling, introduce halving as the reverse. Recognise, find and name a half as one of two equal parts of an object, shape or quantity. Describe position, direction and movement including whole, half, quarter and three quarter turns (Bee-bot) Time – o’clock & half past. Time measurements – hours, minutes, seconds – what can we do in a minute/sec? Use vocabulary related to subtraction. Counting in multiples of 1, 2, 5, 10 backwards & forwards. Recap odd & even numbers. Counting in & recognising multiples of 5. Introduce mathematical symbols x and ÷. 2&3D shape naming & repeating patterns. Recap properties. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 1 Summer 1 Count to and across 100 forwards and backwards to or from any given number Read and write numbers to 100 in numerals. Read and write numbers from 1 to 20 in words. Ordering numbers from smallest to largest. Recap 1/10 more & less. Recap tens & units (value of 2-digit numbers). Compliments to 20. 10 more / 10 less. Formal written additions / subtractions & identifying patterns. Using known facts. Eg 4+5=9, 95=4 to predict unknown numbers. Recap representing and using number bonds and related subtraction facts within 20. Recap doubles to 20. Addition with 2-digit & 1-digit & language of place value. Putting addition into written problem solving activities> Using pattern to predict (place value). Eg. 4+5=9, 14+5=19. Addition & subtraction with 2-digit & 1-digit (multiple of 10 from a 2digit number). Introduce x & ÷ in practical contexts. Symmetry in both regular / irregular shapes. Recap properties & names of 2D & 3D shapes. Introduce to Venn Diagrams & relate to properties of shape. Weighing / length / capacity using standard units. Introduce to cm/m/g/kg/ml/l. Summer 2 Introduce standard units of measure – including g/kg/cm/m/ml/l. Counting on & backwards in 2s, 5s & 10s. Recap on o’clock, half past. Begin to tell the time to quarter past & quarter to and draw the hands on a clock face. Recap position, direction and movement including whole, half, quarter and three quarter turns (Bee-bot) Addition of 3 numbers in the context of money. Doubles up to 15. Halving numbers in problems. Recognise, find and name a quarter as one of four equal parts of an object, shape or quantity. Recap 1 more / 1 less / 10 more / 10 less. Solve one step problems involving multiplication and division by calculating the answer using concrete objects, pictorial representations and arrays with the support of teacher. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 2 Autumn 1 Count in steps of 2, 3 and 5 from zero. Count in tens from any number forwards and backwards. Mentally recall and use multiplication and division facts from 2, 3, 5, 10 multiplication tables (Ongoing throughout year) Place value up to 3-digit numbers – including 0 as a place holder & partitioning. Add mentally a 1-digit number or a multiple of 10. Rounding nos to the nearest 10 / 100. Ordering numbers & position on a number line. Eg 2s, 5s, 10s. Use < & >, number sequences increasing & decreasing. Read & write numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in words. Odd & even number recap. Sequences to include counting in 3s. Identify and describe properties of 2D shapes including the number of sides. Identify and describe the properties of 3D shapes including the number of edges, vertices and faces. Compare and sort, common 2D and 3D shapes and everyday objects. (Venn & Carroll diagrams). Adding multiples of 10, including doubles & corresponding halves. Mental & informal written methods. Recall and use addition and subtraction facts fluently to 20 and related facts to 100 (multiples of 10) Adding in 2’s, 5’s and 10’s by grouping. Add & subtract mentally TU-U & TU-multiples of 10. Money recap – value of coins/notes & recognition. Combine coins/notes to make a particular value using £ & p. Throughout half term link objectives to solving problems in real-life contexts. Autumn 2 Add 3, 1 digit numbers Adding 2, 2 digit numbers Mentally recall and use multiplication and division facts from 2, 3, 5, 10 multiplication tables (Ongoing throughout year) Time to the hour, half-past, quarter-past & quarter-to on analogue & digital clocks including problem solving. Recap of months of the year / days of the week / seasons. Choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure to the nearest appropriate unit using rulers: length and height in any direction (m/cm) Compare and order lengths using more >/less </= Accurately measuring & drawing lines. Rounding to nearest cm or ½ cm. Use informal written methods to add & subtract 2-digit numbers (partitioning). Subtraction as the inverse of addition & related + & - number sentences. Use this to check calculations and solve missing number problems Recall all + & - facts for each number up to 20. Use place value and number facts to solve problems. Doubling & halving up to 20. Interpret and construct simple pictograms, tally charts, block diagrams and simple tables. Ask and answer simple questions by counting the number of objects in each category and sorting categories by quantity Throughout half term link objectives to solving problems in real-life contexts. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 2 Spring 1 Rounding to the nearest 10/100. (revisit) Mentally recall and use multiplication and division facts from 2, 3, 5, 10 multiplication tables (Ongoing throughout year) Introduce multiplication of 2s, 5s, 10s as repeated addition (x2 is the same as doubling). Higher ability formal written method. Calculate mathematical statements for multiplication and division within the multiplication tables and write them using the multiplication x and division ÷ and equals = sign. Demonstrating communativity of addition and multiplication Time – recapping quarter past/to. Seconds/minutes/hours/days. Introduce to the nearest 5 minutes (where appropriate) Order and arrange combinations of mathematical objects in patterns and sequences Use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction and movement including movement in a straight line and distinguishing between rotation as a turn and in terms of right angles for quarter, half and three quarter turns (clockwise/ anticlockwise) 2D shape – recognising right angles and lines of symmetry. 3D shape – properties, visualize, identify & sort, including edges, vertices & faces. Identify 2D shapes on the surface of 3D shapes (for example a circle on a cylinder and a triangle on a pyramid (nets)) Division as sharing & repeated subtraction. The relationship between ÷ & x. Multiplication facts for 2, 5, 10 times tables & related division facts. Formal written methods as number sentences. Use x & ÷ signs to read & write number statements. Solve problems involving multiplication and division, using materials, arrays, repeated addition, mental methods, and multiplication and division facts, including problems in context. Spring 2 Mentally recall and use multiplication and division facts from 2, 3, 5, 10 multiplication tables (Ongoing throughout year) Find different combinations of coins that equal the same amount of money. Solving problems with addition and subtractions using concrete objects and pictorial representations including those involving numbers, quantities and measures and money, including giving change. Children to apply their increasing knowledge of mental and written methods. Choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure to the nearest appropriate unit using scales: mass (kg) (g) / capacity (l and ml) Compare and order mass, volume and capacity using more >/less </= Choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure to the nearest appropriate unit using thermometers: temperature in degrees celsius Compare and order lengths using more >/less </= Fractions of 2D shapes: 1/2s, 1/4s & 1/3s. Count in 1/2s & 1/4s to 10. Fractions of a small number of objects/quantities and shapes and length. Write simple fractions for example, half of 6 = 3 and recognise the equivalence of 2/4 and 1/2. Tell and write the time to 5 minutes including quarter past/ to the hour and draw the hands on a clock face to show these times. Know the number of minutes in an hour and number of hours in a day. Throughout half term link objectives to solving problems in real-life contexts. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 2 Summer 1 Mentally recall and use multiplication and division facts from 2, 3, 5, 10 multiplication tables (Ongoing throughout year) Make comparisons using < > = symbols from 0 to 100. Recap Interpreting and constructing simple pictograms, tally charts, block diagrams and simple tables. Ask and answer questions about totalling and comparing categorical data. (Link to addition and subtraction problems) Revisit R for formal addition & subtraction, multiplication & division in context of problem solving. REVISION SATS Summer 2 Capacity using standard units – ml & l. Compare and sequence intervals of time. To present solutions to problems in an organised way to explain decisions, methods & results in a pictorial, spoken & written way. Solving problems using subtraction Use standard measures to record temperatures. Throughout half term link objectives to solving problems in real-life contexts. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 3 Autumn 1 Mental Objective Counting on from & back to 0 in single digit steps & multiples of 10, 50 & 100. Number bonds to 20 Derive & recall multiplication & associated division facts for 2, 5 & 10 times tables. Add & subtract mentally 3+1, 3+2 and 3+3 digit numbers. Doubles and halves to at least 20 Counting on from & back to 0 in single digit steps & multiples of 10, 50 & 100. Partition and recognise the place value of each digit in at least 3-digit numbers. Reading, writing, ordering whole numbers to 1000 & positioning on a number line. Rounding 2 & 3-digit numbers to the nearest 10/100. Multiply & divide one & two-digit numbers by 10/100 & relate to place value (including decimal notation) – progressing to formal written method if appropriate. Counting in tenths with decimals (link to place value) Recognise that tenths arise from dividing into ten equal parts (1÷10) Derive & recall all addition & subtraction facts for each number to 50, sums & differences of multiples of 10 & number pairs to 100. Doubling & introduce doubling & doubling again (x 4) & halving mentally up to 20. Add & subtract mentally 3+1, 3+2 and 3+3digit numbers. Derive & recall multiplication & associated division facts for 2, 5 & 10 times tables. Recap 2D shape & their properties. Introduce using a set square to draw a rightangle & identify right-angles in 2D shapes. Draw & make the shapes. Recognise angles as a property of shape or a description of a turn Recognise that a straight line is equal to 2 right-angles, 3 make ¾ turn & a full turn 4 right-angles. Autumn 2 Mental Objective Rounding 2 & 3-digit numbers to the nearest 10/100. Partition and recognise the place value of each digit in at least 3-digit numbers. Multiply & divide one & two-digit numbers by 10/100 & relate to place value (including decimal notation). Derive & recall multiplication & associated division facts for 2, 5 & 10 times tables. Add & subtract mentally 3+1, 3+2 & 3+3 digit numbers. Derive & recall all addition & subtraction facts for each number to 100, sums & differences of multiples of 10 & number pairs to 100. Develop written methods for addition of 2 & 3-digit numbers (column method). Add and subtract amounts of money to solve 1 & 2 step problems involving money using both £ and p in practical contexts. Derive & recall multiplication facts for 2, 3, 4 & 8 times tables. Link to doubling & associated division facts. Recap vocabulary of time: seconds/minutes/hours/days/weeks/ months/years/leap year, am, pm, morning, afternoon , evening, noon, midnight Recap telling the time – o’clock, half-past, quarter-past, quarter-to & to nearest minute on an analogue clock. Develop written method for subtraction of 2 & 3-digit numbers. Solve 1 & 2 step problems involving numbers & money using addition & subtraction. Using inverses or knowledge of doubling & halving to check calculations. Shape. Relate to the 4 compass directions – relate to more/less than a right-angle. Draw & complete shapes with reflective symmetry. Draw the reflection of a shape in a mirror line. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 3 Spring 1 Mental Objective Rounding 2 & 3-digit numbers to the nearest 10/100. Partition and recognise the place value of each digit in at least 3-digit numbers. Multiply & divide one & two-digit numbers by 10/100 & relate to place value (including decimal notation). Derive & recall multiplication & associated division facts for 2, 5 & 10 times tables. Add & subtract mentally 3+1, 3+2 & 3+3 digit numbers. Derive & recall all addition & subtraction facts for each number to 100, sums & differences of multiples of 10 & number pairs to 100. Adding tens or hundreds to 3 digit numbers Doubles and halves to 100 linking to the inverse (Using inverses or knowledge of doubling & halving to check calculations.) Use practical & informal written methods to multiply & divide 2-digit numbers by a 1-digit number. Eg 13x3. Relate to simple multiplication/division problems. Eg 6 pencils at 15p. Measures – length: estimating, measuring & recording measurements. Reinforce relationships between mm-cm-m-km. Measures – length: choosing, measuring, comparing, adding, subtracting & using appropriate units of measurement related to practical activities, estimating & recording. Solve one & two step problems involving number & measures (lengths). 12 hour digital clock. Time – Read, compare and calculate time intervals using a number line & find start or end times for a given time interval to the nearest minute if appropriate. Use practical & informal written methods to divide 2-digit numbers. Eg 50÷4. Round remainders up or down, depending on the context. Derive multiplication & division facts for 3, 4 & 8 times tables using doubling & halving. Spring 2 Mental Objective Rounding 2 & 3-digit numbers to the nearest 10/100. Partition and recognise the place value of each digit in at least 3-digit numbers. Multiply & divide one & two-digit numbers by 10/100 & relate to place value (including decimal notation). Derive multiplication & division facts for 4 & 8 times tables using doubling & halving. Add & subtract mentally 3+1, 3+2 & 3+3 digit numbers. Derive & recall all addition & subtraction facts for each number to 100, sums & differences of multiples of 10 & number pairs to 100. Doubles and halves to 100 linking to the inverse (Using inverses or knowledge of doubling & halving to check calculations.) Use of vocabulary such as equal , more than, less than, fewer etc _______________________________________________________________ Recap halves as 2 equal parts. Introduce denominator as a number of parts: 1/3s, 1/4s, 1/5s. Compare & order fractions with a common denominator. Identify & estimate fractions of shapes. Recognise fractions which are equivalent to 1 & pairs of fractions that add up to 1. Recognise, show and perform calculations of fractions with the same denominator. Eg 1/7+5/7=6/7 Recognise, find and write unit fractions of numbers & quantities. Eg ½, 1/3, ¼, 1/6. Identify questions. Present & interpret data in frequency tables, pictograms & bar charts using different scales. Follow a line of enquiry. Make & use lists, tables, tally charts & graphs to organise & interpret information. Introduce 24 hour digital clock (recap 12 hour digital clock). Problems related to time (using number lines) for passage of times & time intervals. Tell time to the nearest minute, including 24 hour clock and using roman numerals (where appropriate!!!) Know the number of seconds in a minute and the number of days in each month, year and leap year Measures – weight: choosing, measuring, comparing, adding, subtracting & using appropriate units of measurements related to practical activities. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 3 Summer 1 Summer 2 Mental Objective Mental Objective Rounding 2 & 3-digit numbers to the nearest 1000. Counting and rounding numerals up to a hundred Partition and recognise the place value of each digit in at least 3-digit Rounding 2 & 3-digit numbers to the nearest 1000. numbers. Partition and recognise the place value of each digit in at least 3-digit Multiply & divide one & two-digit numbers by 10/100 & relate to numbers. place value (including decimal notation). Multiply & divide one & two-digit numbers by 10/100 & relate to Derive multiplication & division facts for 4 & 8 times tables using place value (including decimal notation). doubling & halving. Derive multiplication & division facts for 4 & 8 times tables using Add & subtract mentally 3+1, 3+2 & 3+3 digit numbers. doubling & halving. Derive & recall all addition & subtraction facts for each number to Add & subtract mentally 3+1, 3+2 & 3+3 digit numbers. 100, sums & differences of multiples of 10 & number pairs to 100. Derive & recall all addition & subtraction facts for each number to Doubles and halves to 100 linking to the inverse (Using inverses or 100, sums & differences of multiples of 10 & number pairs to 100. knowledge of doubling & halving to check calculations.) Doubles and halves to 100 linking to the inverse (Using inverses or _______________________________________________________________ knowledge of doubling & halving to check calculations.) Write numbers in words up to thousand Measures – capacity: choosing, measuring, comparing, adding, Number bonds secured to hundred subtracting & using appropriate units of measurements related to Introduce to counting in tenths (if appropriate) practical activities. _______________________________________________________________ Developing written methods for all 4 operations. Column method for addition (expanded if appropriate). Data – Venn & Carroll diagrams linked to topic. Number lines for subtraction/division – progressing to formal written Identify horizontal, vertical, perpendicular, parallel & curved lines in methods if appropriate shapes. Introduce grid method for multiplication. Revisit data handling – interpretation. Recap 2D shape & measure perimeters. Revision of all 4 operations applied in context. Recognise angle larger/smaller than a right angle Use a compass to draw circles & arcs with a given radius. Make & describe 3D using the language & knowledge of 2D shapes to describe faces, edges & vertices. Identify horizontal, vertical, parallel and perpendicular lines (where appropriate) TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 4 Blue = Areas that are not in STAT Autumn 1 Use knowledge of place value to read, write & order whole numbers up to 4-digits (extension 5/6 digits). Rounding & comparing numbers up to 1000 using < = >. Multiply & divide numbers by 0, 1, 10 & 100 (including dividing with decimals). Multiply together three numbers. Count in steps of 6, 7 and 9 Count in steps of 10, 25, 50, 100 & 1000. Find 1000 more or less than a given number. Sums & differences of multiples of 10 & number pairs to total 100/1000. Doubles of 2-digit numbers & multiples of 10/100 & corresponding halves. Add or subtract mentally, pairs of 2-digit whole numbers. Eg 48+47, 91+35. Derive & recall facts up to 12x12. Identify & use patterns & properties of numbers & use in rapid mental calculation. Time – recap to assess prior knowledge – 5 & 1 minute intervals – comes up later. Autumn 2 Recap recognition of fractions of shapes. Add and subtract proper fractions with a denominator as the parts of a whole & the numerator as the number of parts. Use diagrams to recognise, compare and show fractions & establish equivalents. Begin to understand how fractions can be reduced. Recap mental strategies for + and - & informal recording. Refine & use efficient informal written methods (column) for addition and subtraction up to 4-digit numbers (in spring 1 also). Application to solve one & 2 step problems involving numbers & money. Using a calculator to check. Measures – length: use standard units to estimate, measure & record. Draw rectangles & measure & calculate perimeter. Order and compare numbers beyond 1000. Develop written methods to multiply 2-digit and 3-digit by 1-digit numbers. Introduce division as an inverse operation & explain division of a 2digit number by a 1-digit number using a number line. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 4 Spring 1 Rounding & comparing numbers up to 1000 using < = >. Informal recording of mental strategies for subtraction using a number line to find the difference. Vocabulary of subtraction – decrease, minus, less than, difference, etc. Recap subtraction as an inverse. Estimate and use inverse to check calculations. Revisit and then solve using formal written methods for subtraction and addition two-step problems in context, deciding which operations and methods to use and why – including decomposition Revisit efficient informal written methods (column) for addition and subtraction up to 4-digit numbers. Data – organise, present, analyse & interpret discrete and continuous data using appropriate graphical methods including bar charts and time graphs. Data – Solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in bar charts, pictograms, tables and other graphs. Identify lines of symmetry in 2D shapes presented in different orientations. Recap perimeter – measure and calculate perimeter* introduce area. Find the area of rectilinear shapes. Introduce formula of L x W Composite shapes by counting squares. Introduce formula of L x W. If appropriate find perimeter /area of compound shapes Recognise and use factor pairs commutatively in mental calculations. Spring 2 Recap measures – capacity & weight: unit conversion. Choose & use standard metric units – practical activities. Revisit division of 2-digit by 1-digit numbers using a formal method. Introduce remainders. Multiply two and three-digit numbers buy a one-digit number using a formal layout. Count up and down in hundredths; recognise that hundredths arise when dividing an object by one hundred and dividing tenths by 10. Finding fractions of numbers related to division 3D Shapes, recap properties. Visualise 3D from 2D and make nets of common solids Introduce negative numbers on an number line and in context of thermometers Compare and classify 2D geometric shapes in different orientations. Compare a classify geometric shapes including quadrilaterals and triangles based on their properties and sizes. 2D shapes – draw & classify polygons according to properties. Recap Venn & Carroll diagrams. Lines of symmetry. Recap right angles. Sequencing of numbers (including negative) and greater / less than. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 4 Summer 1 Angles & degrees – know that angles are measured in degrees & that 1 whole turn = 360° (relate to compass directions). Identify acute & obtuse angles & compare sizes of different angles. Time recap – 12 and 24 hrs. Read, write and convert analogue & digital times. Solve problems involving converting from hrs to mins; mins to seconds; years to months; weeks to days AM & PM Reading & interpreting timetables. Solve simple time conversion problems (if appropriate) Decimals – use decimal notation for tenths & hundredths. Partition & order decimals. Round decimals to whole numbers Compare numbers with the same number of decimal places up to two decimal places Position 1 & 2-place decimals on a number line. Recognise & write decimal equivalents for ¼, ¼, ¾, tenths & hundredths. Summer 2 Introduce formal short method of multiplication where appropriate. Revision of all 4 operations applied in context & using decimals & money. Solving problems with fractions and decimals to 2 decimal places in the context of money Solve problems involving increasingly harder fractions to calculate quantities, and fractions to divide quantities, including non-unit fractions where the answer is a whole number Add & subtract 2 fractions with a common denominator. Describe positions & movements between positions on a 2D grid & as co-ordinates in the first quadrant. If appropriate introduce to translation of shapes Plot points to draw a polygon. Read Roman numerals to 100, concept of 0 and place value. Solve problems involving integer scaling and distributive law. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 5 Autumn 1 Multiplying & dividing by 10/100/1000 including decimals. Read, write, order & compare numbers to at least 1000,000. Explain what each digit represents in whole numbers & decimals up to 3 decimal places. Partition, round & order. Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number up to 100000. Round numbers to the nearest 10, 100, 1000, 10,000 & 100,000. Use knowledge of place value & addition & subtraction of 2-digit numbers to derive sums & differences. Interpret negative numbers in context, count forwards and backwards in positive and negative whole numbers, including through 0. Add and subtract numbers mentally with increasingly large numbers (e.g. 12462 – 2300 = 10162) Add & subtract numbers whole numbers with more than 4 digits (column method) Estimate sensible answers before calculating. Use rounding to check answers to calculations and determine in the context of a problem. Recap written methods for addition & subtraction – column & decomposition, including 3-place decimals & up to 5-digit numbers. Recap properties of 2D shape. Use knowledge to draw different shapes (with a focus on quadrilaterals & triangles – equilateral, isosceles, right-angle & scalene). Recognise parallel & perpendicular lines. Complete patterns with up to 2 lines of symmetry & draw position of a shape after reflection / translation. Autumn 2 Use known facts to multiply & divide. Use multiplication facts used to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 & 100. Eg 30x20, 300x2. Identify multiples and factors, including finding all factor pairs of a number and common factors of two numbers. Derive corresponding division facts. Know and use the vocabulary of prime numbers and prime factors and composite (non-prime) numbers. Recognise and use square numbers and cube numbers and the notation for squared and cubed. Establish whether a number up to a 100 is prime and recall prime numbers up to 19. Formal written method to multiply ThHTUxU & TUxTU & HTUxTU using formal written method (up to 4 digits) Introduce efficient method of dividing HTU by U (bus stop) and interpreting remainders appropriately for the context. Solve problems involving addition and subtraction, multiplication using their knowledge of factors and multiples, squares and cubes including understanding the meaning of the equals sign. Draw & measure to the nearest mm. Measure & calculate the area & perimeter of composite rectilinear shapes in centimetres and metres. Calculate and compare the area of rectangles (including squares), and including using standard units, square metres. Estimate the area of irregular shapes. Estimate volume (e.g using 1cm cubed blocks to build cuboids) and capacity (e.g. using water) Use standard units to estimate & measure length in a context. Convert between different units of metric measure (for example, kilometre and metre; centimetre and millimetre; gram and kilogram; litre and millilitre). Understand and use approximate equivalences between metric units and common imperial units such as inches, pounds and pints. Revisit time – AM & PM & 24 hour clock. Telling the time to the nearest minute & apply to timetables. Solve problems involving converting between units of time. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 5 Spring 1 Recap finding fractions of numbers, quantities or shapes. Eg 1/5 of 30 plums. Compare and order fractions whose denominators are all multiples of the same number. Identify fractions that total 1. Identify, name and write equivalent fractions of a given fraction, represented visually, including tenths and hundredths. Recognise mixed numbers and improper fractions and converting from one to the other and write mathematical statement > 1 as mixed numbers (e.g. 2/5 +4/5 =6/5 = 1 1/5). Recognise equivalence and relationship between decimals & fractions ½, 1/3, ¼, 1/5, tenths & hundredths (e.g. 0.71 = 71/100). Recognise and use thousandths and relate them to tenths, hundredths and decimal equivalents. Round decimals with two decimal places to the nearest whole number and to one decimal place. Read, write, order and compare numbers with up to three decimal places. Add & subtract fractions with the same denominator to make mixed numbers. Solve problems involving multiplications and division including scaling by simple fractions and problems involving simple rates. Multiply proper fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers, supported by materials and diagrams. Know angles are measured in degress, estimate and compare, acute, obtuse and reflex. Angles – estimate, draw & measure acute & obtuse angles using a protractor. Calculate angles on a straight line. Introduce reflex angles & calculate angles around 360˚. Use the properties of rectangles to deduce related facts and find missing lengths and angles. Distinguish between regular and irregular polygons based on reasoning about equal sides and angles. Order positive & negative numbers on a number line (thermometer). Identify, describe and represent position of a shape following a reflection or translation, using the appropriate language, and know that the shape has not changed. Balancing numerical equations. Spring 2 Read, write, order and compare numbers with up to three decimal places. Solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in a line graph. Complete, read and interpret information in tables, including timetables. Factors – recap finding pairs of factors for 2-digit numbers & common multiples. Introduce to concept of prime factors and composite numbers Counting in steps of 25, 50, 75 leading to 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 etc forwards & backwards & link to reading scales. Measures, weight & capacity – using appropriate standard units, interpret scale & convert g to kg, ml to l & read Newton meters. Apply all 4 operations to the context of measures (1 and 2 step problem solving). TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 5 Summer 1 Summer 2 Calculate the area of regular shapes using a formula, including halving Revisit all 4 operations applied in context & using decimals (word to find the area of triangles. problems). Recognise the percent symbol (%) and understand that per cent Solve problems involving multiplication and division including using relates to ‘number of parts per hundred’, and write percentages as a their knowledge of factors, multiples and squares and cubes. fraction with a denominator 100 and as a decimal. Recap whether a number is Prime and know Prime numbers Solve problems which require knowing percentage and decimal Recap square numbers, square roots, cubed numbers& their notation. equivalents of ½, 1/4., 1/5, 2/5, 4/5 and those fractions with a Use all four operations to solve problems involving measure (for denominator of a multiple of ten or 25 (Understand ‘percentage’ to example, length, mass, volume and money) using decimal notation mean ‘out of 100’ to convert percentages to fractions & vice versa). using scaling. Calculate the area of compound shapes. Read Roman numerals to 1000 and recognise years written in Roman The relationship between fractions, decimals & percentages (4 numerals. column chart). If appropriate Finding 50%, 10%, 5%, 15% etc of numbers & quantities. Use the vocabulary of ratio & proportion. Eg 2:3 & 4:6. 3D shape – properties of. Identify & draw nets of 3D shapes. Estimate proportions. Time – calendars – use to solve problems related to time. Adding and subtracting fractions with different denominators Division of a 3 or 4 digit number by a 2 digit number TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 6 Autumn 1 Mental recall of multiplication facts up to 12x12 including square numbers, prime numbers and cubed numbers Use multiplication facts up to 12x12 to derive multiplication & division facts including decimals. Eg 0.2x0.01 Doubling & halving as inverse operations – plus other inverses. Multiply mentally TUxU HTUxU by partitioning.. Decimal notation for tenths, hundredths & thousandths. Multiplying & dividing by 10/100/1000 including decimals Round any whole number to a require degree of accuracy. Solve problems which require answers to be rounded to specified degrees of accuracy. Read, write, order & compare numbers up to 10,000,000. Use negative numbers in context and calculate intervals across zero. Generate and describe linear number sequences (missing numbers in number sentences) Difference between positive & negative numbers – ordering negative numbers. Addition of decimal numbers using standard methods. Perform mental calculations, including with mixed operations and large numbers Solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above. Angles – Estimating, drawing & measuring. Classifying acute, obtuse & reflex. Recognise angles where they meet at a point or on a straight lint or a vertically opposite and find missing angles. Triangles – angle sums, missing angles in isosceles triangles, properties of all 3 triangles. Autumn 2 Multiply multi-digit numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit whole number using the formal written method of long multiplication. Multiply one-digit numbers with up to two decimal places by whole numbers. Standard written methods for multiplication & division, including remainders written as decimals & fractions Identify common factors, common multiples and prime numbers. Factors of numbers as pairs & relate to square numbers. Prime numbers & relationships with factors. Use written division methods in cases where the answer has up to two decimal places. Divide numbers to 4 digits by a two-digit whole number using the formal written method of long division, and interpret remainders as whole remainders, fractions, or rounding, as appropriate for the context. Use their knowledge of the operations to carry out calculations involving the four operations (BODMAS). Solving addition and subtractions, multiplication and division in context deciding which operations to use and why Use estimation to check answers to calculations and determine, in the context of a problem, an appropriate degree of accuracy. Quadrilaterals – properties of all quadrilaterals, find missing angles, parallel & perpendicular, opposites, diagonals/bisect. 2D shape – Properties, recognising regular & irregular. Solve problems involving similar shapes where the scale factor is shown or can be found. Draw 2-d shapes using given dimensions and angles. Construct, translate & reflect simple shapes. Recognise, describe and build simple 3d shapes including making nets. Compare and classify geometric shapes based on their properties and sizes and find unknown angles in any triangles, quadrilaterals and regular polygons Illustrate and name parts of circles, including radius, diameter and circumference and know that the diameter is twice the radius. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 6 Spring 1 Use common fractions to simplify fractions; use common multiples to express fractions in the same denomination. Compare and order fractions > 1 Add and subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions The relationship and value between fractions, decimals & percentages (4 column chart). Recall and use equivalences between simple fractions, decimals and percentages, including different contexts. Recap finding fractions and percentages of numbers/quantities/amounts/ shapes and solve problems involving the calculations of percentages and the use of using percentages for comparison. Concept of % as fractions to find simple % & apply to multi-step problems. Multiply and divide simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in it’s simplest form ( ¼ x ½ = 1/8). Recognise that shapes with the same areas can have the same perimeters and vice versa. Recognise when it is possible to use formulae for area and volume of shapes Calculate areas of triangles & parallelograms. Calculate the volume of 3D shapes Calculate, estimate and compare volume of cubes and cuboids using standard units including (cm cubed and m cubed), and extending into other units (e.g. mm cubed and km cubed) Spring 2 Using all 4 number operations (multi-step problem solving). Recognise & apply several mental subtraction strategies (near numbers, etc). Subtraction of ThHTU & decimals using standard methods. Solve problems involving the relative sizes of two quantities where missing values can be found by using integer in multiplication and division (scaling up and down) Solve problems involving unequal sharing and grouping using knowledge of fractions and multiples ( e.g. How many four man tents needed for 21 people?) Explore patterns & relationships, construct & use simple formula expressed in words. Data handling – revision of line, bar, etc, pictograms, tallies, Calculate and interpret the mean as an average. Co-ordinates – 4 quadrants, missing scales, symmetry of co-ordinates. Draw and translate simple shapes on the coordinate plane, and reflect them in the axis. Timetables – time intervals, problems related to time. TOWN CENTRE COLLABORATION Maths Long Term Plan Year 6 Summer 1 Recap Roman numerals to 1000. Reflections/rotations/translations. Interpret pie charts and line graphs and use these to solve problems. Construct pie charts and line graphs. Scale - reading circular & lines scales, units (length, weight, volume & time). Use, read, write and convert between standard units, converting measurements of length, mass, volume and time from smaller unit of measure to a larger unit, and vice versa using decimal notation to up to three decimal places. Solve problems involving the calculations and conversion of units of measure, using decimal notation up to three decimal places where appropriate. Recap name parts of a circle, including radius, diameter & circumference. SAT revision, past papers, etc. Summer 2 Use of 2-stage function machines. Algebra – Use simple formulae Multi-step problem solving using all 4 operations. Algebra bridging unit. Recognise binary numbers to 15.