* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download endocrinology - Endo, GIT, Urology, Cardio - misiek
Survey
Document related concepts
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Kallmann syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
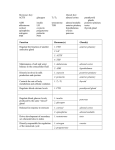
endocrinology.doc (136 KB) Pobierz Львівський національний медичний університет ім. Данила Галицького Кафедра променевої діагностики і терапії «ЗАТВЕРДЖУЮ» Зав. кафедри променевої діагноститки і терапії Обговорена і затверджена на доц. Дац І.В. методичному засіданні кафедри "_____"_______________ 200 р Наказ № ________________ Лекція № 5 Назва RADIONUCLIDE METHODS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY. RPL’S WHICH ARE USED FOR EVALUATION OF THYROID GLAND. ASSESSING OF THE THYROID GLAND FUNCTION BY MEANS OF I131, TC99M -INTAKE TESTS. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY – ESTIMATION OF T3, T4, TTH. RADIONUCLIDE VISUALISATION OF THE THYROID GLAND: SCANNING, SCINTIGRAPHY. DIAGNOSTIC ALGORITHM OF THYROID GLAND, DIAGNOSTIC VALUE. Лекцію підготувала ас. Шатинська-Мицик І.С. Львів Functional types of hormones: a. Releasing factors from the hypothalamus which stimulate anterior pituitary b. Inhibitory hormones - from the hypothalamus or GIT (suppress the secretion of particular hormones). c. Tropic hormones - come from the anterior pituitary gland and have as a target the other endocrine glands. d. Non-tropic or effector hormones secreted by non-pituitary endocrine glands act on tissue cells stimulate a feedback effect upon hypothalamus or anterior pituitary glands a) Negative feedback: an increase in the product causes a decrease in the system b) Positive feedback: an increase in the product causes an increase in the activity of the system a. Primary control = hypothalamus (small gland adjacent to the pituitary gland & connected to it via “pituitary stalk” synthesize ADH (vasopressin) and oxytocin b. Secondary control- pituitary gland: Lobes: posterior lobe = neurohypophysis, anterior lobe = adenohypophysis Tropic hormones secreted: ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH Effector hormones secreted: GH (somatotropin), Prolactin I. Anterior Pituitary Hormones: 1. Growth hormone (GH) (Somatotropin): -men: <5 ng/ml -women: <10 ng/ml -child: 0-10 ng/ml, newborn: 10-40 ng/ml Causes production of somatomedians (peptides secreted by the liver which act as second messengers) Have insulin-like activity in some tissues ▲ Increased Levels: Gigantism Acromegaly Anorexia nervosa. Starvation stimulates GH secretion. Stress, surgery, hypoglycemia, starvation, exercise Deep-sleep state ▼ Decreased Levels: pituitary insufficiency due to tumors, ischemia, or trauma dwarfism. This is a result of GH deficiency in children. hyperglycemid,- elevated glucose levels inhibit GH secretion. delayed sexual maturity. 2. Prolactin (PRL) Function–breast growth during pregnancy and milk secretory activity Major use of determination is to assist in the diagnosis of pituitary tumors Measurement by RIA: male: 0-20ng/ml; women 0-25ng/ml, pregnant: 20-400 ng/ml Increased levels in: Galactorrhea Amenorrhea Prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors Hypothyroiditis Paraneoplastic syndrome Stress (anorexia) Empty sella syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome Renal failure Decreased levels in: Pituitary apoplexy (Sheehan’s syndrome) Pituitary destruction by craniopharyngeoma 3. TSH: for neonatal screens confirming adult hypothyroidism 4. ACTH adrenocorticotropic hormone=corticotropin: target cells–adrenal cortex stimulate production of adrenal steroids has diurnal variation: -highest level occurs between 6-8am -lowest level occurs between 6-11pm Normal Findings: AM: <80 pg/ml or <18 pmol/L (SI units) PM: <50 pg/ml or <11 pmol/L (SI units) Indications: The serum ACTH study is a test of that affords to differentiate the causes of either Cushing's syndrome (overproduction of cortisol) or Addison's disease (underproduction of cortisol). Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is made in the hypothalamus. It stimulates ACTH production in the anterior pituitary gland, which in turn stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce cortisol. The rising levels of cortisol act as a negative feedback mechanism and curtail further production of CRH and ACTH. In the patient with Cushing's syndrome an elevated ACTH level can be caused by: a pituitary ACTH-producing tumor a nonpituitary (ectopic) ACTH-producing tumor, usually in the lung, pancreas, thymus, or ovary. ACTH levels over 200 pg/ml usually indicate ectopic ACTH production. If the ACTH level is below normal in a patient with Cushing's syndrome, an adrenal adenoma or carcinoma is probably the cause of the hyperfunction. In patients with Addison's disease an elevated ACTH level indicates primary adrenal gland failure, due to infarction, hemorrhage, or autoimmunity; surgical removal of the adrenal gland; congenital enzyme deficiency; or adrenal suppression after prolonged ingestion of exogenous steroids. If the ACTH level is below normal in a patient with adrenal insufficiency, hypopituitarism is most probably the cause of the hypofunction. Diurnal variation is lost when disease (especially neoplasm) affects the pituitary or adrenal glands. ACTH is measured in amniotic fluid when anencephaly is suspected. Decreased levels are noted in anencephalic fetuses. Interfering Factors: Stress (trauma, pyrogen, hypoglycemia), menses, and pregnancy cause increased levels of cortisol. This is accomplished through elevation of ACTH. Drugs that may cause increased levels include estrogens, ethanol, vasopressin, amphetamines, insulin, levodopa, and spironolactone. Exogenously administered corticosteroids decrease ACTH levels. Table 1: Cortisol ACTH Levels in Diagnosis of Adrenal Dysfunction Disease Cortisol ACTH Cushing's syndrome High low Adrenal micronodular hyperplasia Adrenal tumor (adenoma, cancer) Cushing's syndrome High High Cushing's disease (ACTH-producing pituitary tumor) Ectopic ACTH-producing tumor (e.g., lung cancer) Addison's disease low ... Adrenal gland failure (e.g., infarction, hemorrhage, congenital adrenal hyperplasia) Plik z chomika: misiek-puchatek Inne pliki z tego folderu: Cardiovascular System.doc (104 KB) endocrinology.doc (136 KB) GIT, LIVER & BILE DUCTS.doc (149 KB) neuroblastomas HCC RT.doc (93 KB) urology my.doc (159 KB) Inne foldery tego chomika: Zgłoś jeśli naruszono regulamin Strona główna Aktualności Kontakt Dla Mediów Dział Pomocy Opinie Program partnerski Regulamin serwisu Polityka prywatności Ochrona praw autorskich Platforma wydawców Copyright © 2012 Chomikuj.pl Lungs radionuclide Radiotherapy