* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hormone Overview of effect Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
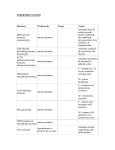
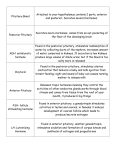
Hormone Overview of effect Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Drives thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormone (T3 & T4) and grow. Adrenal corticotrophic hormone (ACTH) Regulates secretion of corticosteroid hormones from adrenal cortex Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Regulates growth of gametes: oocytes in females and spermatozoa in males. Also stimulates ovarian follicles to grow and secrete estrogens in females. Surge causes ovulation and progesterone production via corpus luteum in females. Also stimulates interstitial cells in testis to make testosterone. Promotes tissue growth. Luteinizing hormone (LH) Growth hormone (GH) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin Oxytocin Mediates sense of thirst and promotes H2O retention by the kidneys. Also likely responsible for pair bonding & monogamy in males. Promotes uterine motility and milk let down (release). Also important in maternal infant bonding and female pair bonding. Prolactin Induces milk synthesis after pregnancy T3 & T4 (thyroid tormone) Elevates metabolic rate, O2 consumption and heat production. Stimulates respiration and circulation (HR & BP) Calcitonin Reduces Ca+2 in ECF stimulates bone deposition and ossification. Effects primarily children. Parathyroid Hormone Increases Ca+2 in ECF stimulates bone demineralization. Melatonin Influences sleep, mood and probably sexual maturity. Atrial Naturetic Peptide/Factor Stimulates kidneys to excrete (lose) Na+ and H2O. Lowers blood volume and pressure. Epinephrine Mediates global part of the sympathetic response. Affects metabolism (increases blood glucose) and increases heart rate & blood pressure Cortisol /Corticosterone Suppresses immune (defense) system. Controls metabolism and response to stress. Increases blood glucose. Aldosterone Promotes Na+ retention and K+ secretion by kidneys, maintains or increases blood pressure & volume. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) Regulates male embryonic development and sex drive in adult females. Testosterone Stimulates male growth, secondary sex characteristics, sperm production and libido. Estrogen Regulates menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Promotes growth of uterine lining (endometrium). Also stimulates female growth and development. Erythropoietin Stimulates red blood cell production by bone marrow. Gastrin Stimulates gastric acid secretion. Ghrelin Increases appetite Leptin Suppresses appetite Secretin Stimulates pancreas to secrete bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid in duodenum. Cholecystokinin Promotes gallbladder contraction and pancreatic secretion of digestive enzymes. Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) Promotes the release of FSH & LH (gonadotrophs) from anterior pituitary Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) TSH (thyrotroph) release from anterior pituitary Corticotropin releasing hormone ACTH (corticotroph) release from anterior pituitary Dopamine (prolactin inhibiting hormone or PIH) Inhibits prolactin secretion from anterior pituitary Growth hormone releasing hormone (GRH) Promotes growth hormone release from anterior pituitary Renin Enzyme that regulates blood pressure by activating a prohormone in the blood. Angiotensin II Potent vasoconstrictor and stimulates the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone. Insulin Affects metabolism (reduces blood glucose) Glucagon Affects metabolism (increases blood glucose and fatty acids) Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) Maintains corpus luteum for ~3 months following successful embryonic implantation. Detected by EPTTM or ClearBlueTM