* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download four operations number progression rubric
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical calculator wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
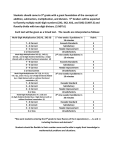
Year 1 Year 2 Phase 1-2 Adds whole numbers using materials Models addition of whole numbers Subtracts whole numbers using materials Models subtraction of whole numbers Counts on in ones, twos, fives and tens Uses the written method to add whole numbers Shares objects into even groupings Subtracts whole numbers Models multiplication of whole numbers Four operations of number Year 3 Year 4 Phase 2-3 Four operations of number Objectives Model addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers Model addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers Uses efficient written methods to add whole numbers Uses efficient written methods to add whole numbers Uses efficient written methods to subtract whole numbers Uses efficient written methods to subtract whole numbers Multiplies whole numbers Uses efficient written methods to multiply whole numbers Models division of whole numbers Uses efficient written methods to divide whole numbers with no remainders Year 5 Year 6 Phase 3-4 Model addition and subtraction of decimals. Model multiplication and division of whole numbers Uses efficient written methods to add whole and decimal numbers Uses efficient written methods to subtract whole and decimal numbers Uses efficient written methods to multiply whole and numbers Uses efficient written methods to divide whole numbers with remainders Model addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals Uses efficient written methods to add whole and decimal numbers Uses efficient written methods to subtract whole and decimal numbers Uses efficient written methods to multiply large whole numbers and decimals Uses efficient written methods to divide large whole numbers and decimals. Display remainders as a decimal fraction Phase 1 Addition Uses doubles Uses materials to add 2 digit to 1 digit numbers showing recording Adds mental combinations of one digit and two digit combinations Recognises 10 more/ 10 less etc. Solves simple number problems using addition Estimates using addition to check for reasonableness Recalls addition facts to 10 Subtraction Models subtraction using materials Four operations of number Indicators Phase 2 Phase 3 Addition Uses materials to add 2 digit to 1 digit numbers with regrouping showing recording. Describes written strategies for adding 2 digit numbers. Explains the process of regrouping Recognises 100 more / 100 less etc. Solves worded problems using 2 digit addition Uses effective strategies to estimate to check for reasonableness Recalls addition facts to 20 Subtraction Addition Uses mathematical language, materials and recording to add three digit numbers Explains the process of regrouping Solves worded problems Uses effective strategies to estimate to check for reasonableness Recalls addition facts to 20 Subtraction Uses mathematical language, materials and recording to subtract two digit numbers from three digit. Explains the process of regrouping Solves worded problems Phase 4 Addition Uses efficient written strategies to add large whole numbers (positive and negative) Uses efficient written strategies to add decimal numbers Selects and uses an appropriate sequence of operations to solve word problems Uses effective strategies to estimate to check for reasonableness Subtraction Uses efficient written strategies to subtract whole numbers (positive and negative) Uses efficient written strategies to subtract decimal numbers Recalls subtraction facts to 10 Multiplication Recognises and makes groups that are of the same number Records the grouping informally Division Groups and shares collections of objects equally Records the sharing informally Uses materials to subtract 2 digit Uses materials to subtract 2 digit numbers with regrouping showing recording Describes written strategies for subtracting 2 digit numbers Explains basic subtraction facts connecting to addition Recalls subtraction facts to 20 Multiplication Explains what multiplication is Make and records repeated groups of the same number Recognises and uses the multiplication symbol Explains the relationship between multiplication and addition Explains the relationship between table facts (e.g. can make a connection between the 5x and the 10x) Recalls tables facts (e.g. 2s, 5s and 10s) Knows the commutative rule of multiplication (e.g. that 5 x 2 is the same as 2 x 5) Division Explains what division is Explains the relationship between division and subtraction Explains the inverse relationship between multiplication and division Divides 2 digit numbers with 1 digit numbers (no remainders) Recalls division facts (e.g. 2s, 5s and 10s) Estimates using subtraction to check for reasonableness Recalls subtraction facts to 20 Multiplication Explains what multiplication is Explains the relationship between multiplication and addition Explains the relationship between table facts (e.g. can make a connection between the 5x and the 10x) Memorizes, practices and recalls timetables to 10x10 Multiplies by 10 and 100 (using place value) Uses factors and multiples of numbers Multiplies 2,3,and 4 digit numbers by 1 digit Multiplies 2 digit by 2 digit numbers Division Explains what division is Explains the relationship between division and subtraction Explains the inverse relationship between multiplication and division Divides 3 digit by 1 digit numbers with remainders Divides 4 digit numbers with divisors of 10, 100 and 1000. Memorizes, practices and recalls division facts to 100 Uses actors and multiples of numbers up to 100 Selects and uses an appropriate sequence of operations to solve word problems Uses effective strategies to estimate to check for reasonableness Multiplication Explains written method Models (use materials) long multiplication and multiplication of decimals. Memorizes, practices and recalls timetables to 10x10 Multiplies 3/4 digit numbers by a 2/3 digit Multiplies decimals by a whole number e.g. 1.5 x 4 = 6. Division Explains what division is Explains the relationship between division and subtraction Explains the inverse relationship between multiplication and division Divides large number 4, 5 and 6 digit by 1 and 2 digit numbers (internal zeros in answer) with decimal remainders Divides 4 digit numbers with divisors of 10, 100 and 1000 (e.g. 2390 ÷ 10 OR 2390 ÷ 100) Memorizes, practices and recalls division facts to 100 Uses factors and multiples of numbers up to 100 Divides decimals by whole numbers e.g. 2.5 ÷ 5 = 0.5