* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eukaryotic Cell Structure Quiz #1
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
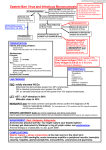
Cells are under constant threat from viruses. When a cell senses that a virus is nearby, it produces antibody proteins. Antibodies are large proteins made from thousands of amino acids joined together and folded into a characteristic “Y” shape. Simplified diagram of an antibody: Virus Virus Virus- binding site The tips of the Y are designed to lock together with the virus. Virus Virus Virus- binding site Meanwhile, the base of the Y is free to communicate with the immune system. Virus Virus Virus- binding site The characteristic “Y” shape of antibodies allow these proteins to do two jobs at once: blocking viruses and alerting the immune system that viruses are present. The eukaryotic cell below has detected a virus nearby. It must now respond by producing antibodies. 1. Identify the organelle below, and describe its role in the production of antibodies. 2. Explain why the nuclear membrane is dotted with pores. The diagram below show antibodies being produced and shipped out of the cell. B A C D 3. Identify the organelles labeled “A,” and describe their role in the production of antibodies. B A C D 4. Identify the organelle labeled “B,” and describe its role in the production of antibodies. B A C D 5. Identify the organelle labeled “C,” and describe its role in the production of antibodies. B A C D 6. Identify the structure labeled “D” in the diagram, and explain how it helps the antibody proteins leave the cell. B A C D