* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Can you Identify the picture below?
Survey
Document related concepts
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
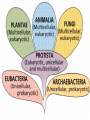
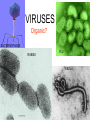
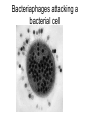
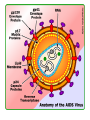
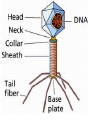
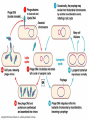
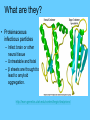
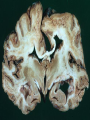
What do the following have in common? Can you Identify the picture below? Characteristics of Life • • • • • • Made of Cells Reproduce Metabolize (energy) Grow Respiration Respond to environmental changes • How can you prevent the spread of disease? (3) • How could know if an individual is infected with a pathogen? explain • What do we know about viruses? • Why are viruses not classified in any of the 6 kingdoms? – Have to have a host in order to reproduce – Don’t have independent metabolism – Don’t grow – NOT CELLULAR Virus Characteristics • • • • • Do not use energy Do not reproduce Do not grow Do not respond to environment Are not cellular • Obligate intracellular parasites Why do some scientists consider viruses to be “alive?” • Contain all organic compounds – Carbs, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids – (same chemicals as a living organism) • Under right conditions, being inside of a host cell, they can carry out life process. • They replicate (NOT reproduction) Obligate intracellular parasites • Commit inside a cell and uses the cell as a host to function VIRUSES Organic? BACTERIOPHAGE RABIES FLU EBOLA Virus Defined • Infectious pathogen that infects living cells, replicates inside cells making new viral particles causing disease • DNA encased in a protein/carbohydrate coat Types of Viruses Polyhedral helical enveloped Bacteriaphages attacking a bacterial cell Types of Viral Diseases • • • • • Rabies Ebola (hemorrhagic) Flu (influenza) HIV Hepatitis WE can only treat symptoms of viruses!!! We can not CURE!! • • • • • • • • • Chicken pox Measles Rubella Mumps Smallpox Polio Yellow fever Parvovirus (canine) Dengue fever (hemorrhagic) • Herpes • How a Virus invades your cells – http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=Rpj0 emEGShQ&feature=fvwp • Lysogenic: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_J9xKitsd0 • http://biology.about.com/gi/o.htm?zi=1/XJ &zTi=1&sdn=biology&cdn=education&tm= 2&gps=342_220_1020_583&f=00&tt=2&bt =0&bts=1&st=14&zu=http%3A//student.cc Virus Hunters 1. What factors influenced the spread of disease? 2. What helped to prevent the spread of disease. 3. Discuss one virus you learned from the video and describe symptoms, treatment, or interesting fact of the virus. Vaccinations • Stimulates Active immunity • Injection of portion of virus (virus particles) that stimulate an immune response….causes body to make antibodies against particular diseases http://health.howstuffworks.com/vaccine.htm Immune Responses • Passive – Formation of antibodies – To the fetus thru the placenta, thru breastmilk, thru administration of plasma (artificial) • Active – Formation of your own antibodies – Vaccinations – by contracting an infectious disease by exposure of an antigen 1 2 4 3 • Lysogenic Infection: • Similar to lytic infection however important differences exist • Instead of immediately replicating, viral DNA incorporates itself into the host cell's DNA. • Will remain dormant for significant amounts of time. • Give certain conditions (stress), the virus will enter it's lytic phase similar to a normal lytic infection Prions Proteinaceous infectious particles What are they? • Proteinaceous infectious particles – Infect brain or other neural tissue – Untreatable and fatal – β sheets are thought to lead to amyloid aggregation. http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/prions/ Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy • Also known as "Mad Cow Disease" • Infected animals act strangely and can be aggressive • Spread rapidly through Britain by rendering infected animals into cattle feed Scrapie • Recognized in sheep and goats for more than 250 years • 1982 1st identified as a prion disease Kuru “laughing death” • • • • New Guinea Muscle weakness, loss of coordination, tremors, inappropriate episodes of laughter or crying Was the most common death of women Mortuary feasting – Forbidden by Australian government in 1950’s Viroid • Single strand of RNA (THAT’S IT!!) • Infects plants • 1 viroid disease has killed over 10 million coconut palms in the Philippines