* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glycolysis Puzzle: Concept Map of "Splitting of Glucose"
Survey
Document related concepts
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
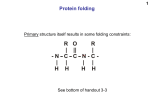
Glycolysis Puzzle: Concept Map of "Splitting of Glucose" Glucose = 6 carbon sugar. This 6 C compound is made possible by photosynthesis! Glucose 1 A phosphorylation reaction adds a_____ group to the glucose. This reaction uses ____ ATP [delta G = -8.0 kcal/mol] 2 2 This 6 C compound undergoes an enzyme catalyzed isomerization, i.e., a rearrangement of functional groups. [delta G = -0.6 kcal/mole] 3 Phosphorylation reaction uses ________ for substrate level phosphorylation. [delta G = -5.3 kcal/mole] In this reaction, the 6 C sugars is split into 2, 3 carbon compounds. [delta G = -5.3 kcal/mole] 4 5 In this reaction, isomerase converts 1 of 3C molecules so that there are two molecules of glyceraldehydes 3phosphate [delta G = +0.6 kcal/mole] Only one of two molecules of glyceraldehydes is shown here. Recognize that the following reactions happen to the other molecule. 6 In reaction 6, the enzyme catalyzes two sequential reactions: (1) The glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate is oxidized. The energy resulting from the oxidation of this 3 C compound is conserved by the reduction of the coenzyme _______________ to form ____________________. This coenzyme has "reducing potential." 6 7 (2) In place of the H that is removed, an inorganic PO4 group is added, producing a 3C compound that has _______ PO4 groups. [delta G = -0.4 kcal/mole] The phosphate group added above is transferred at this reaction step to ADP to produce ATP via substrate level phosphorylation. [delta G = +0.3 kcal/mole] At this point in glycolysis, _________ATP’s have been used and ________ATP’s have been produced 8 This 3 C compound now has ______PO4 group(s). This 3 C compound undergoes an isomerization reaction which relocates PO4 group from the 3rd to 2nd carbon [delta G = + 0.2 kcal/mole] 9 A molecule of water is removed causing a double bond to form within the C backbone. In this chemical state, the phosphate bond isdestabilized, which facilitates the next reaction. [delta G = -0.8 kcal/mole 10 The PO4 group is removed and transferred to ADP resulting in the production an ______molecule via substrate level phosphorylation. [delta G = -4.0 kcal/mole] The end product of glycolysis is called pyruvate. For every one molecule of glucose, there are __________________ molecules of pyruvate produced. Identify which reactions (by number) that are exergonic: Identify which reactions (by number) that are endergonic: Is the overall glycolysis reaction an exergonic or endergonic reaction? Pyruvate has two biochemical fates, depending upon whether or not oxygen is present. In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration (fermentation) occurs. In animal cells ________________________ is reduced to lactic acid (lactate) By the oxidation of the coenzyme __________________________ In yeast cells, a two step reaction occurs in which _______________________ is reduced to ethanol, and generates CO2. For both types of cells, the main purpose of anaerobic respiration is to regenerate the oxidized state of the coenzyme _________________________, which then can be used in ___________________(Hint” “splitting sugar reaction”), resulting in ____________ net molecules of ATP. Anaerobic respiration buys some time for animal cells. "Happy hour" is made possible through the anaerobic respiration of yeast!