* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
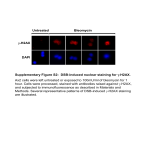
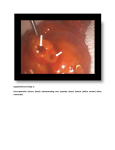
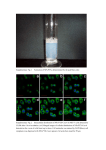
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence detection: Data shown are representative of at least three different mice per group. Briefly, frozen sections were fixed in acetone for 10 minutes in -20C, blocked in 3% fish gel for 30 mins, and stained with primary antibodies diluted in 3-5% fish gel overnight at 4C (1-3). Next, sections were washed three times in PBS, blocked in 3-5% fish gel solution at room temperature for 15-20 minutes, and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature in secondary antibody diluted in 4.5% fish gel. Briefly, these antibodies were used: ETAR (1:800, Fisher), ETBR (1:800, Fisher), F4/80 (1:100, AbD Serotec), p53 (1:100, Novus), Ki67 (1:400, eBioscience), ET1/2/3 (1: 100, Santa Cruz), anti-mouse pERK1/2 (1:100, Santa Cruz), albumin (1:800, Abcam), anti-mouse TNF-PE (1:50, eBiosciences), anti-mouse IL6-PE (1:50, eBiosciences). anti-mouse IgGAlexaflour 488 (1:800, Life Technologies), anti-rat IgG-Alexaflour 488 (1:800, Life Technologies), anti-rabbit IgG- Alexaflour 555 (1:800, Life Technologies), anti-rabbit IgGAlexaflour 647 (1:800, Life Technologies). Pictures were acquired using Nikon Eclipse Ti microscope, phospho-p53-S15 (1:50, Cell Signaling). Western Blot: Briefly, liver tissue was snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. Tissue was homogenized in lysis buffer, and supernatants were quantified for protein amount (4). 160 ug of cell lysate was loaded in 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and incubated with primary antibody overnight at 4° C (1000x dilution for anti-p53 (Novus), 2500x anti-GAPDH, 5000x anti-mouse IgG-HRP (Santa Cruz), 500x anti-pERK1/2 (Santa Cruz), 500x anti-MDM2 (Santa Cruz). Picrius Red Staining. Picrius Red Staining was performed according the manufacturer’s instructions (IHC World). Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining of Liver Sections and Scoring of Liver Lesions. Sections of paraffin-embedded tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The pathological readings were scored by a pathologist at our institution. Images were taken Nikon Eclipse Ti microscope. During time course experiments, the lesions were counted under a 200× microscope, where 15 fields per slide were counted. The small lesions typically observed early in the liver consist of hepatocellular degeneration and hepatocyte necrosis along with Kupffer cell hyperplasia attended by a small number of lymphocytes were quantified as previously described(5). Image J quantifications: To calculate corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF), we used the method described by Burgess et. al. (13). Briefly, the following formula was used: CTCF= Integrated Density – (Area of Selected cell X Mean Fluorescence of background reading). Isolation of liver immune cells: In order to isolate the immune cells from the liver, the liver of the mice was perfused using 10 ml of PBS by injecting it into the superior vena cava (6). Following perfusion, the liver was minced in small pieces and passed through a 40 µm cell strainer. The cell suspension was washed and suspended in 20 ml of Percoll-HBSS. The cell suspension was centrifuged at 800 x g for 20 minutes at room temperature without any brakes. Following centrifugation, red blood cells were 1 lysed with 10 ml of RBC lysis buffer. After the last wash, the cells were used for flow cytometry staining. Bone marrow isolation and staining: Bone marrow cells were isolated as previously described(5). These cells were treated with recombinant IL27 (20 ng/mL, R&D Systems) or PBS for 3 hours or overnight and ETAR levels were detected via immunofluorescence. Kupffer cell isolation Wildtype mice were injected with LPS intraperitoneally at 5mg/kg body weight. Mice were euthanized 3 hours post LPS injection. Kupffer cells were isolated as previously described (7). Isolated kupffer cells were treated with LPS (1 µg/mL) in presence or absence of rIL27 (20ng/ml). 24 hours later, cells were stained with ETAR and DAPI. Liver fibrosis induction by CCL4 Briefly, fibrosis of the liver was induced by injecting CCL4 (diluted in 1:3 ration in corn oil) intraperitoneally twice a week for 4 weeks at 1µL/g of body weight (6) 2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS: Supplementary Figure 1: Photomicrograph demonstrating steatosis and fibrosis occurrence Fibrosis was assessed based on Sirius red staining (upper). Enlarged area of HE photomicrograph (below). Supplementary Figure 2: Recombinant IL27 lowers ETAR levels in bone marrow cells. Bone marrow cells were treated with recombinant IL27 (20 ng/mL) or PBS for 3 hours or overnight. ETAR levels were monitored via immunofluorescence. Supplementary Figure 3: Recombinant IL27 lowers ETAR levels in isolated kupffer cells. Kupffer cells were isolated from LPS-treated wildtype mice, re-stimulated with LSP (1µg/mL) in vitro in presence or absence of recombinant IL27 (20 ng/mL) overnight. ETAR levels were monitored via immunofluorescence. Supplementary Figure 4: IL27 lowers ETAR levels in vivo in CCL4-induced fibrotic liver. Representative photomicrographs of CCL4-induced fibrotic livers of wildtype or IL27RA-/- mice analyzed for ETAR levels via immunofluorescence (N=3-4 mice). Supplementary Figure 5: No changes amongst in p21 levels in F4/80 positive cells in the liver of mice from different genotypes. Immunofluorescence staining for p21 and F4/80 showed rare p21-positive cells in the liver of aged mice. (i)WT, (ii) IL27RA-/-, (iii) p53H/+, or (iv) IL27RA-/-p53H/+. Supplementary Figure 6: ETAR signaling maintains p53 stability via inducing phosphorylated p53 at Serine 15. Representative photomicrographs of immunofluorescence staining for phosphorylated p53 levels at serine 15 in the livers of IL27RA-/-p53H/+ in the presence or absence of ETAR signaling inhibitor ZD4054. Pictures takes at 200X. (N=3 independent mice). 3 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 4 Supplementary Figure 3 5 Supplementary Figure 4 6 Supplementary Figure 5 Supplementary Figure 6 7 REFERENCES 1. Mitra A, Ross JA, Rodriguez G, Nagy ZS, Wilson HL, Kirken RA. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (Stat5b) serine 193 is a novel cytokine-induced phospho-regulatory site that is constitutively activated in primary hematopoietic malignancies. J Biol Chem 2012;287:16596-16608. 2. Satelli A, Brownlee Z, Mitra A, Meng QH, Li S. Circulating Tumor Cell Enumeration with a Combination of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule- and Cell-Surface Vimentin-Based Methods for Monitoring Breast Cancer Therapeutic Response. Clin Chem 2014. 3. Satelli A, Mitra A, Cutrera JJ, Devarie M, Xia X, Ingram DR, Dibra D, et al. Universal marker and detection tool for human sarcoma circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res 2014;74:1645-1650. 4. Nagy ZS, LeBaron MJ, Ross JA, Mitra A, Rui H, Kirken RA. STAT5 regulation of BCL10 parallels constitutive NFkappaB activation in lymphoid tumor cells. Mol Cancer 2009;8:67. 5. Dibra D, Cutrera J, Xia X, Kallakury B, Mishra L, Li S. Interleukin-30: a novel antiinflammatory cytokine candidate for prevention and treatment of inflammatory cytokine-induced liver injury. Hepatology 2012;55:1204-1214. 6. Mitra A, Satelli A, Yan J, Xueqing X, Gagea M, Hunter CA, Mishra L, et al. IL-30 (IL27p28) attenuates liver fibrosis through inducing NKG2D-rae1 interaction between NKT and activated hepatic stellate cells in mice. Hepatology 2014;60:2027-2039. 7. Bourgognon M, Klippstein R, Al-Jamal KT. Kupffer Cell Isolation for Nanoparticle Toxicity Testing. J Vis Exp 2015:e52989. 8