* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations, Communities, Ecosystems and the Biosphere
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Deep ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Ecogovernmentality wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
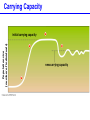
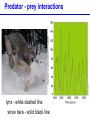
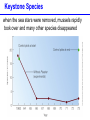
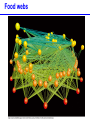
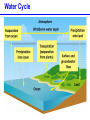
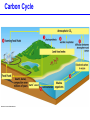
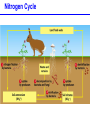
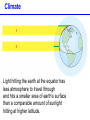
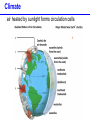
Populations, Communities, Ecosystems and the Biosphere Population Ecology -- Ch. 26 What factors affect the size and age structure of a population? Learning Outcomes Explain carrying capacity. Explain life history ecology and population structure. Compare opportunistic and equilibrial life histories. Explain life history evolution. Describe trends in human population growth. Population Growth when there are no restrictions, populations will increase exponentially Population Growth Where did we hear this before? Malthus 1766 - 1834 However, in reality, no environment has unlimited resources. Carrying Capacity these wood ducks will only nest in holes in particular trees Carrying Capacity Population size (number of individuals) initial carrying capacity 2 3 4 new carrying capacity 1 Life History Ecology survivorship trends affect population structure Type I Type II Type III Life History Ecology Life History Evolution control = guppies with predator that eats LARGE guppies moved = guppies with predator that eats SMALL guppies Human Populations Human Populations Community Ecology -- Ch. 27 How do different species interact with each other? Learning Outcomes Define symbiosis, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Explain the interdependence of predator-prey populations. Explain ecological succession. Explain keystone species and consequences of removal. Community Ecology Commensalisn and Mutualism Predator - prey interactions lynx - white dashed line snow hare - solid black line Parasitism parasites feed off another organism without killing it Ecological Succession Keystone Species one species that can affect the occurence and/or abundance of many other species Keystone Species when the sea stars were removed, mussels rapidly took over and many other species disappeared Ecosystems -- Ch. 28 light energy Producers plants; photosynthetic protists and bacteria energy in chemical bonds materials cycling Consumers animals; fungi; heterotrophic protists, bacteria, and archaeans heat energy Learning Outcomes Define ecosystem. Describe food chains, food webs, and trophic levels (producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, decomposers). Describe ecological pyramids and the distribution of biomass and energy at the different trophic levels. Explain the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle. Food Webs Food webs Trophic pyramid top carnivores (gar and bass) 1.5 carnivores (smaller fishes, invertebrates) 11 herbivores (plant-eating fishes, invertebrates, turtles) 37 producers (algae and aquatic plants) 5 809 Biomass (kg per m2) detritivores (crayfish) and decomposers (bacteria) Ecosystems ecosystems include all living and non-living components of the environment Water availability is a key factor. Water Cycle Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Atmospheric CO2 The Biosphere -- Ch. 29 The Biosphere Biomes on earth are mainly defined by climate. Climate rotation and tilt of the earth influence climate Climate Light hitting the earth at the equator has less atmosphere to travel through and hits a smaller area of earth’s surface than a comparable amount of sunlight hitting at higher latitude. Climate air heated by sunlight forms circulation cells Climate heat energy from sunlight drives ocean currents Biomes hatched = montane/alpine Tropical Rain Forest Temperate Forest Boreal Forest Temperate Grassland Chaparral Desert