* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory system
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
•
General
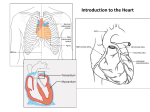
Circulatory system
Heart
•
•
1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima
•
1
Heart
•
2-Tunica media:
•
3-Tunica externa: aka tunica adventitia
2
3
•
Heart = pump
•
•
Heart
auricle; lower, outer part of atrium
auricle = 'ear'
looks like a dog's ear.
•
•
Pressure pushes blood into the atria
•
4
Heart
Ventricles contract, ejecting blood into the
elastic arteries.
•
no exogenous stimulation
With adequate 02 and chemical energy
heart will beat
5
Heart
•
Wall structure
•
Tunica interna: endocardium.
•
•
.
Medium to large hearts
6
7
Heart
•
Tunica media: myocardium.
•
Tunica externa: epicardium.
8
9
•
•
Special structures:
Cardiac Valves
Heart
•
R and L semilunar valves
10
Heart
Chordae tendonae and papillary
muscles
Tension-cords
•
•
Ventricles contract, cords prevent
valve inversion
11
Heart
The tunica media of all four chambers
of the heart are continuous
•
Membrane impulse begins at sinoatrial (SA) node
•
12
Heart
Medium to large hearts, Purkinje
fibers
•
•
Only weakly contractile;
13
Heart
Impulse reaches the interatrial septum
and the auricle 0.1 sec later.
•
Bottom of the interatrial septum;
impulse reaches the atrio-ventricular
node (AV node)
Takes another 0.1 sec to pass through
the AV node
14
Heart
Atrial tunica media thinner than
that of the ventricles
•
15
Heart
Purkinje fibers extends down the
interventricular septum and
•
•
Membrane impulse reaches the upper
ventricular walls
16
Heart
The outer wall of the RV is much
thinner than that of the LV.
•
Less force is required to pump
blood into the pulmonary trunk
than into the aortic trunk.
•
Thickness of the
interventricular septum =outer
wall of the LV.
•
LV lumen much more apparent
in sections of the heart than
lumen of the RV.
•
17
18
Heart
19
Heart
The heart sounds; closure of the
two sets of valves.
•
First sound ('lubb') does not
occur when the atria contract,
•
•
Second sound ('dupp')
20
Heart
The depolarization and
repolarization of the cardiac
muscle tissue
•
•
21
Heart
•
P wave
•
QRScomplex
T wave
no wave due to atrial repolarization
22