* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What do the following values refer to?
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
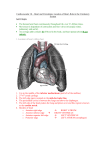
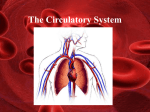
WORKSHEET QUESTIONS What branch of the autonomic nervous system regulates vasoconstriction of arterioles? In times of stress, why do skeletal muscles arterioles vasodilate? The blood vessels to the brain and heart never vasoconstrict - why? Kidneys can reabsorb water (into the bloodstream). What effect does this have on blood pressure? When you cut a vein, blood flows out evenly, but an artery spurts – why? Why must the aorta have elastic walls? If the CO is 5000 ml/min, what % of the total blood volume is pumped per minute? How many ml of blood is pumped from each ventricle in a heart beat? If the SV is too low, how would an increase in heart rate compensate? If the AV node is damaged, what would happen? Why does arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) increase blood pressure? What do the following values refer to? 75 pH 7.4 = blood 55% 5 - 6 million/mm3 130 ml 800 milliseconds 120/80 mm Hg 5 liters 100.4 10,000 mm3 17,000 ml/minute 80 ml 6,000 ml/minute 120 days 45% 70% 2 million/second 50 ml 60% of EDV Which oxygenated, which deoxy or both? RA Pulmonary trunk Umbilical arteries LV 0 Aorta 0 Right semilunar valve Lungs 0 Placenta Pulmonary arteries Capillaries 0 Arterioles 0 Right ventricle Coronary sinus Cardiac veins Left coronary artery 0 Umbilical vein Pulmonary veins 0 inferior vena cava Where are these layers found? Endocardium Endothelium Myocardium Epicardium Visceral pericardium Tunica media Tunica interna Pericardial space Tunica interna with valves Tunica media with elastin T. media that can vasodilate Endothelium only Parietal pericardium Mediastinum Fibrous pericardium with collagen Lumen Other molecules in circulatory system What is the role of the following substances? Iron Hemoglobin Fibrinogen Oxygen Vitamin K Carbon dioxide Nitrous oxide Vitamin B12 Calcium ions Histamine LDL Heparin Albumin Intrinsic factor Antibodies Stem cells Plasma Where are these structures found, what do they do? Vasomotor center Muscular pump Chemoreceptors Precapillary sphincter Papillary muscle Brachial artery Thrombus Fenestrated capillaries SA node AV node Vein valve Chordae tendinae Coronary sinus Ligamentum arteriosum Vasa vasorum Foramen ovale CV center 2 ways to: Click for answer Locally vasodilate (autoregulation) Increase heart rate Decrease blood pressure Vasodilation, decrease HR Increase EDV Execise, increase venous return to RA Monitor blood pressure Aortic and carotid baroreceptors Increase resistance to blood flow More blood vessels, vasocontrict Send blood out of heart Nitric oxide and low O2 in cells Epinephrine, exercise Through RA and RV 1. Fill in for the following using these choices: Tunica interna Tunica media Tunica externa The only layer found in capillaries A single layer of endothelium A middle coat, composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers Supporting, protective layer Plays a role in blood pressure regulation In direct contact with the lumen Thicker in an artery than in a vein Can vasoconstrict Thicker in artery, thinner in vein Valves in veins Provides elasticity to elastic arteries Which blood cell(s)? rbc, platelet, neutrophil, basophil, eosinophil, monocyte, B-cell or T-cell (lymphocytes) clotting Enucleate Lives for 120 days Multi-lobed nucleus Makes antibodies Iron Parasitic infection Macrophage helper and killer Erythrocyte Diapedisis leukocyte releases histamine phagocyte hemoglobin chemotaxis 2 million/sec Explain SA node SL valves close QRS complex Atrial diastole Ventricular systole End diastolic volume Stroke volume Pulmonary trunk and aorta Bundle branches and purkinje fibers P wave AV node Ventricular diastole Atrial systole Ejection AV valves close End systolic volume AV valves open SL valves open LUBB DUPP conductile cells contractile cells isovolumnetric contraction ejection fraction cardiac output venous return preload