* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cardiovascular system review answer key 2
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
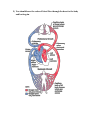
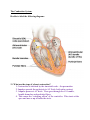
Cardiovascular System Review (This review is meant to be a guide for you but not the ONLY item that you should study from. You should also look over your notes, previous class work, homework, and warm up activities.) 1) What is the MAIN function of the cardiovascular system? The function of the cardiovascular system is to deliver oxygen and nutrients and to remove carbon dioxide and other waste products. 2) Explain the location of the heart within the body. Location a. Thorax between the lungs (mediastinum) b. Pointed apex directed toward left hip & rests on the diaphragm -About the size of your fist 3) What is the purpose of the Pericardium? Serous fluid fills the space between the layers of pericardium, decreases friction 4) What is Pericarditis? What are the symptoms? Inflammation of pericardium causes a decrease in serous fluid. This leads to friction when the heart beats which can cause chest pains. – Pericardial layers touch, stick and form painful adhesions 5) You should know the order of blood flow through the heart to the body and back again. VALVES: 7. What is Valvular Stenosis? What are the symptoms? -Valvular Stenosis – Valve flaps become stiff, usually due to a bacterial infection. -Valves may not close completely, allowing backflow. 8. Atrioventricular valves (AV) – between atria and ventricles • Bicuspid valve (left) (mitral) – 2 flaps • Tricuspid valve (right) – 3 flaps – CHORDAE TENDINAE anchor the valve flaps to the ventricle to keep them from being pushed inside the atria during ventricular contraction. » Called your “heart strings” – SEMI-LUNAR valves between ventricle and artery • What are the two valves called between the ventricles and arteries? PULMONARY AND AORTIC_ 9. What supplies the heart muscle itself with blood? – Coronary arteries branch from the base of the aorta (BRING O2) • They are compressed during ventricular contraction and fill during relaxation. – Cardiac veins empty blood into the right atrium via the coronary sinus (TAKE AWAY CO2) 10. What is angina pectoris? What are the symptoms? What can it lead to? -CHEST PAIN caused by rapid heartbeat or a decreased amount of O2 to the myocardium. 11. What is a Myocardial Infarction? What causes this issue? -HEART ATTACK = If the heart muscle goes without oxygen long enough, damage occurs or an infarct. The Conduction System Be able to label the following diagram: 11. What are the steps of a heart contraction? 1. Contraction is initiated by the sinoatrial node – the pacemaker 2. Impulse spreads through atria to AV Node, both atria contract 3. Impulse pauses at AV node. Then goes through the AV bundle, bundle branches and purkinje fibers. 4. This causes the “wringing action” of the ventricles. This starts at the apex and moves up towards the atria. Blood Vessels -Be familiar with the physical anatomy of blood vessels (Tunica intima, Tunica media, Tunica externa) –Differences between Arteries, veins, and capillaries. -What is meant by “milking” the veins? Why is this necessary? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ -What is the main function of Hepatic Portal circulation? Veins from digestive organs, spleen and pancreas take blood to the liver • • After a meal, this blood is nutrient rich. Liver stores glucose and further processes nutrients. -Blood Pressure -Systolic : Pressure at the peak of ventricular contraction -Diastolic: Pressure when ventricles relax What are some factors that affect blood pressure? • Temperature – Heat has a vasodilation effect – Cold has a vasoconstricting effect • Chemicals – Alcohol – vasodilator – Nicotine - constrictor • Diet – low in salt, saturated fats & cholesterol help prevent hypertension 12. You should know the definition or general concept of the following: -Heart block: Damage to AV node causes ventricles to contract on their own at a slower rate. -Ischemia: Lack of blood flow to heart which leads to fibrillation. -Fibrillation: Shuddering of heart, no pumping, can lead to death. -Tachycardia: Heart rate GREATER than 100 bpm, can become fibrillation. -Bradycardia: Heart rate LESS than 60 bpm -Heart Murmur: Unusual heart sound caused by faulty valves and a back flow of blood. -Cardiac cycle: Events of one complete heart beat -Varicose veins: Valves are faulty, blood pools & vein twists -Thrombophlebitis: Clot forms in a vein -Hypertension: High systolic (above 140 mm HG) • Can be dangerous if it is chronic – Strains the heart & damages arteries – Eventually myocardium enlarges, heart weakens & walls become flabby – Causes small tears in arteries where clots can form, leading blockage -Hypotension: Low systolic (below 110 mm HG) Often associated with illness -Atherosclerosis: Damage to tunica interna & clot response • Continual injuries to area & plaque begins to form • Fats & cholesterol enter & collect, eventually protrude into the lumen • -Blood pressure: Pressure exerted on inner walls of blood vessels 13. Explain “Lub” “Dub” when referencing the heart. • Lub is AV valves closing • Dub is semilunar valves closing