* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CXXC5 plays a role as a transcription activator for myelin genes
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
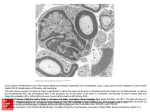
CXXC5 plays a role as a transcription activator for myelin genes nvolving interhemispheric activity and social stress Kang-Yell Choi [email protected] Department of Biotechnology, College of Life Science and Biotechnology, Translational Research Center for Protein Function Control (TRCP/ ERC), Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea E-mail: [email protected] Abstract Myelination in corpus callosum plays important role for normal brain functions by transferring neurological information between various brain regions. However, the factors controlling expression of myelin genes in myelination are poorly understood. Here, CXXC5, a recently identified protein with CXXC-type zinc finger DNA binding motif, was characterized as an activator of major myelin genes. CXXC5 was specifically expressed in the white matter of the central nervous system (CNS) in adult mice. Expressions of myelin genes were simultaneously reduced during differentiation of neural stem cells (NSCs) of CXXC5-/- mice. CXXC5 directly bind to the MBP promoter via the CXXC DNA-binding motif. The CXXC5-/- mice exhibited severely reduced expression of myelin genes as well as abnormalities in myelin structure in the corpus callosum on postnatal day 14. The disrupted structural integrity of myelin in the CXXC5-/- mice resulted in both reduced conduction amplitudes as well as reduced aversive response to social stress.