* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reduced CXCR5 expression on B cells during HIV-1
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
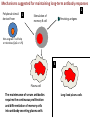
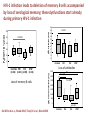
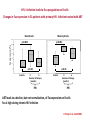
Routine vaccination and maintenance of serological memory in HIV infected children Moderators: Berhanu Gudeta, Ethiopia Francesca Chiodi, Sweden Cell Damage during HIV infection Francesca Chiodi, Sweden Vaccination of immuno-compromised children and mechanisms of long-term serological memory Anna Nilsson, Sweden Novel therapy approaches to restore antibody responses during HIV infection Kehmia Titanji, Cameroon and USA Towards therapeutical HIV vaccination and ameliorated vaccination schedules in HIV infected children Britta Wahren, Sweden Cell damage during HIV-1 infection Francesca Chiodi Several B cell abnormalities were reported to occur during HIV-1 infection. • loss of antibodies to vaccination antigens and antigens previously met in life • high level of circulating IgG (hypergammaglobulinemia) of unknown specificity • hyperactivated status of B cells (and other cells of the immune system) as detected by surface markers • declined number of memory B cells (resting) • increased number of circulating transitional B cells, activated and tissue like memory B cells Antibodies are important components of effective vaccines Rino Rappuoli, Novartis Vaccines should induce long-term serological memory Mechanisms suggested for maintaining long-term antibody responses Polyclonal stimuli derived from 2 1 Stimulation of memory B cell Persisting antigens Non-cognate T cell help or microbes (CpG or LPS) 3 Plasma cell The maintenance of serum antibodies requires the continuous proliferation and differentiation of memory cells into antibody-secreting plasma cells Long-lived plasma cells HIV-1 infection leads to deletion of memory B cells accompanied by loss of serological memory; these dysfunctions start already during primary HIV-1 infection 100 P<0.001 60 40 Anti-measles IgG CD27+ B cells (%) 80 20 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 P<0.01 0 Controls Loss of memory B cells CHI LTNP Loss of antibodies 3500 Anti-pneumococcus IgG Controls PHI CHI LTNP (n=34) (n=41) (n=80) (n=14) PHI De Milito A et a., Blood 2004; Titanji K et al., Blood 2006 3000 P<0.001 n.s. P<0.001 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 Controls PHI p<0.02 CHI LTNP Studies to understand the mechanisms leading to depletion of memory B cells may result in: a) Improved vaccination for HIV-1 infected children and adults b) Novel immunomodulatory therapy to improve B cell immunology Some examples in that direction… Two phase-model for depletion of memory B cells from circulation Altered migration Apoptosis Chiodi, Journal of Clinical Investigation 2010 ALTERED EXPRESSION OF THE RECEPTOR-LIGAND PAIR CXCR5/CXCL13 IN B-CELLS DURING CHRONIC HIV-1 INFECTION CXCR5 directs B cell migration into lymphoid organs. CXCL13, the ligand, is secreted by stromal cells, FDCs and T(FH) cells in B cell follicles. Alberto Cagigi and Anna Nilsson Blood, 2008 Reduced CXCR5 expression on B cells during HIV-1 infection, in relation to CD4+ T cells Increased levels of CXCL13 (both mRNA and ex-vivo secretion) were detected in purified B cells from HIV-1 infected patients Altered expression of the chemokine receptor-ligand pair, CXCR5/CXCL13 may participate in the impairment of B cell homing and establishment of B-cell dysfunctions during HIV-1 infection. Increased cell-death of B cells may take place during HIV-1 infection T and B cells are primed for apoptosis during HIV-1 infection and Fas is an important molecule in this context HIV-1 infection leads to Fas upregulation on B cells Changes in Fas expression in 31 patients with primary HIV infection treated with ART Naive B cells Memory B cells Fas expression (%) 120 100 p=0.003 p<0.001 80 60 40 20 p=0.42 0 Controls p<0.01 0 6 Duration of therapy (months) PHI Controls 0 6 Duration of therapy (months) PHI ART leads to a decline, but not normalization, of Fas expression on B cells Fas is high during chronic HIV infection K Titanji et al., AIDS 2005 IL-7 promotes Fas expression on B cells via IFN-γ released from IL-7 treated T cells Sammicheli S et al., PLoS ONE 2011 PD-1 signaling is highly involved in B cell survival signals Fp7 EU project Thanks to: Next Generation HIV-1 Immunogens inducing broadly reactive Neutralising antibodies European Vaccines and Microbicides Enterprise Fp6 Network of excellence 2007-2011 Swedish MRC Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency Karolinska Institutet