* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rastaldi TTO
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
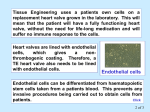
3D CO-CULTURE OF PODOCYTES AND ENDOTHELIAL CELLS Summary Cells live in a three dimensional (3D) microenviroment which deeply influences their function. The present invention relates to a new 3D co-culture method of podocytes and endothelial cells and a relative co-culture system and the use of this co-culture system as an in vitro study model of pathologies affecting the kidneys, and in particular the renal glomerular filtration barrier. Technology description. Although classical culture methods are essential to define basic properties of single cell types, cells live in a three-dimensional microenvironment and particularly, podocytes in the glomerulus make adhesions to the external side of the glomerular basement membrane, where endothelial cells line the internal side. Podocytes, endothelial cells and the intervening glomerular basement membrane form together the glomerular filtration barrier. Though the need of coculturing podocytes and endothelial cells is widely recognized in the nephrology research community, this is the first successful 3D system for culturing them in vitro. Competitive advantages. With our method, podocytes and endothelial cells are grown on a isoporous membrane, covering the external and internal side respectively. Thus, cells make adhesion only to the membrane itself, though on the opposite sides. This method resemble more the in vivo situation, and allows multiple analyses on both cell types. The presence of the membrane between the two cell types and the complete separation of their own supernatants permit to perform permeability assays and separate assays in the two compartments, and to challenge one cell and then measure the effects on the other cell type. Further, cells on both sides of the membrane can be immunostained for any molecule of interest, and analysed by light microscopy, electron microscopy and transmission microscopy, allowing direct evaluation of cell protein expression. Compared to artificial capillaries, our system is cheaper, easier to use, and does not require particular equipment. Stage of development. We are presently using the system to test the importance of neuronlike signaling between podocytes and endothelial cells. The co-culture system could be extremely useful to evaluate alteration of permeability of the filtering barrier in different conditions. A better understanding of the processes at the basis of glomerular damage and of the physiological properties of the glomerular filtration barrier are mandatory to improve diagnosis and find more targeted therapies. Besides the evident help to basic research studies, we believe that our device can help in discovering and testing potential novel biomarkers, individual patient samples, and the effects of new drugs. Fondazione seeks a commercial partner interested in the acquisition of new disease models to be exploited for the identification of new therapeutic agents and/or for the development of diagnostic/prognostic tools. Technology offer □ A new 3D co-culture method of podocytes and endothelial cells. Inventor Rastaldi Maria Pia and Li Min Applications □ Morphological and functional assays. □ In vitro model for pathologies. □Cellular toxicity assay for drugs. Novel aspects and advantages □Effective 3D method for culturing podocytes and endothelial cells. □ □ Cheaper and easier to use. Current development stage Applied basic research. Intellectual property rights □ Italian Patent application MI2009A00221617 □ International Patent application PCT/IB20110/003298 Offer □ collaboration for product development □ patent licensing