* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleic Acids
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
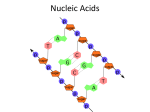
Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acid Basics • Contain instructions to build proteins • 2 types: – DNA – RNA Proteins built from DNA instructions Blueprint to build a boat Nucleic Acid Basics • Contain instructions to build proteins • 2 types: – DNA – RNA • Composed of smaller units called nucleotides – Monomer: Nucleotide – Polymer: Nucleic acid Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide Nucleic acid (polymer) Nucleotide Structure • What’s a nucleotide? Monomer of nucleic acids • Three parts – Sugar molecule – Phosphate group – 1 of 4 Nitrogen bases • • • • Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) adenine Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide thymine Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide Nucleic acid (polymer) cytosine Monomer: nucleotide Monomer: nucleotide guanine Nucleotide Structure • What’s a nucleotide? Monomer of nucleic acids • Three parts – Sugar molecule – Phosphate group – 1 of 4 Nitrogen bases (A, T, C, or G) • Nucleotides combine to make nucleic acids • Instructions for ribosomes to make protein 1 min: Discuss with your neighbor 1. How many nucleotides are pictured? Six 2. What is this long chain of nucleotides called? Nucleic acid 3. Name the blue shaped pentagon molecule. Sugar 4. What are these individual monomers called? Nucleotides 5. What will these instructions be used to create? Protein Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Double Helix: 2 chains of nucleotides • Hydrogen bond connects the two nucleotides Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Double Helix: 2 chains of nucleotides • Hydrogen bond connects the two nucleotides • 4 DNA Bases: – A pairs with T – C pairs with G Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Double Helix: 2 chains of nucleotides • Hydrogen bond connects the two nucleotides • Chargaff’s Rules: – A pairs with T – C pairs with G • Gene: section of DNA that codes for a protein Gene A: Hemoglobin protein Gene B: Keratin protein Gene C: Collagen protein 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10 5 11 6 12 Ribonucleic Acid • Single chain of nucleotides • Nitrogen bases: Adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine Ribonucleic Acid Physically builds the protein Instructions to build protein • Single chain of nucleotides • Nitrogen bases: Adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine • Function: Deliver instructions from DNA to ribosomes 1 min: Discuss with your neighbor Carbohydrates Monomer Polymer A? B? monosaccharide Proteins C? Amino acid Lipids D? polysaccharide Protein (polypeptide) Lipid Fatty acid, Glycerol Nucleic acids E? Nucleotide Nucleic acid Review Vocabulary: Monomer, Polymer, Nucleotide, Double helix, Nitrogen base 1) Name the monomer of nucleic acids. 2) Draw & Label a nucleotide. 3) How are the four nitrogen bases of DNA abbreviated? RNA? 4) What does the phosphate molecule of a nucleotide bond with? 5) What do you call a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein? 6) If the DNA nitrogen bases were TACCGGAT, how would the attached DNA strand read? 7) How are DNA and RNA different? Same?